2021 - Multiple Choice Questions
The majority of iron is stored in:
- Haemoglobin
- Ferritin
- Myoglobin
- Cytochromes
Ferritin 25% body stores
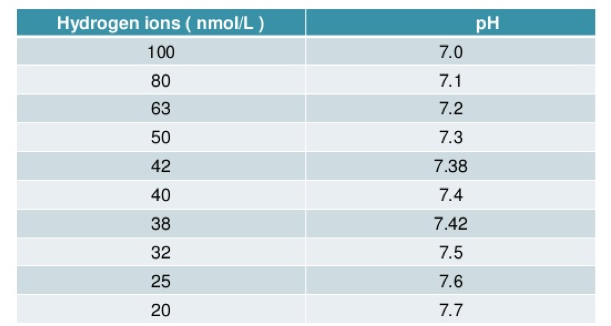
A pH of 7.4 is equivalent to a H+ concentration of (nmol/L)
- 50
- 42
- 38
- 40
Which of the following contributes to oxygen transfer in the placenta
- Haldane effect
- PO2 50mmHg Umbilical Vein
- L) shift in Maternal ODC when oxygen binds
- PO2 gradient is 30mmHg
- Double Haldane effect explains maternal release of O2 & uptake of CO2 with increase in foetal blood O2 uptake
- HbF undergoes L shift (becomes alkalotic) to give itself greater O2 affinity
- PO2 28mmHg Umb V
- PO2 maternal blood = 100mmHg
- PO2 intervillous space = 50mmHg
- PO2 Umb A = 20mmHg
- 30mmHg gradient favouring O2 diffusion
Which of the following vasodilates smooth muscle without acting via the endothelium
- Bradykinin
- Adenosine
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
- Histamine
- BK is a potent endothelium-dependant vasodilator
- VIP increases NO and is a positive endothelial cell proliferator
- VPAC2 receptors are also present in the aortic endothelium, heart, pancreas, renal medulla, adrenal cortex, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue
- Histamine binds endothelial cells
- An intact endothelium is not necessary for an adenosine response in vitro
- Activation of A2A and A2B adenosine receptors producespotent vasodilation of most vascular beds including thecoronary circulation
- A2B receptorsare found on human mast cells and are thought to producemast cell degranulation and bronchial constriction(15).A3receptors are mainly peripherally located but are thought toplay a role in mediating pre-conditioning.The use of adenosine for stress testing and induction ofsystemic (and coronary) hyperemia is primarily related to theactivation of A2A receptors and the resultant increase inmyocardial bloodflow
With regards to monitoring systems, the natural frequency is
- Directly proportional to length
- 100 times the fundamental frequency
- The frequency at which the material oscilates
- Inversely proportional to lumen radius
- The fundamental frequency is just the lowest possible frequency among all the natural frequencies of vibration of an object.
- The “natural” frequency of a system, is that system’s response to an impulsive forcing function. So hitting (impulsive forcing function) a 256 Hz tuning fork (system) on a table will cause the tuning fork to oscillate at 256 Hz (its natural frequency).
- Directly proportional to lumen radius
- Inversely proportional to tube length, compliance, fluid density
What is the mechanism of a Type III Hypersensitivity reaction?
- Complex mediated
- Cell mediated
- Complement mediated
- Mast cell mediated
In Sickle Cell Anaemia
- The alpha chain of haemoglobin has a valine replacing glutamic acid
- The beta chain of haemoglobin has a valine replacing glutamic acid
- The ODC displays a L shift
- Is due to a mutation at position 7 of the globin chain
The respiratory control centre which is inactive during normal respiration and becomes more active during forceful or high tidal volume respiration
- Dorsal Respiratory Group
- Ventral Respiratory Group
- Pneumotaxic Centre
- Apneustic Centre
Which of the following is true regarding the carotid baroreceptors:
- Their discharge rate increases with increasing blood pressure
- They have a firing threshold of 80mmHg
- They are innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve
- They have a minimum firing rate at a blood pressure of 200mmHg
These receptors respond to stretching of the arterial wall so that if arterial pressure suddenly rises, the walls of these vessels passively expand, which increases the firing frequency of action potentials generated by the receptors. If arterial blood pressure suddenly falls, decreased stretch of the arterial walls leads to a decrease in receptor firing.
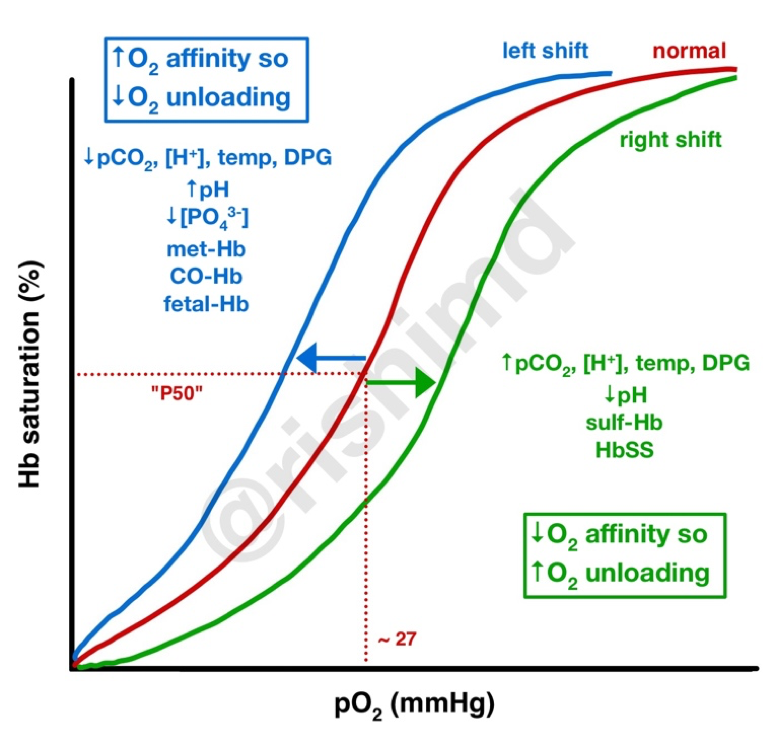
Which of the following shifts the Hb-O2 dissociation curve to the Right
- Low H+
- Hyperventilation
- Decreased 2,3 DPG
- Hyperthermia
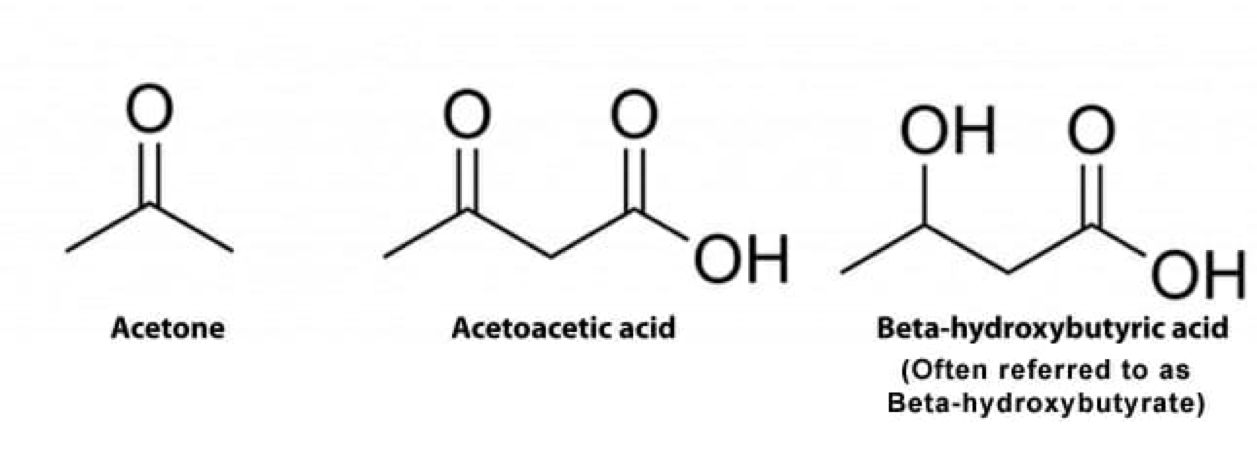
Which of the following is not a Ketone
- Beta-Hydroxybutyrate
- Acetoacetate
- Alpha-ketoglutarate
- Acetone
Which of the following is true about Sodium Nitroprusside toxicity?
- It produces green discolouration of urine and hair
- It results in high blood pressure and tachycardia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency increases the risk of toxicity
- Thiamine deficiency increases the risk of toxicity
SNP + Hb -> NO + MetHb + 5x Cyanide
Toxicity from SNP is because of:
- Cyanide toxicity (mostly rate dependent) – lactic acidosis, cytotoxic shock
- Thiocyanate toxicity (depends on duration of infusion) – Nausea, fatigue, weakness, seizure, psychosis, hypothyroidism
- Binding to MetHb -> Cyano-Met-Hb
- Binding to Vitamin B12 (Hydroxycobalamin) -> Cyanocobalamin
- Binding to Thiosulfate (catalysed by Hepatic Rhodanase) -> Thiocyanate
How much does the blood oxygen content increase when breathing FiO2 1.0 compared to room at (at sea level) in a healthy person?
- 1-2%
- 10-20%
- 20-30%
- 30-40%
- Blood Oxygen Content = CO2
- CO2 = (SpO2 x Hb x 1.34) + (0.003 x PaO2)
- At FiO2 0.21 (RA):
- CO2 = (0.98 x 140 x 1.34) + (0.003 x 100) = 183.85 + 0.3 = 184.15mLO2/L blood
- At FiO2 1.0:
- CO2 = (1.0 x 140 x 1.34) + (0.003 x (760-47 – 1.25×40) = 187.6 + 1.99 = 189.59mLO2/L blood
- % change = (189.59-184.15)/184.15 = ~2%
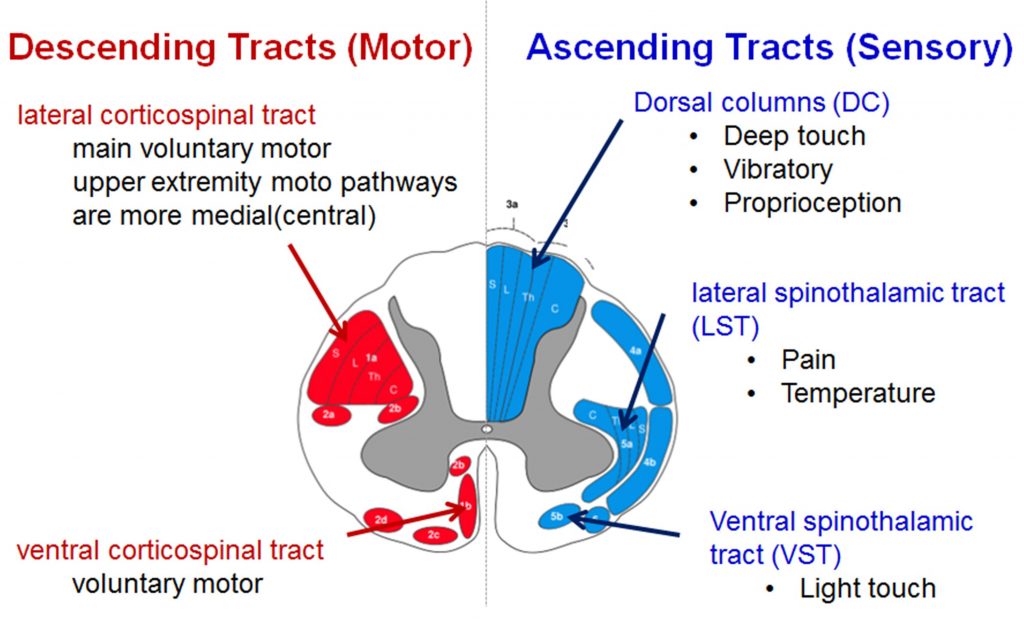
Which of the following is true about the spinal cord sensory pathways?
- The dorsal column carries vibration, the anterior spinothalamic tract carries crude touch, and the lateral spinothalamic tract carries pain & temperature sensations
- The dorsal column carries vibration, the anterior spinothalamic tract carries pain & temperature, and the lateral spinothalamic tract carries crude touch sensations
- The dorsal column carries crude touch, the anterior spinothalamic tract carries vibration, and the lateral spinothalamic tract carries pain & temperature sensations
- The dorsal column carries crude touch, the anterior spinothalamic tract carries pain & temperature, and the lateral spinothalamic tract carries vibration sensations
Which drug has the shortest biological half-life?
- Alfentanil
- Methadone
- Morphine
- Remifentanil
Drugbank Online
| Drug | Half-Life |
| Alfentanil | 90-111 min (100 min) |
| Methadone | 7-59 hours (35 hour) – long, variable |
| Morphine | 2-3 hours (170 min) |
| Remifentanil | 1-20 min (10 min) |
Meropenem lowers the serum drug level of which of the following drugs?
- Warfarin
- Voriconazole
- Sodium Valproate
- Vancomycin
Results: Thirty-nine patients were treated simultaneously with valproate and meropenem. The pharmacokinetic interaction was observed in all 39 patients, with an average drop in valproate plasma concentrations of 66%.
How many mmol of Mg2+ are in 10mL of 50% Magnesium Sulfate solution?
- 2 mmol
- 10 mmol
- 20 mmol
- 40 mmol
- 50% Magnesium Sulfate is the standard solution in ICU
- MgSO4 comes as the heptahydrate (7 x H2O)
- Molar Mass = 246g/mol (24 + 32 + (4×16) + (7 x (16+2))
- 1mmol = 246mg
- 10mL of 50% Solution contains 5g of MgSO4
- 5000/246 = 20.3mmol in 10mL of solution
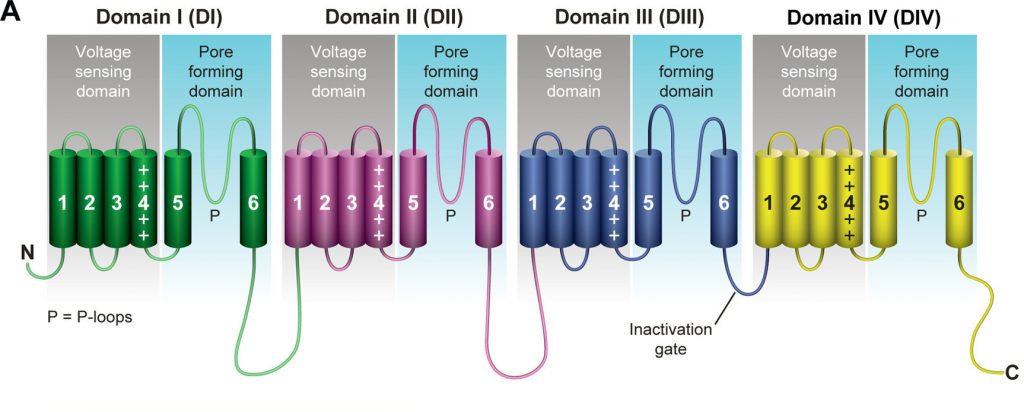
The human voltage-gated sodium channel contains a pseudo-tetrameric alpha subunit with 4 domains. Which segment of each domain is primarily responsible for detecting changes in voltage?
- Segment 2
- Segment 3
- Segment 4
- Segment 6
Segment 4 is positively charged and is thought to move towards the extracellular surface as the cell becomes depolarised. This movement is transmitted to the pore forming domains by an intracellular linker.
 Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications
 Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications
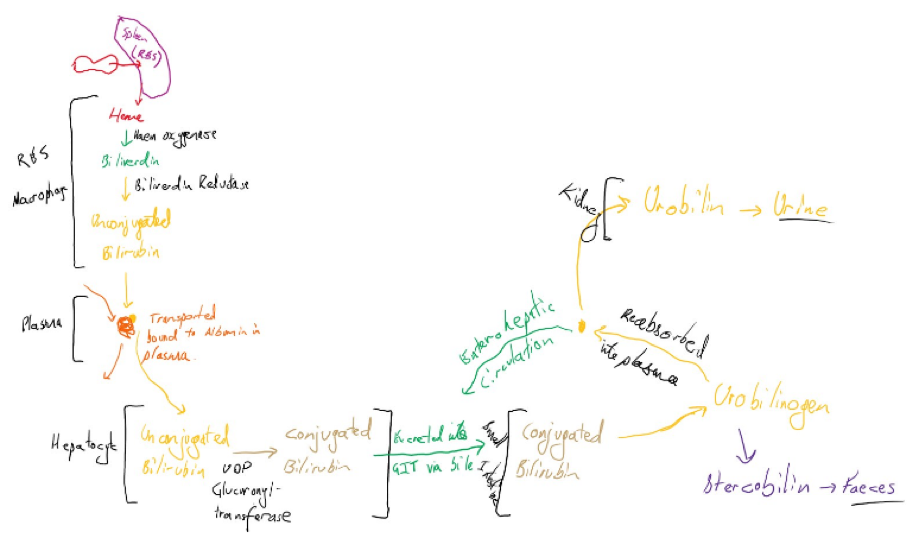
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications In regard to Bilirubin:
- It is transported to the small bowel for excretion bound to Albumin
- It is metabolised to stercobilin by bacteria in the small bowel
- It is more water soluble in its unconjugated from
- It is formed from the breakdown of the globin portion of haemoglobin
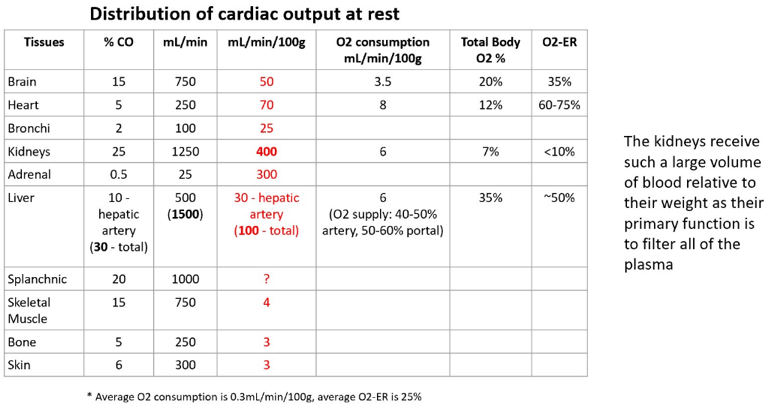
Which of the following organs receives the highest blood flow per 100g of mass at rest?
- Brain
- Heart
- Kidneys
- Liver