2020 - Multiple Choice Questions
Which structure is most cranial:
- Coeliac trunk
- SMA
- IMA
- Renal arteries
Which structure is most caudal
- Laryngeal incisure
- Hyoid bone
- Thyroid Notch
- Cricoid Cartilage
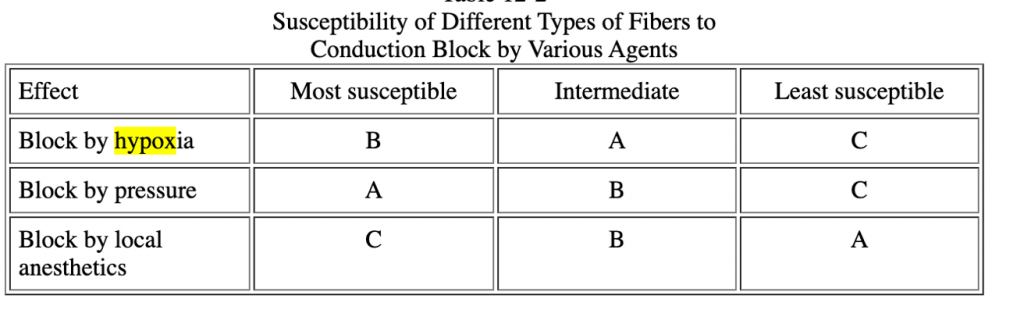
Which nerve fibres are the first to be affected by hypoxia
- A fibre
- B fibres
- C fibres
- D fibres
 Hypercapnic acidosis decreased exhaled NO during hypoxia more than hypercapnia with normal pH and normocapnia, whereas intravascular NO release was unchanged
Download HPVC PDF
Hypercapnic acidosis decreased exhaled NO during hypoxia more than hypercapnia with normal pH and normocapnia, whereas intravascular NO release was unchanged
Download HPVC PDF By which mechanism is Sotalol metabolised in the body?
- Not metabolized
- Hepatic metabolism
- Plasma esterases
- Renal metabolism
Which of the following is action of DOP receptor
- Analgesia
- Miosis
- Euphoria
- Bradycardia
The DOP receptor was the first to be cloned and is less widely distributed relative to the other opioid receptors. Highest densities are found in the olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, nucleus accumbens and the caudate putamen. DOP receptors are located presynaptically on primary afferents where they inhibit the release of neurotransmitters. Through both spinal and supraspinal sites, the receptor is involved in the antinociceptive/analgesic actions of some opioids. However, DOP receptor agonists have also been shown to reduce gastrointestinal tract motility and cause respiratory depression.5 Studies with DOP receptor knockout mice revealed that they display hyperlocomotor activity and it is assumed the receptor, under basal conditions, may dampen locomotor behaviour. DOP receptor knockout mice also displayed anxiogenic and depressive-like responses, suggesting that the receptor may act to regulate mood.
Which is true for GTN
- Protein binding 5%
- Half life 1-3mins
- Bioavailability 30%
- Hepatic Metabolism
Which of the following attenuate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
- Acidaemia
- Hypercapnia
- Iron deficiency
- Alveolar hypoxia
MCQ was recalled as shown, however…
All enhance HPVC
Attenuation via alkalosis and volatiles
Mixed venous O2 will decrease with:
- Hyperbaric oxygen treatment
- Decreased tissue oxygen consumption
- Severe anaemia
- Muscle relaxation
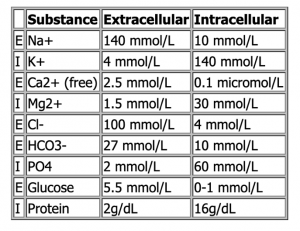
What is the intracellular concentration of Cl- (mmol/L)
- 4
- 26
- 65
- 110
Which is true of hepatic extraction ratio
- Diazepam has high HER
- GTN has low HER
- HER is high for capacity dependent drugs
- HER is high for flow dependent drugs
- Intrinsic clearance = hepatic metabolism of drugs if unlimited & all drug was unbound
- High intrinsic clearance (lignocaine, M, propranolol)
- Almost all drug presented to liver removed
- ∴limited by HBF
- Low intrinsic clearance (warfarin, diazepam)
- Liver already maximally metabolising
- ∴limited by enzyme activity
- PPB → only unbound drug can be metabolised
- High IC → ∆ PPB has maximal effect on clearance
- Low IC → ∆ PPB has significant effect on clearance
- Hepatic BF →↑BF = ↑drug presented for metabolism per unit time
- High IC = ↑BF = ↑Clearance
- Low IC = ↑BF = not much ∆ clearance
Measurement of blood volume is Plasma Volume divided by
- 1- Hematocrit
- 1 – ECF
- 1 – Interstitial water
- 1- Packed Cell Volume
Evaporation
- Accounts of 50% heat loss at ambient temperature
- Body temperature does not have to exceed ambient temperature
- Increases in high humidity environments
- Accounts for 500ml of water loss per day
Evaporation = transfer of heat by evaporation of water
600-700ml of water evaporates / day
20% heat loss
The only way to lose heat when ambient temp > Body temp
Evaporative heat loss depends on the vapour pressure of water in air so at higher humidities the rate of evaporation decreases
Normal thermal neutral zone in awake adult
- 0.2-0.5 °C
- 36.5-37.3 °C
- 25-30 °C
- 32-34 °C
Thermoneutral Zone = ambient temp where we do not have to actively regulate our body temp
The Respiratory Quotient for a protein diet
- 0.5
- 0.7
- 0.8
- 1.0
Proteins: The respiratory quotient for protein metabolism can be demonstrated by the chemical equation for oxidation of albumin:
C72H112N18O22S + 77 O2 → 63 CO2 + 38 H2O + SO3 + 9 CO(NH2)2
The RQ for protein is approximately 0.8. RQ = 63 CO2/ 77O2 = 0.8
Due to the complexity of the various ways in which different amino acids can be metabolized, no single RQ can be assigned to the oxidation of protein in the diet; however, 0.8 is a frequently utilized estimate
Openanaesthesia.org
An example of a 3rd generation cephalosporin
- Cefepime
- Cefuroxime
- Ceftazidime
- Cefazolin
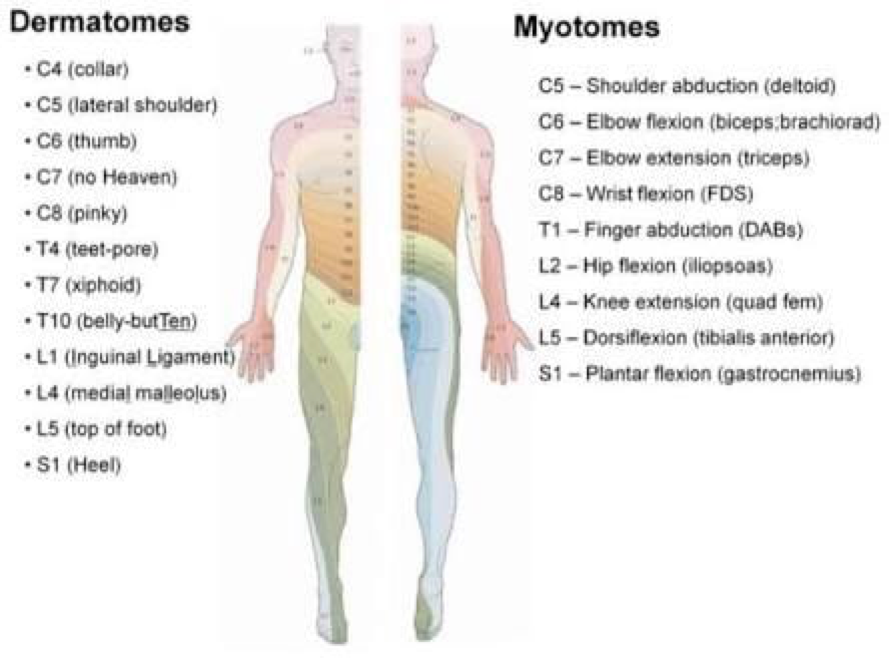
The myotome for the ankle reflex
- L4
- S1
- L5
- S2
The action of Levosimendan on KATP channels
- closes
- opens
- stabilises
- removes Ca2+ plug
The action of Levosimendan on KATP channels
The central venous pressure ‘c wave’ corresponds to which ECG event
- QRS
- P wave
- end of QRS
- begining of T wave
Due to RV valve bulging backwards into RA as RV contracts
Daily volume of saliva secretions
- 1-2L
- 0.5-1L
- 0.6ml/min
- 0.3ml/min
The myotome for the knee reflex
- L4
- S1
- L5
- S2
