2022 - Multiple Choice Questions
Which of the following has the highest partial pressure of oxygen in fetal circulation?
- IVC
- Aorta
- Left atrium
- Ductus venosus
 Straight from the placenta
Straight from the placenta Osmolality of 8.4% bicarb
- 100 mOsm/Kg
- 200 mOsm/Kg
- 1000 mOsm/Kg
- 2000 mOsm/Kg
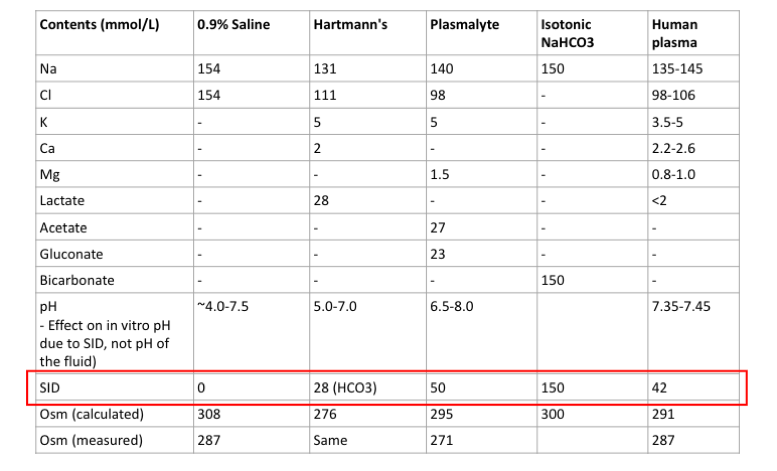
Which solution has the largest strong ion difference
- NaCl 0.9%
- Hartmann’s solution
- Plasma-Lyte
- Isotonic sodium bicarbonate
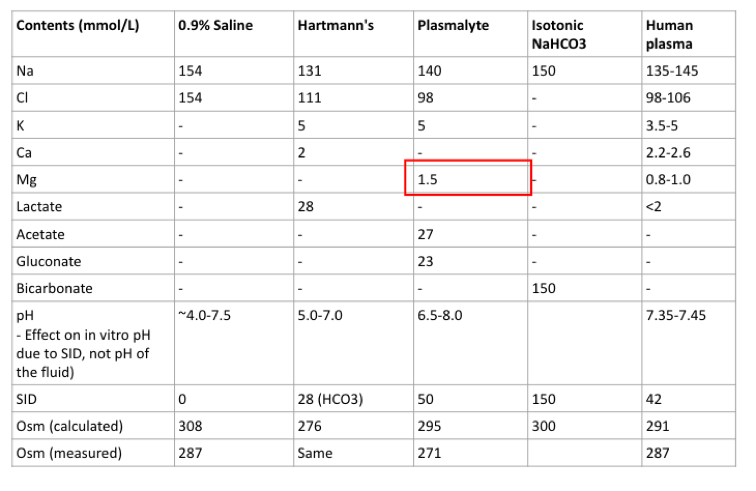
How much magnesium (in mmol/L) is in Plasma-Lyte148
- 0
- 1.5
- 8
- 10
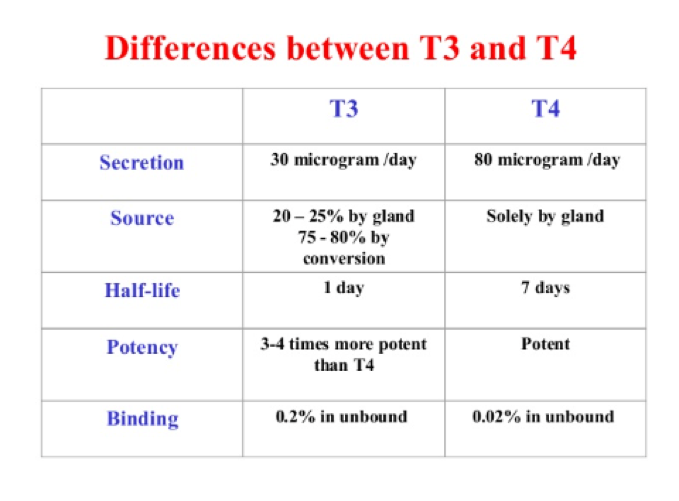
What is the half-life of triiodothyronine?
- 5-10 mins
- 1 hour
- 6 hours
- 1 day
Which of these is a pro-drug:
- Hydrocortisone
- Dexamethasone
- Prednisone
- Prednisolone
Drugs with a low hepatic extraction ratio are most affected by a change in:
- Hepatic blood flow
- Protein binding
- Enzyme activity
- Bioavailability
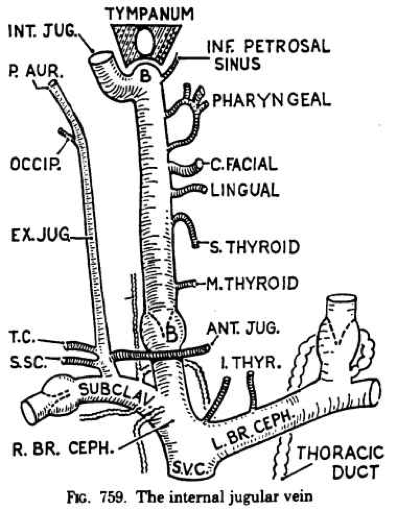
Which of the following is NOT a tributary of the internal jugular vein?
- Lingual vein
- Superior thyroid vein
- Middle thyroid vein
- Posterior auricular vein
What is the binding site for ATP during skeletal muscle contraction?
- Actin
- Myosin
- Tropomyosin
- Troponin
To which of the following side effects of opioid analgesics does tolerance MOST develop?
- Bradycardia
- Constipation
- Miosis
- Nausea and vomiting
What is the normal duration of the P-R interval?
- 0.6 – 0.12 secs
- 0.12 – 0.2 secs
- 0.2 – 0.25 secs
- 0.12 – 0.25 secs
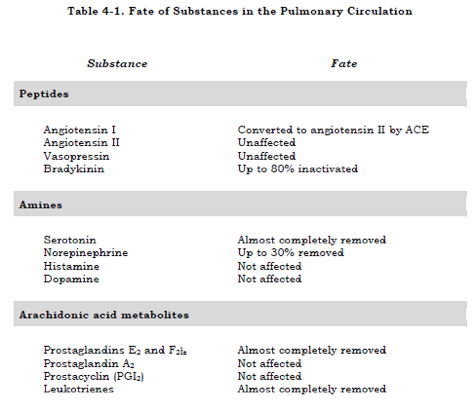
What factor is almost completely removed by the lung?
- Histamine
- Serotonin
- Noradrenaline
- Vasopressin
Reference: West’s Respiratory Physiology

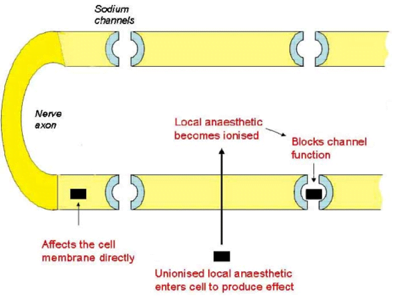
What is the benefit of adding sodium bicarbonate to local anaesthetic for spinal anaesthetic?
- Reduce the onset time
- Increases duration of action
- Reduces the dose of local anesthetic required
- Reduces the risk of local anaesthetic toxicity
- Explanation Alkalinisation of LA solutions → pH of injected solution more quickly approach that of normal tissue pH → faster formation of mixture with charged & uncharged forms → more rapid drug diffusion → quicker onset of nerve blocking
- Reference: https://www.nps.org.au/australian-prescriber/articles/alkalinisation-of-local-anaesthetic-solutions
Effect site equilibration is important for:
- Determining the volume of distribution
- Onset of action
- Maintenance of effect
- Clearance
- Effect site concentration is the concentration of drug at the site of its biological activity, eg. bound to the receptors
- Effect site concentration is proportional to pharmacological effect, whereas plasma concentration may not be
- The rate of effect onset is determined by the rate of distribution of the drug from other compartments (i.e. central compartment) into the effect site.
- Reference: Deranged Physiology- Effect site equilibration
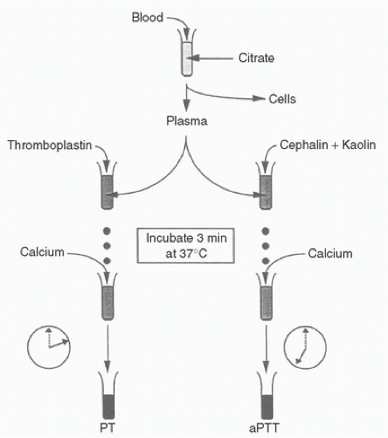
Measuring APTT involves the addition of which of the following to citrated plasma?
- Kaolin
- Thrombin
- Tissue factor
- Phosphate
Regarding REM Sleep
- Respiratory minute ventilation increases
- Cerebral blood flow is comparable with wakefulness
- The EEG shows high-voltage slow wave activity
- Episodes of REM sleep become progressively shorter as the duration of sleep increases
- Respiratory minute ventilation increases
- MV decreases – tidal volumes fall by ~25% in REM sleep compared with wakefulness.
- Cerebral blood flow is comparable with wakefulness
- CBF falls during NREM sleep – up to 22%. However CBF during REM sleep is similar to wakefulness.
- The EEG shows high-voltage slow wave activity
- MV decreases – tidal volumes fall by ~25% in REM sleep compared with wakefulness.
- Episodes of REM sleep become progressively shorter as the duration of sleep
increases
- Periods of REM become longer throughout the night
Alcohol and chlorhexidine do not kill:
- Clostridium difficile
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Which of the following is a Phase II Metabolism Reaction:
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Hydroxylation
- Sulfation
|
Ethyl alcohol |
Iodophors |
Chlorhexidine |
|
| Spectrum | |||
| Gram positive |
+++++ |
+++++ |
+++++ |
| Gram negative |
+++++ |
+++ |
+++ |
| Spores (e.g. C diff) |
No |
+ |
No |
| Mycobacteria |
+++ |
+++ |
+ |
| Yeasts |
+++ |
+++ |
++ |
| Virus |
+++ |
+++ |
+++ |
| Onset |
Immediate |
Intermediate |
Intermediate (fast with alcohol) |
| Residual activity |
No |
Some |
Excellent |
What is the circulating half-life of Angiotensin-II?
- 30 seconds
- 90 seconds
- 5 minutes
- 15 minutes