Levosimendan
Chemical
A calcium sensitizer inotropic agent
Presentation
Clear, yellow solution 2.5mg/mL in 5 & 10mL ampoules
Which needs to be diluted prior to administration
Route/Dose
IV infusion
Load: 6 – 12mcg/kg over 10 mins
Infusion: 0.1 – 0.2mcg/kg/min
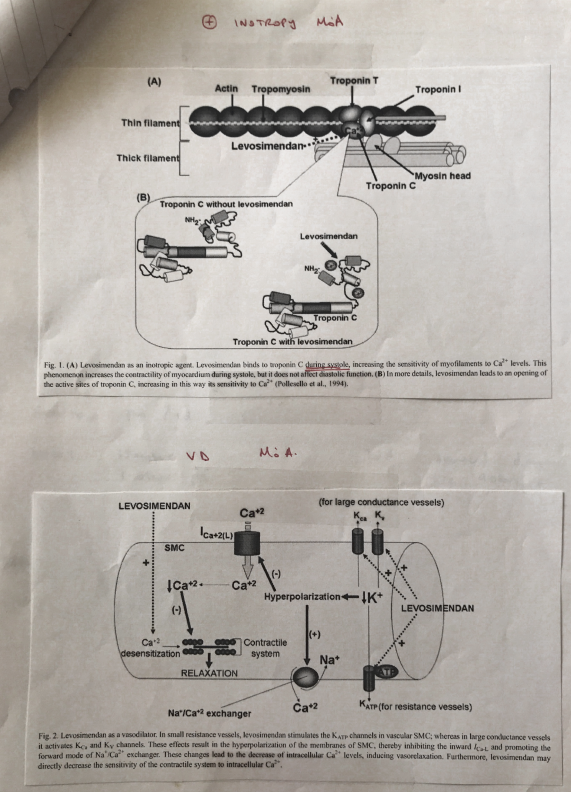
MoA
INOTROPY
- ↑affinity of TnC for Ca2+
- Directly stabilizes the TnC – Ca2+ conformation
- Magnifies the contraction produced when Ca2+ binds TnC
- Levo’s binding to TnC is directly dependent on cytosolic Ca2+ (∴ it’s significantly weaker with minimal Ca2+ sensitization during diastole)
VASODILATION
Large conductance vessels
- Opens KCA (Ca2+ activated) & KV (voltage dependent Ca2+ ch)
- K exits
- ↓intrac. K+ = HYPERPOLARISATION
- Inhibits inward Ca2+ current via L-type Ca2+ channel
- ↓intrac. Ca2
- Relaxation of vessel
Resistance vessels
- Opens KATP channels → K exits
- ↓intrac. K+ = HYPERPOLARISATION
- Promotes Na/Ca2+ exchanger → Ca2+ exits
- ↓intrac. Ca2 = relaxation of vessels
PD
CVS
- ↑myocardial contractility without ↑myocardial O2 consumption
- ↑CO (↑SV + ↑HR)
- Coronary + peripheral VD
- ↓SVR
GU: ↑UO + GFR 2° ↑CO
PK
A
Good oral absorption but administered IV
D
97% PPB → albumin
VD 0.2L/kg
M
95% → liver → hepatic conjugation to cysteine conjugates
5% → intestinal reduction → activate metabolites OR-1855 & OR-1896
E
55% renally excreted
44% faecally excreted
t ½ B = 3hrs
Active metabolites OR-1855 & OR-1896 reach peak plasma [ ] 2 days after infusion cessation → excreted in urine
Adverse Effects
- Hypotension 2° ↓SVR
- Headache, Dizziness, N&V 2° ↓ blood
- Small no’s of ↓K & arrhythmia reported
- Expensive