UFH
Chemical
A sulphated mucopolysaccharide of variable chain lengths
Extracted from porcine intestine mucosa & bovine lung
MW: 3000 – 30,000 Da
pH: strongly acidic (high sulphate content) ∴negatively charged
Solubility: hydrophilic & poorly lipid soluble. Cannot cross lipid barriers 2° high MW & poor lipid solubility
Use
- Tx thrombi
- Prevent thrombi
- Extracorporeal circuits
- Prevents thrombus formation in vascular procedures
Presentation
Clear solution for injection. IU/mL
Dose
- Commercial heparin is a family of molecules of different molecular weights
- ∴ level of heparin doesn’t correlate to anticoag activity
- Expressed as units of activity
- 1 unit = volume of heparin that will prevent 1mL of sheep’s blood from clotting for 1hr
Prophylaxis: 5000 IU (SC) BD
Therapeutic: 5000IU IV load → 10IU/kg/hr to an APTT 1.5 – 2.5 x normal (S/C) = 1mg/kg
Route
IV/SC → cannot be given IM 2° high risk haematoma at site
Onset / DoA
Peak
Time to normal haemostasis after cessation
IV UFH
1 min
4 – 6hr
S/C UFH
45 min
4 – 6hr
MoA (mechanism)
- Impairs coagulation
- Alone has no anticoagulant activity
- Requires AT III as cofactor
- Binds AT III → conformational ∆ → exposes active site & ↑its rate of reaction by x 1000
- AT III
- Inhibits all intrinsic pathway enzymes (XIa, XIIa, IXa)
- Inhibits common pathway factors (IIa, Xa)
- You need a long stretch of heparin to inhibit THROMBIN
- UFH = long ∴ Xa thrombin inhibition is 1 : 1
- You only need short stretch to inhibit Xa
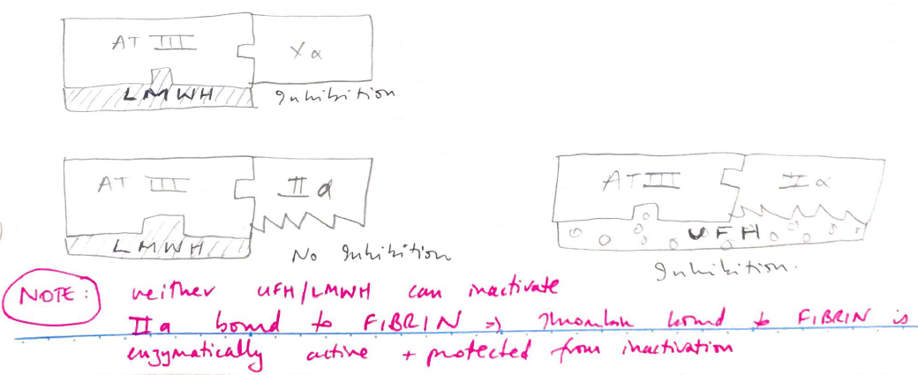
2. Inhibits platelet function → strong platelet inhibition
3. ↓ TAG levels → released lipid hydrolysing enzyme
4. ↑ vascular permeability
PD
- Impairs coagulation
- Inhibits platelet aggregation by Fibrin
- ↑plasma FFAs
- Osteoporosis & aldosterone suppression (long T)
PK
A
High MW/low lipid solubility
Poor oral absorption
IV/SC
D
High PPB
→ Binds plasma proteins, endothelial cells, vascular wall proteins
→ Accounts for large interpatient variability
VD 40 – 100mL/kg
DOES NOT CROSS PLACENTA
∴ anticoagulant of choice in pregnancy
M
Heparinases in liver
RES & kidneys
E
Metabolites renally excreted
Kinetics not affected by renal impairment
↓elimination with hypothermia
Adverse Effects
- HMMRG → ↑ risk
- ↓platelets → non immune (type 1): 0 – 4 days → platelet count recovers spontaneously
→ Immune (type 2 thrombocytopenia = HIT/HITT): 4 – 14 days → IgG mediated → heparin forms complex with platelet factor 4 → causes platelet aggregation & thrombus
- Osteoporosis (↑ clast activity = bone reabsorption → osteoporosis)
- Alopecia
- ‘Resistance’ = requires AT III for anticoagulant activity. Tx with FFP
Haemorrhage
Elevated temp & ↓BP (with high doses given for CPB)
Platelets (thombocytopaenia)
Anaphylaxis & alopecia
Ruins bones (osteoporosis)
Impaired mineralocorticoid production (hypoaldosteronism)
Noci (pain @ injection site)
Monitoring
Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT)
- APTT used to measure Intrinsic Pathway Factors (VIII, IX , XI, XII)
- Can also be used for X, V, II but PT assays more commonly used
- Blood sample is exposed to negatively charged activator + Ca2+
- Inhibition of F IX activity by heparin prolongs APTT
- Once they add Ca2+ to sample → measure time for clot to form → normally 28 – 35 secs
- Heparin → ↑APTT x 1.5 – 2.5 for therapeutic effect
- Not required for prophylactic dose because doesn’t elevate APTT
Activated clotting time
- Used for high dose heparin (CPB)
- Point of care bedside test, must faster cf. APTT
- Normal 90 – 150 sec
- Blood incubated with Kaolin to activate intrinsic pathway
- Seconds for whole blood to clot is measured
Affected by many things: warfarin, G IIb/IIIa inhibitors, hypothermia, (coag factor deficiencies, hypovolaemia, thrombocytopaenia)
Anti-Xa assays
- Considered more accurate
- Guidelines for the titration of heparin infusions using Anti-Xa levels
- Particularly useful if you have a patient with a prolonged baseline APTT ie a lupus anticoagulant where the APTT will not be reflective of their heparin level
Reversal
Protamine sulphate
1mg neutralises 100 units