Warfarin
Chemical
Synthetically derived coumarin anticoagulant
NB: coumarin is a chemical in many plants
The term comes from the French ‘tonka bean’ = COUMAROU, from where coumarin was first isolated
Use
- Prevent emboli in AF, value disease, prosthetic valves
- Tx DVT/PE
Presentation
Oral tablets 1 – 10mg
Racemix mixture
S-isomer x 4 potent
Dose / Route
5 – 10mg OD orally for 3 days
→ Daily bloods
→ Then alternate days for 1/52
→ Then fortnightly
Dose/route overlap for a minimum of 5 days, until target INR has been reached for at least two consecutive days (Pisters et al. 2010; Rossi 2015).
Because of the shorter half life of protein C and S they drop prior to the clotting factors and as such warfarin can produce an pro-thrombotic phenotype in the first few days
Target INR
AF 2 – 2.5
Prosthetic valve 2.5 – 3.5
All else 2 – 3
Onset
8 – 12hrs onset
- Warfarin halts production of new clotting factors
- No effect on already active factors
- ∴requires hours for full effect (for all of those factors to be degraded) → mainly F II (PRO THROMBIN)
DoA
Half lives:
of Protein C/s → 7 → 9 → 10 → 2
= 7 6 24 40 60hrs
DoA → effects last 2 – 5 days (life of clotting factors)
Very slow clearance 3mL/kg/min & new clotting factors need to be synthesised
MoA (mechanism)
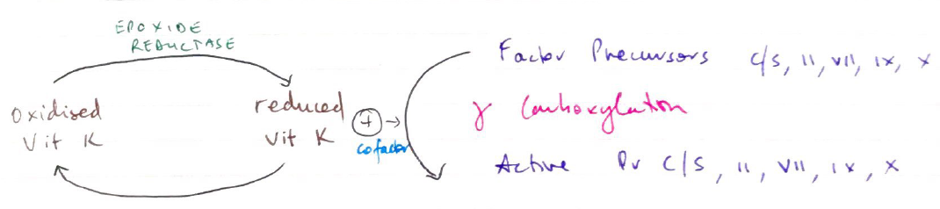
- Inhibits production of Vit K dependent clotting factors & proteins
- Vit K is required to synthesise:
- 4 clotting factors: II, VII, IX, X (TV channels)
- 2 anticoag proteins; Pr C & S
- Formation of these requires y-CARBOXYLATION
- Reduced Vit K (as cofactor)
- Warfarin inhibits EPOXIDE REDUCTASE. This enzyme reduces oxidised Vit K so it may be used again
- ∴ no cofactor for carboxylation → ↓ synthesis clotting factor & protein
NB: y-CARBOXYLATION allows activated factors to chelate Ca2+ → binds phospholipids → procoagulant
PK
A
High lipid solubility
100% OBA
Rapid absorption
Peak plasma 4h
D
99% PPB (albumin)
VD 0.1L/kg
Small due to high PPB
M
Entirely by liver
Phase 1 & 2 reaction
CYP450
Metabolites then conjugated & glucoside
E
Metabolites excreted in urine & faeces
t ½ = 40hrs prolonged
Predictability
Highly variable
- VIT K AVAILABILITY
- Diet
- ↓synthesis
- ↓absorption (requires bile salts)
- Albumin alters Vit K absorption
- LIVER DISEASE
- ↓synthesis clotting factors
- Altered metabolism of warfarin
- METABOLISM
- Fever/hyperthyroid → ↑breakdown coag factors
- Myxoedema → ↓breakdown coag factors
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Susceptible due to high PPB & sole liver metabolism
Enhanced Effect
NSAIDs/Aspirin (high PPB)
EtOH → prolongs clearance
Other PPB competitors
- Amiodarone
- Cimetidine
- Metronidazole
- Erythromycin
Decreased Effect
Liver enzyme inducers
- Barbituates
- OCP
- Phenytoin
- Rifampicin
Adverse Effects
- Bleeding (nose, urine, head, menstrual, GI etc)
- Teratogenic → crosses placenta
- Cutaneous necrosis → may occur in patients with ↓activity of Pr C
Monitoring
- Warfarin is reported by monitoring INR, which is the Prothrombin Time (ext & common pathway) according to International Reference Thromboplastin
Reversal
- Cease warfarin!
- Vitamin K
- FFP
- Prothrombinex
- Activated FVII