Paracetamol
Chemical
An acetanilide derivative
Use
- Analgesia
- Antipyretic
Presentation
- Tablets
- Syrup
- Rectal suppositories
- IV → glass vial & argon, drug is unstable in O2 rich environment
Dose
1g QID
Route
PO/PR/IV
Onset
- Peak [ ] 1hr 30mcg/mL
- Therapeutic range 10 – 20mcg/mL
- In 4hrs [ ] <10mcg/mL
MoA (mechanism)
Antipyretic
- Inhibits central PG synthesis
- Especially PGE in anterior hypothalamus
Analgesia
- Inhibits peripheral Subs P actions
- Potent central PG synthesis
- Peripherally blocks impulse generation with BK sensitive chemoreceptors
PD
CNS
- Analgesia
- Antipyretic
PK
A
High lipid solubility
Rapid absorption
OBA 60 – 90%
More PR (OBA)
D
pKa 9.5 (weak acid)
<1% PPB
Highly UNIONISED at pH 7.4
Lipid soluble
Penetrates BBB +++
VD 1L/kg
M
HER 0.3
80% to glucuronide & sulphate
10% to NAPGI via CYP450 which is then conjugated with glutathione
E
<5% unchanged in urine
Metabolites actively secreted into renal tubules
t ½ B 2 – 4hrs
Adverse Effects
PARACETAMOL TOXICITY
Toxicity = the degree to which something is poisonous
- Paracetamol therapeutic range = 10 – 20mcg/mL
- Toxicity occurs if >10g ingested/24hrs
Metabolised by 2 pathways
- 90% metabolised to glucuronide & sulphate
- 10% metabolised by CYP450 to NAPQI → then conjugated to glutathione
Mechanism of toxicity
- ↑NAPQI levels
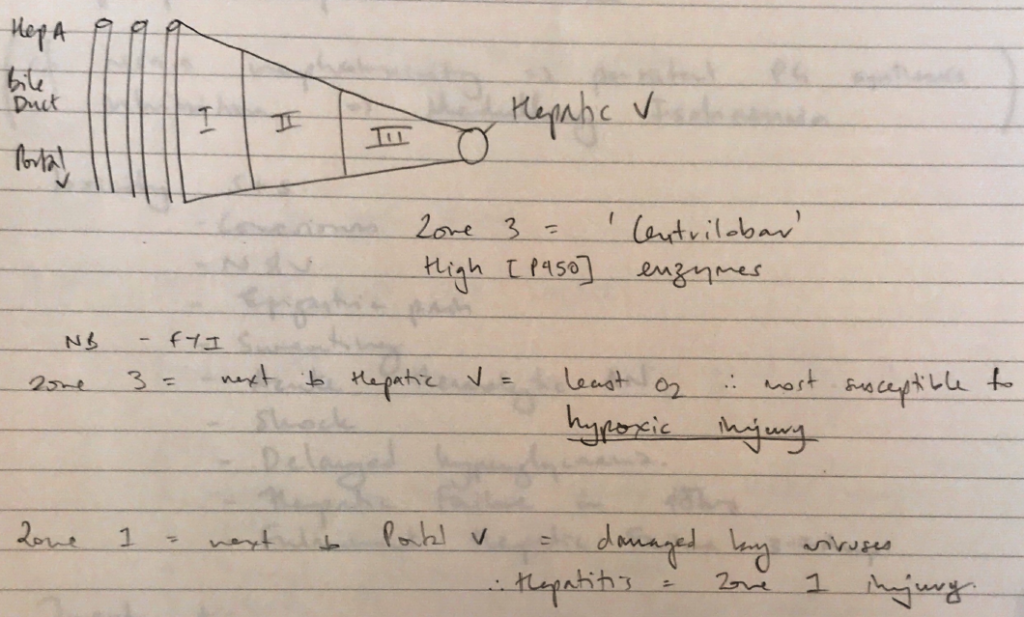
- Forms covalent bonds with sulphadryl groups on hepatocytes → cell death → centrilobular necrosis
4 mechanisms of liver damage
- Excess paracetamol
- Excess CYP261 activity → inducers (phenytoin; rifampicin)
- ↓ capacity to metabolise to glucuronide/sulphate
- ↓ glutathione stores
When NAPQI reacts with hepatocytes = IRREVERSIBLE INJURY
Nephrotoxicity
- Metabolite p-aminophenol accumulates in renal papillae
- Causes necrosis because binds covalently to sulphydryl groups & depletes glutathione
Cf. NSAID nephrotoxicity → persistent PG synthesis inhibition → medullary ischaemia
Toxicity S+S
- N&V
- Epigastric pain
- Sweating
- Acute haemolytic AN
- Shock
- Delayed hyperglycaemia
- Hepatic failure in 48hrs
- Fulminant hepatic failure 3 – 7 days
TREATMENT
- Activated charcoal in 4hrs
- ABC, IV glucose
- NAC → metabolized to glutathione which can conjugate with NAPQI
- Treatment based on normogran (Rumack-Mathew)