Theophylline Aminophylline
Chemical
A methylxanthine derivative
Use
Tx bronchoconstriction
Presentation
Tablet, syrup, solution for IV injection
Route/Dose
Loading Dose 7mg/kg calculated by IB and given over 30 minutes
Maintenance 0.6mg/kg/hr (IV) or 7mg/kg (PO)
MoA
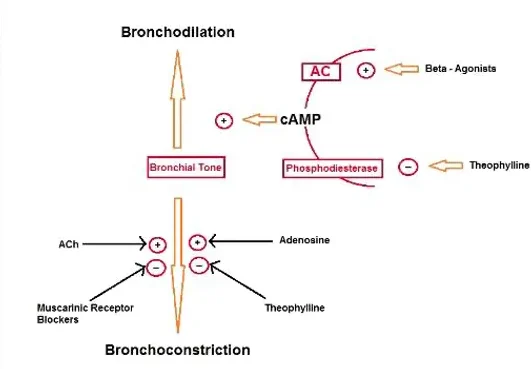
PHOSPHODIESTERASE INHIBITOR
- ∴↑cAMP
- ↑Protein kinase A
- Inhibits phosphorylation of myosin + ↓Ca2+ = smooth m. relaxation + bronchodilation
ADENOSINE RECEPTOR BLOCKER
- Blocks adenosine mediated bronchoconstriction
PD
Resp
- Bronchodilation
- ↑respiratory centre sensitivity to CO2
- Disturbs HPVC
CVS
- +ve chonotropy & inotropy
- *** arrhythmogenic at high doses
GU
- ↓RBF & GFR
- ↓Na+ reabsorption → diuresis
PK
A
- Rapidly + completely absorbed PO route
D
- 0.3 – 0.7L/kg, PPB 40%
M
- 90% of the dose is metabolised in the liver
- Hepatic Demethylation occurs and then further hydroxylation to metabolites
- Caffeine & 3-methylxanthine are the only active metabolites
- Both these pathways are capacity-limited and there is wide intersubject variability in the rate of metabolism
- The relationship is non linear and any increase/decrease in dose should be monitored with levels
- Clearance is reduced in patients with hepatic impairment
E
- Renally excreted
- 10% unchanged
- t ½ 8hrs
Therapeutic Index & Drug Monitoring
Bronchodilation occurs over a concentration of 5-20mcg/ml
As concentrations >20mcg/ml so do the frequency & severity of adverse events
Adverse Effects
Metabolic
- Hypokalaemia 2° diuresis
- Abnormal LFTs
- Inappropriate ADH secretion
CNS
- Convulsions → if administered rapidly
CVS
- Arrhythmias → including VF at high doses
MSK
- Antagonises non-depol NMB @ high doses
P50 interactions
↑[Theophylline]
- Cimetidine
- Propanolol
- Erythromycin
↓[Theophylline]
- Barbiturates
- Alcohol
- Phenytoin