F1i: Structure and function of the nose
Structures
- Breathing is via nose/mouth → both airways converging in the oropharynx
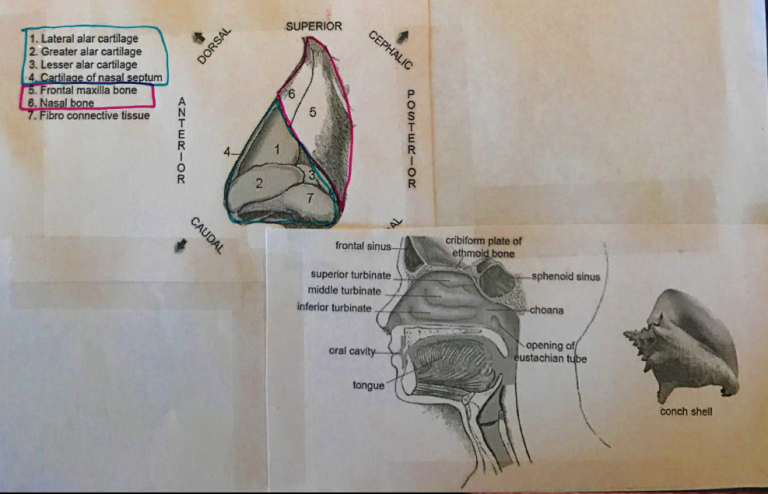
- Nose consists of bony & cartilaginous sections
- Bony section
→ Superior half
→ Nasal bone & frontal maxilla bone
- Cartilaginous
→ Inferior half
→ Cartilaginous portions are connected to each other & bones by a tough fibrous membrane
- 2 nostrils = openings of nose
- Nostrils separated by NASAL SEPTUM
- Nostrils open into VESTIBULES → 2 NASAL CHAMBERS
- Nasal cavity separated from cranial cavity by CRIBIFORM PLATE
- CRIBIFORM PLATE is perforated, many small openings to allow OLFACTORY N (CN I) passage
- Nasal Chambers contain 3 passageways KA SUPERIOR, MIDDLE, INFERIOR CONCHAE (conch seashell shape)
- Posterior to these are OVAL shaped orifices KA CHOANAE (1.5 – 3cm diameter); openings allow air passage. Once air has passed through CHOANAE it is in the upper resp tract; THE PHARYNX
- Paranasal sinuses
- 4 empty air spaces which open/drain into nasal cavity
- Named for their location
- FRONTAL
- MAXILLARY
- SPHENOID
- ETHMOID
Function
Passageway
- For air to pass from environment → lungs
Humidify & Filter Air
- Stratified squamous epithelium at entrance to nasal cavity
- Contain sebaceous glands + NOSE HAIRS which filter out inhaled particles
- Main nasal passage → RESPIRATORY MUCOSA
- Pseudo-stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
- Contain:
- GOBLET CELLS → secrete mucous which traps inhaled particles (dust, bacteria)
- SEROUS GLANDS → produces watery fluid with bacterial enzymes
- CILIA → mucociliary rhythmical actions transport secreted mucous + trapped particles to throat where it is swallowed
Humidifying Air
- Thin walled veins line nasal epithelium
- Heat is transferred from blood to warm inspired air
- Turbinate structure allows ↑SA for this
Smell
- Olfactory receptors for smell located in nose
- Olfactory nerve transmits these via nasal passage