F3v: Explain the concept of time constants
Definition
- A time constant (t) = time taken for an exponential process to be 63% complete if the initial rate continues
- An exponential process is complete after 3 time constants
- g. t1 = 63% complete
- t2 = 86.5% complete (100 – (37 x 37))
- t3 = 95% complete (100 – (37 x 37 x 37))
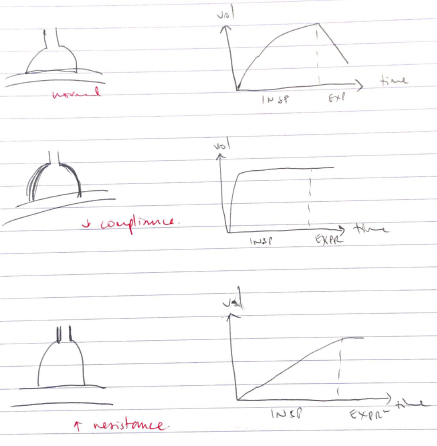
Normal Lung Unit
- Flow of air in & out of alveoli is an exponential process
t = compliance x resistance
= 100mL/cm H2O x 2cm H2O/L/sec
= 0.2 seconds
- ∴normal lung unit, filling completed 63% after 0.2 sec
- ∴t gives indication of alveoli filling/emptying velocity
Heterogeneity Slow & Fast Time Constants
- Altered TCs give unequal ventilation at any level
- ↑R = requires prolonged emptying due to narrow airway
- ↑C = slower emptying due to ↓elastic recoil
- ↑either will ↑ t (C x R)
- For even distribution of ventilation, lung units require same t (it doesn’t matter if the R/C is ↓/↑)
- Fast alveolus
↓ C/R = shortens t
∴ slows greatest volume ∆ first → then approaches equilibrium
- Slow alveolus
↑ C/R = longer t
∴takes longer for volume ∆
In Disease
Compliance
Resistance
↑C = Emphysema = ↑t
↑R = asthma = ↑t
Effect of Uneven Time Constants
- Fast & flow alveoli are out of sync
- Fast alveoli are ventilated first & always subject to greater pressures
- At end INSP, slow alveoli have not filled
- EXPR starts → gas redistributed from FAST → SLOW (KA PENDELLUFT EFFECT)
- But these SLOW ALVEOLI are filling with air already partaken in gas exchange → ↑V/Q mismatch
- Exacerbated at ↑RR = ↓redistribution tie = ↓DYNAMIC COMPLIANCE