F8i: Compare & contrast the carriage of O2 & CO2 in blood
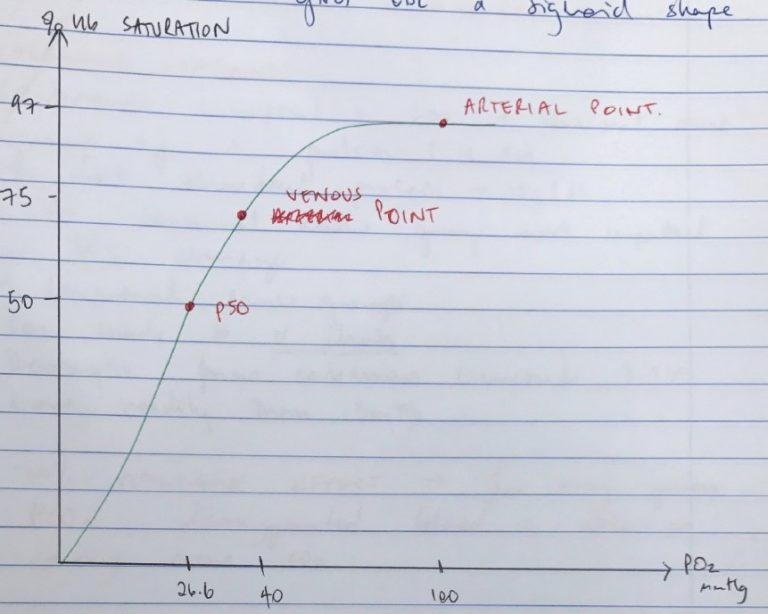
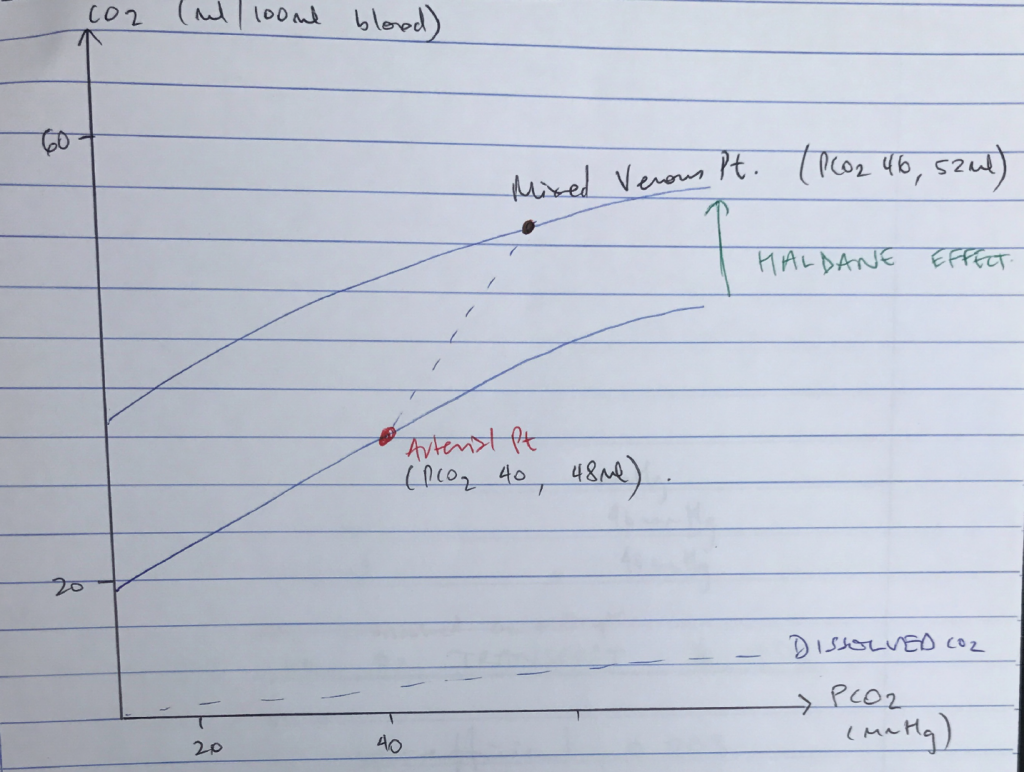
Content of Arterial Blood
mL/dL
mmHg
CO2
48mL
40mmHg
O2
21mL
100mmHg
Content of Venous Blood
mL/dL
mmHg
CO2
52mL
46mmHg
O2
15mL
40mmHg
Mechanism of O2 Transport & ODC
CaO2 = Dissolved O2 + OxyHb
Dissolved O2
- Solubility co-efficient 0.003
- Obeys Henry’s Law → the amount carried dissolved in solution is directly ∝ to the partial pressure
- ∴pO2 x 0.003 = O2 mL/dL
Oxyhaemoglobin
- O2 binds reversibly to Hb: Hb + O2 ⮂ HbO2
- HUFFNER’S CONSTANT = 1.34mL O2 per 1g Hb
- O2 binds to heme portion of Hb
- 4 x heme → ∴1Hb can bind up to 4 O2
- Displays +ve COOPERATIVITY → affinity for O2 is lowest at first O2 binding because DeoxyHb Is in TENSE configuration
- With each subsequent O2 binding heme is ↑O2 affinity
R) Shift ODC
- ↑CO2
- ↑H+
- ↑Temp
- ↑2, 3 DPG
- ↓pH
= ↓affinity = offloads O2
L) Shift ODC
- ↓CO2
- ↓H+
- ↓Temp
- ↓2,3 DPG
- ↑pH
= ↑affinity = binds O2 tighter
CO2 Carriage in Blood & CO2 Dissociation Curve
Carbamino Compounds + Dissolved + HCO3–
Carbamino Compounds
- Carbamino compound = CO2 + terminal amine group of a protein (i.e. Hb)
- Hb most abundant protein → 15g/dL
- ∴its terminal amine group most important for CO2 carriage
- 4 terminal amine groups
- CO2 binds to α-chain
- DeoxyHb forms carbamino compounds 3.5 x more readily than OxyHb
NB: 70% HALDANE EFFECT → for any given PCO2, deoxygenated blood is able to carry more CO2
Dissolved
- Obeys HENRY’S LAW → the [ ] of a gas in liquid is ∝ to its partial pressure
- CO2 is x 20 more soluble cf. O2
- Solubility co-efficient 0.03
- ∴ Dissolved CO2 (mL) = 0.03 x pCO2