23A17: Exam Report
Explain the following components of an electrocardiogram (ECG) machine; electrodes, leads, amplifiers and filters. (70% of Marks) Outline methods employed to reduce artefact. (30% of Marks)
39% of candidates passed this question.
Good answers described electrode components, intensity of signals measured (requirement for and levels of amplification), lead position and differences between unipolar and bipolar leads.
Rationale and mechanisms of filtering were less well described. Description of high- and low-pass filtering along with detail on monitoring and diagnostic modes scored marks. Patient-related, electrical and environmental methods of reducing artefact attracted marks
21B17: Exam Report
Explain the components of an ECG (electrocardiogram) monitor (70% marks). Outline the methods employed to reduce artefact (30% marks)
46% of candidates passed this question.
Excellent answers described the function of the ECG device and its components. Components include electrodes, which form leads (unipolar and bipolar), the amplifier and an output device. The process of amplification and filtering (e.g., high and low pass filters), as well as monitoring and diagnostic ECG modes were described. A comprehensive list of ways to reduce artefacts, including strategies to address both patient and equipment factors was generally provided.
16A09: Exam Report
Describe the essential components of an ECG monitor (80% of marks). Outline the methods employed to reduce artefact (20% of marks).
50% of candidates passed this question.
The ECG device detects and amplifies the small electrical changes on the skin that are caused when the heart muscle depolarizes (0.5 – 2 mV).
This is reflected as rises and falls in the voltage between two electrodes placed either side of the heart which is displayed either on a screen or on paper.
Usually more than 2 electrodes are used and they can be combined into a number of pairs (For example: Left arm (LA), right arm (RA) and left leg (LL) electrodes form the three pairs LA+RA, LA+LL, and RA+LL). The output from each pair is known as a lead. Each lead is said to look at the heart from a different angle.
Electrodes are commonly made of silver or silver chloride components that are attached to the main unit of the machine. Most ECG machines use 12 electrodes. Better answers made mention of the two lead types: unipolar and bipolar.
Methods to reduce artefact include improving signal detection (conductive paste, skin preparation (dry, no hair, etc.)) and minimizing external electrostatic forces (common earthed environment, diathermy, etc.,) or patient environment (avoid shivering).
The amplifier has three essential functions: High input impedance so as to minimize signal loss and reject interference (50 – 60 Hz), differential amplification, (to amplify the potential difference detected by the skin electrodes), and high common mode rejection (e.g. > 50Hz) to aid eliminating muscle artefact or electrical interference from the power grid.).
Vector analysis is not a component of the ECG machine and so was not required to answer the question.
G6i / 23A17 / 21B17 / 16A09: Describe the essential components of an ECG Monitor (80 marks) + Outline methods employed to reduce artefact (20 marks)
ECG: detects & amplifies the small electrical ∆ transmitted to the skin when heart muscle depolarises + repolarises over time
- Each heart beat → all APs summated produce a voltage → detected on body surface
Components
Detection Device
Electrodes → silver/silver chloride
- Conductive gel (embedded with Cl–)
- Secured to skin by adhesive
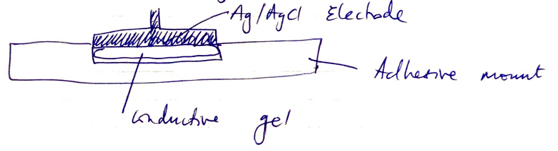
- The biological electrical potential caused by heart contraction causes a small current of flow through electrode → altering distribution of ion between metal & electrolyte solution
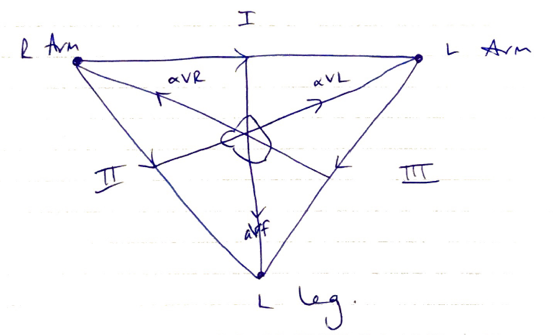
Leads → heart is displayed as a series of leads
Bipolar: I, II, III
- Measure voltage between 2 electrodes
- View heart in frontal plane
Unipolar: aVR, aVL, aVF
- Measure potential between electrode & null pt
Precordial leads: V1 – V6
- Also unipolar
- Measure potential between heart & null pt (middle of heart)
Cardiac vector = sum of all electrical activity occurring in the heart
- Cardiac depol. travelling toward electrode = +ve deflection
- Cardiac depol. travelling away from electrode = -ve deflection
- Current at 90° to electrode = no deflection
Amplifier
Signal amplification
- Signal arriving to amplifier can be spoiled by large amount of interference
- Amplifier designed to extract + amplify correct signal
- Ability of this is KA SIGNAL-TO-NOISE-RATIO
System Gain
- Gain = logarithmic scale of size signal produced vs size of signal detected
- Describes sensitivity of the system
- Should match size of signal detected i.e.
- High gain → small voltages not part of signal will be amplified, creating noise
- Low gain → amplifier will not detect signal
Bandwidth
- Describes the range of frequencies the amplifier will respond to
- ECG bandwidth = 0.5 – 100Hz
- Voltage range = 0.1 – 1.0mV
Processing
- Common Mode Rejection is high to eliminate artefact or electrical interference from power grid
Display
- Electrical signal is amplified, processed & displayed as KINETIC ENERGY
- Movement of beam on monitor
- Movement of pen on paper
& SOUND ENERGY
- Beeping pulse oximeter
- Further processing can display numbers
- Algorithms in monitor software can calculate various properties of ECG wave i.e.
- R-R
- ST ∆
- Arrhythmias
Modes of Monitor
- MONITOR MODE: smaller freq. 0.5 – 40Hz
- Narrow bandwidth
- ↓artefact
- High freq. filters
- DIAGNOSIS MODE: wider freq. 0.05 – 100Hz
- Assesses ST, QRS, arrhythmias
- Low freq. allows ST & T-wave assessment
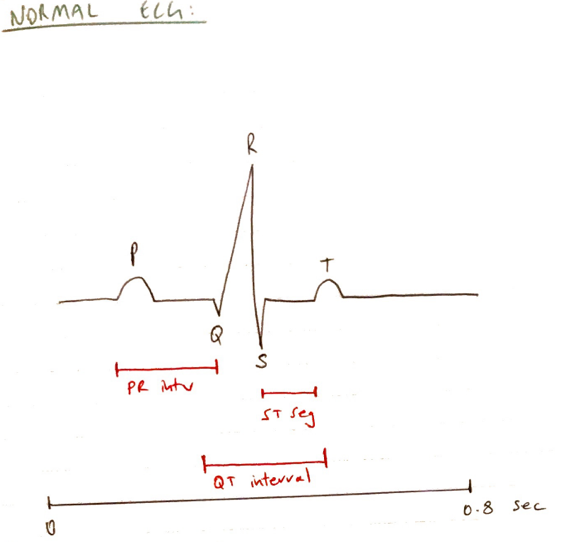
Standard Conditions
- Scroll paper 25mm/sec
- Large sq. 5mm = 0.2sec
- Small sq. 1m = 0.04sec
- 1cm height = 1mV (2 large squares)
Methods to ↓ Artefact
1. Patient
- Keep still, minimise movement
- Clean, shave + alcohol wipe skin
- Electrode placement (↓artefact over bone)
2. Electrode
- Good skin contact
- Adequate gel conductors
3. Lead factors
- ECG length with copper leads
4. Central processor
- Multiple electrode to improve Common Mode Repetition Ratio
5. Display device
- Accurate display with printer timing, square height & length