18A04: Exam Report
Describe the renal handling of sodium.
46% of candidates passed this question.
A description of filtration and reabsorption, including amounts was required. Better answers described sodium handling in a logical sequence as it progressed through the nephron including the percentages reabsorbed in each segment. In addition to the amounts reabsorbed, the mechanisms of transport across the tubular luminal and basolateral membranes into interstitial
space should have been described.
H1v / 18A04: Describe the renal handling of sodiu
Definitions/Values
- Sodium = major cation of ECF
- Plasma level 140mmol/L
- 180L/day GFR → 25,000 mol Na+ filtered/day
- 140mmol excreted → 0.5% fractional excretion
PCT
- 65% reabsorbed
- Co-transport with nutrients (amino acids, glucose) → driven by Na/K/ATPase
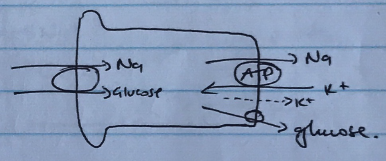
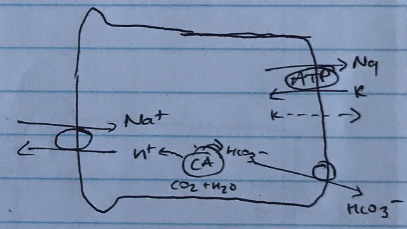
- Counter-transport with Na/H exchange
- HCO3– reabsorbed
- Driven by Na/K/ATPase
- Stimulated by AII
- Inhibited by Acetazolamide
- Passive diffusion by SOLVENT DRAG
- Late DCT favours osmosis because early PCT does major solute reabsorption
- This will drive Na+ reabsorption by solvent drag with H2O
Thin Desc. LoH
- Permeable to H2O, impermeable to solutes
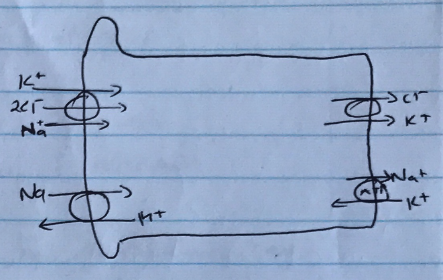
Thick Asc. LoH
- 25% reabsorption
- Permeable to solutes, impermeable to H2O
- Co-transporter Na/K/2Cl
- Counter transporter Na/H
- Driven by Na/K/ATPase
- ADH ↑activity of Na/K/2Cl
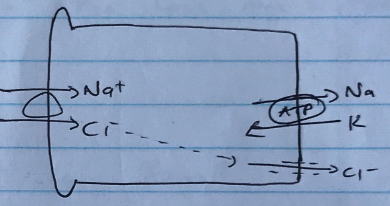
DCT
- 6% reabsorption
- Co-transporter Na/Cl
- Driven by Na/K/ATPase
- Blocked by thiazides
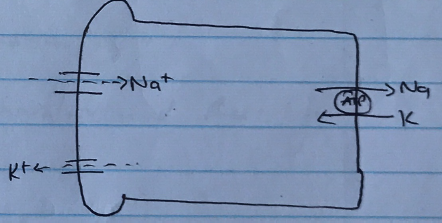
Principle Cells → Collecting Duct
- 3% reabsorption
- Apical Na+ channels
- Driven by Na/K/ATPase
- Controlled by aldosterone
Regulation of Na+
Systemic
- SNS → sympathetic stimulation (e.g. hypovolaemia) → aff. arteriole VC → ↓GFR → ↓Na+ loss
- Glomerulotubular balance
- Na reabsorption at PCT matches GFR
- ↑GFR will = ↑Na+ reabsorption at PCT
- 2 mechanisms:
- ↑filtration glucose, amino acids
↑Na+ reabsorption coupled with nutrients
2. ↑GFR = ↑protein in peritubular caps
↑oncotic P = ↑ movement H2O & solutes
- Overall: minimises Na+ & H2O loss due to ↑GFR
Hormonal
Aldosterone
- ↓Na → ↓ECF → detected by BaroR
- ↑SNS activity & ↓Na+ presentation to Mac. Densa
- ↑RENIN release by GRANULAR CELLS
- \( \textbf{Angiotensin } \xrightarrow{\text{RENIN }} \textbf{AI} \xrightarrow{\text{ACE }} \textbf{AII} \)
AII = ↑aldosterone secretion - Aldosterone acts on mineralocorticoid receptors of Principle Cells to:
- Upregulate Na/K/ATPase pump
- Upregulate Apical Na+ channels of Principle Cells
- ↑Na+ reabsorption
Renin
- Stimulates Aldosterone secretion
- Produces AII
- Powerful VC, esp. of eff. Arterioles = ↓peritubular hydrostatic P → ↑Na+ reabsorption
- Upregulates Na/K/ATPase of all tubule cells
- Upregulates PCT counter-transport Na/H exchange
ANP/BNP
- Stretching of atrial due to ↑circulating volume
- Inhibits apical Na+ channels of Principle Cells
- ↓Na+ reabsorption also inhibits ADH stimulated reabsorption
ADH
- ↑Thick Asc. LoH Na/K/2Cl activity = ↑Na+ reabsorption