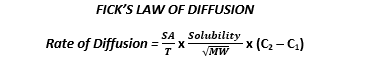15A03: Exam Report
Describe the structure and function of the blood brain barrier.
33% of candidates passed this question.
There was general lack of understanding of the conceptual framework of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and its function. To attain a pass, candidates were required to describe the concept of BBB as a physical and a transport barrier, describe the role of tight junctions and glial cells and identify important barrier functions with some examples of things commonly transported across or excluded.
K1iv / 15A03: Describe the structure and function of the BBB
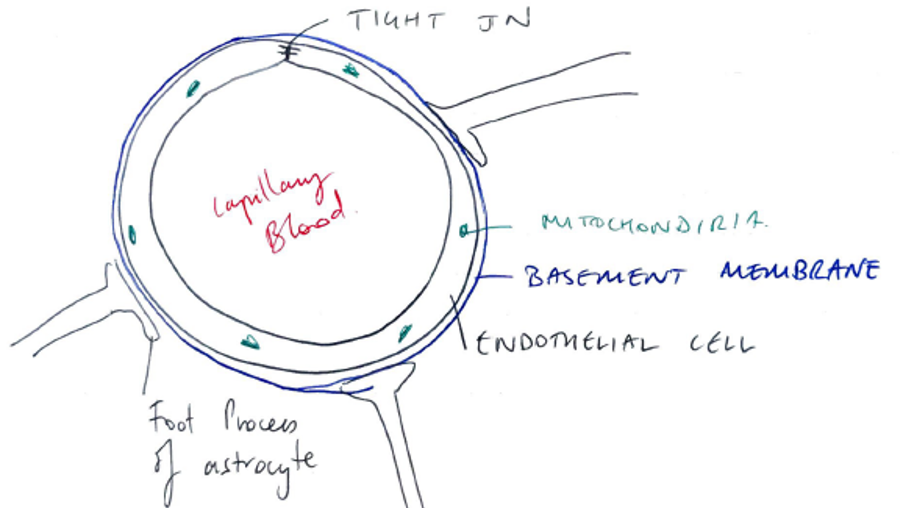
- BBB = highly regulated interface which separates the CNS from the blood
Function of the BBB
- CNS homeostasis → provides a stable environment for neurons
- Protect brain from toxins
- Tight control of electrolytes
- Protects brain from transient ∆BGL
- Prevents release of central NT into systemic circulation
Endothelial Cells
- No fenestrations
- Have TIGHT JUNCTIONS
- Prevents passage of molecules from blood → brain
- Multiple mitochondria → large amounts of Active Transport
Astrocytes
- Contain many enzymes which metabolise substances before they can reach BBB
Drugs Metabolised by BBB
- MAO → breaks down dopamine & NA
- ∴we can’t give dopamine to Rx PD
- We must give L-DOPA which is then converted to dopamine
- Cholinesterases → metabolise ester Las
Substance Regulation
(Small + lipid soluble)
- CO2
- O2
- EtOH
- Nicotine
- H2O
↓
PASS
Cannot Pass
- Electrolytes
- Proteins
- Ab’s
- Hydrophyllic
BBB Transport
- Diffusion: CO2, O2, EtOH, H2O
- Facilitated: amino acids, glucose (GLUT – 1)
- Receptor mediated endocytosis (Insulin)
- Paracellular transfer
Circumventricular Organs
- Area where BBB is absent
↓
- Have neuroendocrine role ∴need access to systemic circulation
- Vomiting centre (area postrema)
- Pineal gland (secretes melatonin)
- Neurohypophysis of the PPG (releases oxytocin + ADH)
Disruption to BBB
- Inflammation
- Oedema
- HTN (stretching & weakening tight junctions)
- Epilepsy (↑BP → weakens TIGHT JUNTIONS → restored 1hr post seizure)
Drugs to Penetrate CNS
- Solubility = required to be lipid soluble. CNS covered by 2 layers of membrane → BBB & PM of neurons
- Size = smaller = better. Must be <400Da
- Ionisation = penetration is in the UNIONISED FORM
∴ weak acids penetrate CSF better
- CNS Metabolism = drugs metabolised in CNS will create a gradient for diffusion
- Inflammation = loss of BBB integrity will ↑SA available & ↑rate of drug diffusion e. antibiotics for meningitis