K1v: Describe the major sensory and motor pathways (including anatomy)
- Spinal cord from brainstem → L2
- Part of CNS
- Covered by 3 membranes of CNS: dura, arachnoid, pia
- Protected by vertebral column
Ascending Tracts
Descending Tracts
- SENSORY
- Starts with ‘spino’
- MOTOR
- Ends in ‘spino’
- CNS transmits motor commands in response to sensory info
3 tracts
- POSTERIOR COLUMN TRACT
- SPINOTHALAMIC TRACT
- SPINOCEREBELLAR TRACT
2 tracts
- CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
- SUBCONSCIOUS TRACTS
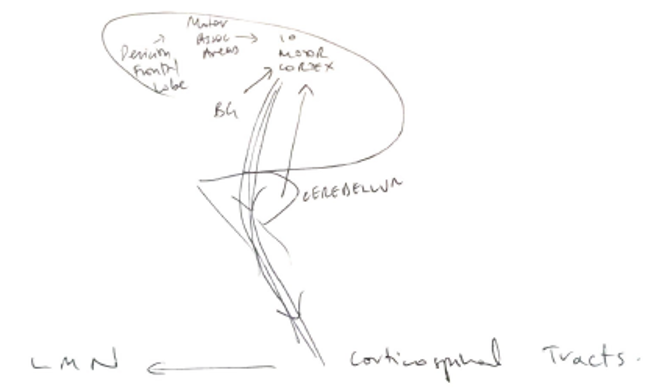
- Chain of neurons: 1st order, 2nd order, 3rd order
* via SNS (somatic) → contraction of skeletal m.
UMN → motor nuclei → LMN → skeletal m.
* via ANS (autonomic) → glands, smooth m., cardiac m.
Neurons running up sensory tracts are arranged according to:
- Sensory modality e. fine touch has own tract
- Somatotropic e. arranged according to site of origin
- Medial → lateral rule e. sensory n. that enters at a low level of SC are more medial
- Sensory n. that enters at a higher level is more lateral
Preganglionic → autonomic ganglia → ganglionic n.
NOTE:
31 pairs of spinal nerves:
Nerves
Vertebral Level
8 cervical
C1 – C7
12 thoracic
T1 – T12
5 lumbar
L1 – L5
5 sacral
Sacrum
2 coccygeal
Coccyx
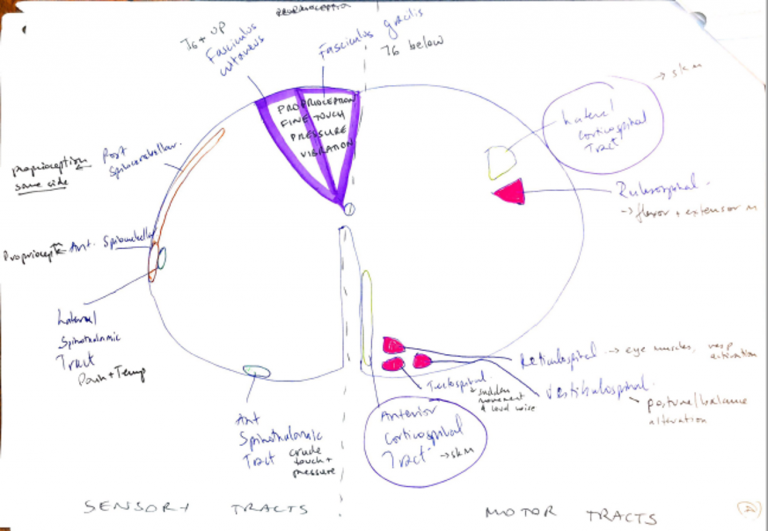
Ascending Tracts: Sensory
Posterior Column
- Proprioception
- Fine touch
- Pressure
- Vibration
- Fasciculus gracilis (from below T6)
- Fasciculus cutaneous (from T6 + up)
- Carry to sensory cortex opposite stimulus
Spinothalamic Tract
- Lateral Spinothalamic Tract
- Pain & temperature
- Anterior Spinothalamic Tract
- Crude touch & pressure
- To sensory cortex opposite side
Spinocerebellar Tracts
- Posterior Spinocerebellar
- Proprioception
↓
To cerebellar cortex on same side as stimulus
- Anterior Spinocerebellar
- Proprioception
↓
To cerebellar cortex primarily on same side as stimulus
Descending Tracts: Motor
Spinal Cord Arterial Supply
Anterior Spinal Artery → anterior 2/3 of SC
- Comes off vertebral arteries
- Unites @ Foramen Magnum
- Descends as single vessel
- Penetrates medial sulcus
2 Posterior Spinal Arteries
- Two from:
- Vertebral arteries
- Posterior inferior cerebellar arteries
- Supply → posterior 1/3 of SC
Radicular Branches
- Arises from local arteries
- Supply local areas of SC
Venous Drainage: 2 median, 2 ant-lat, 2 post-lat VENOUS CHANNELS
Anterior Spinal Artery Syndrome
- Sudden back/neck pain
- Rapid progressive flaccid & areflexic paralysis
- Loss pain + temp to sensory level
- Preserved proprioception & vibration
- Urinary incontinence
Posterior Spinal Artery Syndrome
- Loss of proprioception & vibration
- Preserved pain + temp
- Loss reflexes below segment
- No motor deficits