K1vii: Gaba Receptors
- γ-aminobutyric acid = principle inhibitory NT of CNS; 1/3 of all CNS synapses
- Synthesis: decarboxylation of glutamate
- Storage: pre-synaptic nerve terminals
- Removal
- METABOLISM by Transamination
- REUPTAKE into nerve terminal
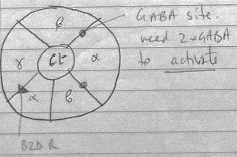
- 2 classes of GABA receptor; GABAA + GABAB
Gabaₐ
Structure
- Pentametric
- Inotropic (Cl–)
- Many subunits: α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ
- Different GABA R have diff no. of subunits ∴30 types!
- You need α, β, γ subunit for full function
Gabaь
- Metabrotopic (GPCR)
- ↑K+ or ↓Ca2+ channel conductance
- Pre & post synaptic location
- Presyn = ↑release of GABA from storage sites
- Postsyn = generates inhibitory postsynaptic membrane potential
- BACLOFEN = GABAB AGONIST
- GABAB mediated inhibition of muscle contraction not affecting NMT
- ∴↓muscle spasm in MS & SC lesions
Glycine Receptor
- Major inhibitory NT of spinal cord & brainstem
- Assoc with Cl– channel like GABAA
- Volatiles markedly potentiate action of GLYCINE