18A14: Exam Report
Classify anticholinesterase drugs according to chemical interaction with an example of each (30% of marks). Outline the pharmacodynamic effects of anticholinesterase drugs and their clinical indications (70% of marks).
32% of candidates passed this question.
Many candidates who scored poorly confused anticholinesterase drugs with anticholinergic drugs. Some described pharmacokinetics when it was not asked. Similarly, treatment of organophosphate poisoning and/or cholinergic crisis was not asked for in the question.
15A21: Exam Report
Describe the pharmacodynamic effects and indications for the use of anticholinesterase drugs.
25% of candidates passed this question.
It was expected the answer would provide a structured approach to describing the pharmacodynamics (what the drug does to the body) of this discreet class of drugs. A brief acknowledgement of the drugs in this class followed by a catalogue of the various clinical uses of this class of drugs would be a good start. If this was followed up with a description of the effects of these drugs on the CVS, GIT, Salivary glands, eye, NMJ and the lungs a good mark would have been awarded.
A number of candidates described the actions at the receptors in detail which did not attract marks. The extensive range of clinical uses for this class of drugs was poorly appreciated.
Few answers demonstrated any understanding of the PD effects of the drug class. There was generally a good knowledge of representative drugs within this class. Failing to achieve a pass mark reflected scant/brief answers that just did not cover enough of the expected material.
L2i / 18A14 / 15A21: Classify Anticholinesterase drugs according to chemical interaction with an example of each (30). Outline the PD effects of anticholinesterase drugs and their clinical indications (70)
Definition
Anticholinesterase Drug = drug that increases duration of action of ACh by binding to and inhibiting the Aceytlcholinesterase enzyme (AChE)
Mechanism of Action AChE
AChE has two binding site; anionic & esteratic
Anionic site binds Quaternary amine group of Ach
Esteratic site binds ester group of Ach
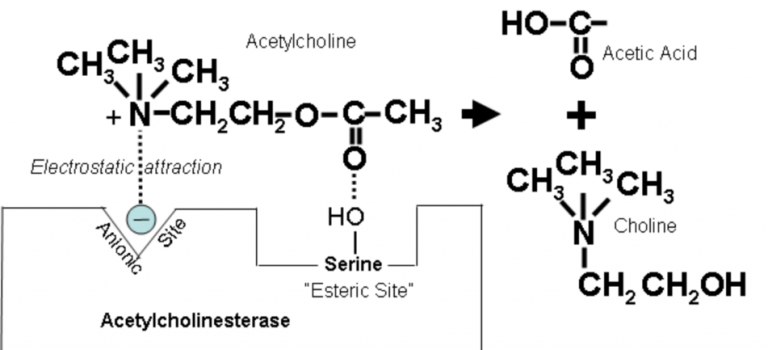
Binding → hydrolysis → breaks down to Choline + AcetylCoA and regenerates original enzyme
Classification
Length of Action
Short
Edrophonium
Medium
Neostigmine
Long
Organophosphate
Binding
Reversible
Edrophonium
Neostigmine
Irreversible
Organophosphate
(technically takes 100hrs to hydrolyse this so it is classified as irreversible)
Physiochecmical
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
Group
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Quaternary amine
Neostigmine
Quaternary amine
Organophosphate
Organophosphates
Presentation
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Clear soln
10mg/ml
Neostigmine
Clear soln
2.5mg/ml
Tablet 15-30mg
Organophosphate
Multiple
ie Sarin
Use
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Reversal NDMR
Diagnose MG (Tensilon test)
Assess MG crisis
Neostigmine
Reversal NDMR
Tx MG
Urinary retention
Paralytic Ileus
Organophosphate
Insectisides
Nerve gas
Onset
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
1-2min
Neostigmine
7-10min
Organophosphate
Fatal in minutes
X500 more toxic than cyanide
Duration
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
10min
Neostigmine
50min
Organophosphate
Long – requires new AChE synthesis
Dose
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
2-10mg for Tensilon test
0.1mg/kg for reversal NDMR
Neostigmine
0.05mg/kg
Low dose = muscarinic effects
High dose = nicotinic effects
Organophosphate
Pharmacodynamic
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
MoA
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Reversibly binds AChE
Weak electrostatic bond
Quaternary prevents crossing BBB
↑[ACh]
Neostigmine
Reversible binds AChE
Covalent bond
Hydrolses enzyme at slow rate
↑[ACh]
Hydrolysis regenerates enzyme
Organophosphate
Irreversible
Covalent bond with AChE
Recovery requires new AChE synthesis
NMJ
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
↑[ACh] @NMJ
overcomes NDMR
ACh can bind nAChR and allow muscle contraction
Organophosphate
Muscle weakness
Fasciculations
CVS
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
Bradycardia
↓CO
↑conduction time
RESP
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
Bronchospasm,↑ secretions
CNS
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Nil cannot cross BBB
Organophosphate
Excitation, seizures → then CNS, CVS, RESP depression
GI
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
Diarrhoea, ↑secretions
Renal
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
Incontinence
ANS
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
DUMB BELLS
Diarrhoea, Urinarytion, Myosis, ‘deadly Bs’ Bronchoconstriction & Bradycardia, Emesis, Lacrimation, Lethargy, Salivation
Mx SE
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Atropine,
Glycopyrrolate
Organophosphate
Pralidoxime – releases ACh by promoting hydrolysis
Anticonvulsants
Atropine
Pharmacokinetic
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Organophosphate
A
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Neostigmine
Poor, 1% OBA
Organophosphate
V lipid soluble
transcutaneous
D
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
VD 1L/kg
Neostigmine
10% PPB
Highly ionised
0.5L/kg
Organophosphate
Large
M
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
Liver: glucuronidation
Neostigmine
Plasma esterases
Organophosphate
E
Edrophonium (Tensilon)
35% biliary metabolites
65% renally unchanged
Neostigmine
65% urine
renal unchanged
Renal failure = prolonged DoA
Organophosphate
Long
NB Pyridostigmine
- Analogue of Neostigmine
- ¼ potency
- MoA Neostigmine
- Slower onset 16mins (so not used to reverse NDMR)
- DoA 6hrs (used for MG)