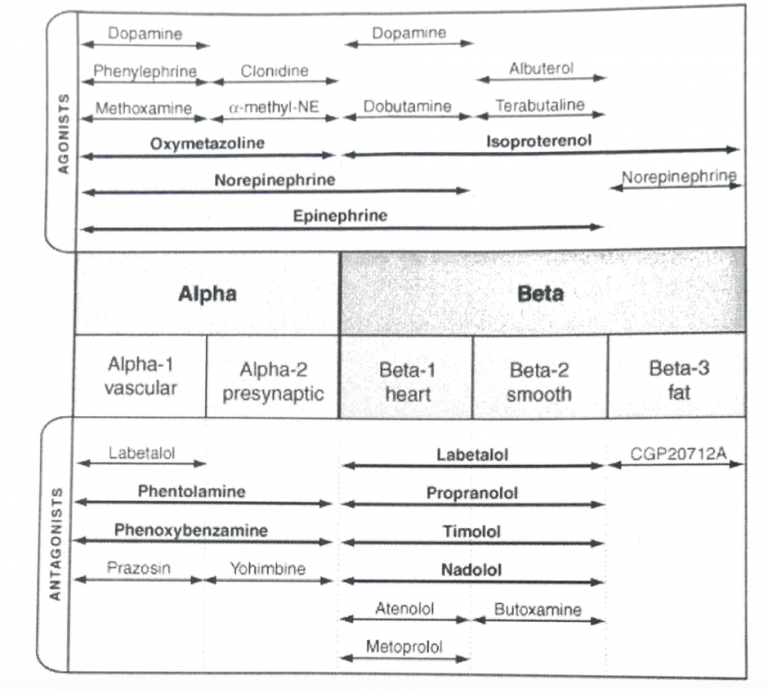
M1i: Adrenergic Receptors
α1 RECEPTOR: POST SYNAPTIC
- G Protein: Gq
- 2nd msg: stimulates PHOSPHOLIPASE C → ↑IP3 & DAG → opens Ca2+ channel
- Location
- Smooth m. → VC
- Cardiac → weak +ve inotropy, weak -ve chronotropy
- Metabolic → ↑BSL (inhibits insulin secretion, stimulates glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis)
α2 RECEPTOR: PRE SYNPATIC (peripherally) & POST SYNAPTIC (CNS)
- G Protein: Gi
- 2nd msg: Inhibits AC → ↓cAMP = ↓Ca2+
- Opens K+ channels → membrane hyperpolarisation
- Location
- CNS = Post synaptic nerve terminals ↓ outflow
- Peripheries = pre-synaptic nerve terminals inhibit NA release by -ve feedback
- Platelets = ↓plat aggregation
β1 RECEPTOR: POST SYNAPTIC
- G Protein: G5
- 2nd msg: ↑AC → ↑cAMP → ↑Ca2+
- Location
- Heart = +ve inotropy, chronotropy, dromotropy
- Metabolic = lipolysis = ↑FFAs & insulin
- Renal = ↑RENIN by stimulating juxtaglomerular cells → formation AII → VC
β2 RECEPTOR: POST SYNAPTIC
- G Protein: G5
- 2nd msg: AC = ↑cAMP
- Cardiac cells → ↑Ca2+
- Smooth m. → inhibits MLCK
- Liver → activates glycogen phosphorylase
- Location
- Heart = ↑FoC
- Smooth m. = relaxes smooth m. of uterus, bronchi, vessels
- Skeletal m. = fine tremor