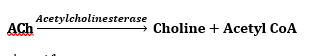M1i: Outline the production, release & fate of cholinergic transmitters and their end products
ACH = the 1° neurotransmitter (NT) of the ANS
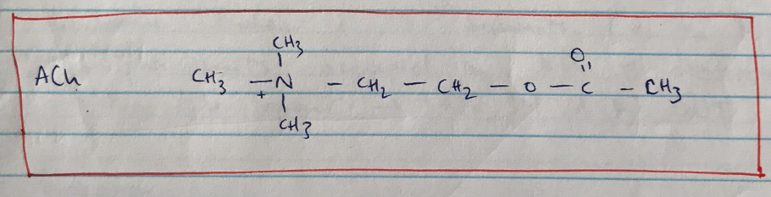
Synthesis
- In cytoplasm of preganglionic n. & postganglionic (presynaptic) n.
Acetyl CoA + Choline →(enzyme choline acetyle transferase) → ACh
- Acetyl CoA in abundance from mitochondria (Kreb’s cycle)
- Choline enters n. endings cytoplasm from ECF by active transport ( = RATE LIMITING STEP OF ACh SYNTHESIS)
Storage & Release
- Stored in synaptic vesicles
- Each n. ~300,000 ACh vesicles
- Arrival AP → depolarisation → Ca2+ influx → release ~100 ACh vesicles
- Ca2+ in ECF is essential → antagonised by Mg2+
ACh NT
- Entire parasymp. NS (nerves & ganglia)
- ganglia, adrenal medulla, sweat glands
- Somatic nerve innerv. to skeletal m.
- Some CNS nerves
Cholinesterases
2 types
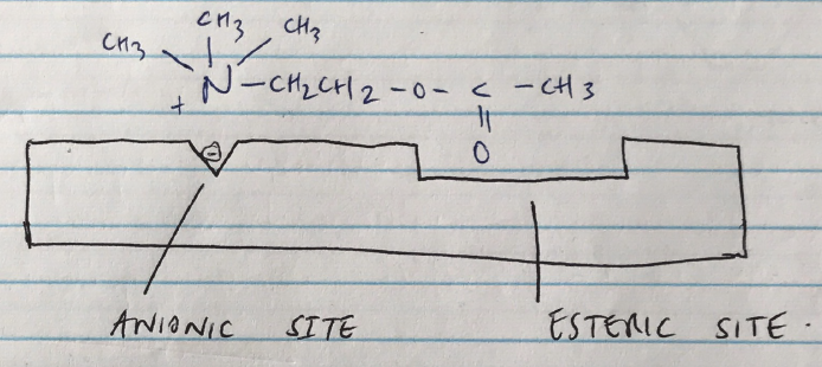
1. Acetylcholinesterase
- Located at cholinergic synapses
- Pre-post junctionally
- Hydrolyses: ACh → choline + Acetyl CoA
- The enzyme has an ANIONIC SITE & ESTERIC SITE
- Once AChE hydrolyses ACh the enzyme becomes acetylated & choline is released
- The enzyme is then ready to hydrolyse the next ACh
- AChE can hydrolyse 300,000 x ACh per minute!
- 50% choline is recycled to form new ACh
2. Plasma Cholinesterase
- Less specific
- Can hydrolyse many esters inc. ACh, procaine, suxamethonium
- Synthesised in liver → present in plasma
Cholinergic Receptors
- Classified depending on their reaction to alkaloids
1. Nicotinic Receptors
- LIGAND-GATED ION CHANNELS
- Membrane protein with 5 subunits (α1, α2, β, γ, δ)
- 2 alpha units occupied by ACh → conformational ∆ → ion channel opens → Na+ IN and K+ OUT
- Location
- Entire parasymp. NS
- All autonomic ganglia
- Adrenal medulla
- Sweat glands
- NMJ
2. Muscarinic Receptors
- G PROTEIN LINKED
- 5 subtypes:
- Even No’s = Gi = regulate AC
- Odd No’s = Gq = regulate phospholipase C
SUBTYPE
2nd MSG
LOCATION
EFFECT
M1
Gq activates phospholipase C
↑ IP3 & DAG
↑ intracell. Ca2+
CNS
Gastric parietal cells
Membrane hyperpolarisation → ↑memory & seizure activity
↑Acid secretion
M2
Gi → inhibits AC
↓CAMP
↓Ca2+
Heart conducting tissue
-ve CHRONO
-ve DROMO
-ve INOTROPY
M3
Gq → activates phospholipase C
↑ IP3 & DAG
↑ intracell. Ca2+
Glands
Smooth muscle
Vessels
↑ smooth muscle contraction
↑ gland secretion
M4 & 5
Gi / Gq
?CNS
?Facilitates dopamine release