M2ii: Sympathomimetics
Classification
- Sympathomimetic = a drug that evolves a similar response produced by endogenous activation of the SYMP NS.
- Natural/synthetic
- Catecholamine / non-catecholamine
- Direct/indirect
- α/β agonists
Catecholamine
- All sympathomimetics derived from β-phenylethylamine
- β-phenylethylamine with an -OH at C3 & C4 of the benzene ring designates the drug a catechol.
Structure Activity Relationships
The relationship between the structure of a molecule and its biological action
Benzene ring substitutions
- Catechols have low lipid solubility
- ∴do not cross BBB in sufficient amounts to cause stimulation
- Nothing on benzene ring = ↑lipid solubility & ∴cross BBB → stimulate CNS but it would also make it a non-catechol i.e. amphetamine = synthetic non-catecholamine
C3 & C4 hydroxylation
- = drug is catechol.
- ∴taken up by neurons
- Susceptible to COMT metabolism
- ∴short DoA
- Maximal α & β adrenergic activity requires OH on C3 & C4
C3 & C5 hydroxylation
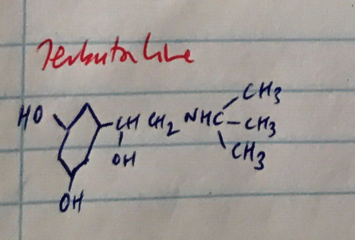
OH on C3 & C5 = β2 selectivity in compounds with long chain substituents
∴Terbutaline = relaxes bronchial smooth m. without any β1 effects
Terminal Amine Substitutions
- Substituting with large groups at terminal amine = ↑β activity & ↓α activity
- Also = ↓affinity for uptake e. NA has free amino group & minimal β (cf. adrenaline)
- Adrenaline = optimal for producing β & α effects
- e. Isoprel = large substitution at amine = maximal β1 & β2 activity and not taken up by neurons
β-carbon
- The carbon next to benzene ring
- Substitution will:
- ↓lipid solubility = ↓CNS stimulation effects
- ↑α & β agonist activity
α-carbon
- Substitution will block MAO
- ∴Prolong DoA
- of non-catechols that cannot be metabolised by COMT i.e. ephedrine
Isomerism
- Levorotary forms are more active
Administration
The relationship between the structure of a molecule and its biological action
Catecholamine
- Not effective oral → metabolised by GI enzyme & liver
- Adrenaline → subcut, IV, ETT
- NA, Dopamine, Dobutamine → CVC
Non-catecholamine
- Absence of 3-OH & 4-OH or α-carbon substitution makes drug resistant to COMT & MAO absorption
- ∴↑oral availability
- Cocaine can be administered intranasally
Distribution
- 25% of NA is metabolised during a single passage through lungs
- No change to Adrenaline
- 20% Dopamine metabolised during one lung passage
Clearance
Catecholamines
- Cleaved by reuptake or metabolism by COMT & MAO
- Short t½ = 1 – 2 mins
- Steady state achieved in 5 – 10 mins of starting infusion
Synthetic non-catecholamines
- Not affected by COMT
- α carbon substitution will inhibit MAO
- ∴prolonged DoA of catecholamines
Sympathomimetic MoA
- Adrenoreceptors & Dopamine receptors are all G PROTEINS
- 7 transmembrane structure
- Adrenoreceptors α1 & α2 / β1, β2, β3
- Dopamine receptors → D1, D2, D3, D4
- Sympathomimetics exert their effect by activating or inactivating these receptors → directly or indirectly
Indirect Acting Sympathomimetics
- Enter postganglionic n. endings by neuronal uptake
- Displace NA from storage vesicles
- Evoke release of NA into synaptic cleft to act on adrenoreceptors
- Because NA is released, most effects are α & β, as NA has minimal β2 activity
Direct Acting Sympathomimetics
- Bind directly to receptors & activate them
- α receptors: Adrenaline > NA > Isoprenaline
- β receptors: Isoprenaline > Adrenaline > NA
- α agonists:
- Phenylephrine α1 > α2 >>>> β
- Clonidine α2 > α1 >>>> β
- α & β agonists:
- Adrenaline β2 > β1 > α1 = α2
- NA α1 = α2 > β1 >> β2
- NB: β1 receptors like NA & Adrenaline the same. Β2 receptors prefer Adrenaline
- Β agonists:
- Dobutamine β1 >> β2 >>>> α
- Isoprenaline β1 = β2 >>>> α
- Terbutaline β2 >> β1
- Dopamine agonist
- Dopamine D1 = D2 >> β >> α
α1
Gq protein
α2
Gi protein
Β
GS
D1
GS
D2
Gi
Drug Interactions
MAO Inhibitors
- Synthetic catecholamines = not metabolised by COMT
- Rely on MAO for their metabolism
- ∴MAOI’s prolong their DOA
Digoxin
- Na / K / ATPase is required for neuronal uptake of Indirect Agents
- RECALL: amphetamine is taken up at nerve ending & stimulates NA release
- ∴Digoxin inhibition of Na / K / ATPase = ↓response to Indirect Agents

