N2ii: Describe the functional anatomy of the liver
Gross anatomy
- Largest visceral organ in body
- Weight: 1.8kg
- Can be divided up into lobules
- Hexagonal shape and have several portal triads in periphery
- Portal triad consists of: hepatic artery, portal vein and bile duct
- Central vein (branch of hepatic vein) present in centre of lobule surrounded by hepatocytes
- Sinusoids drain blood from peripheral portal triads to central vein
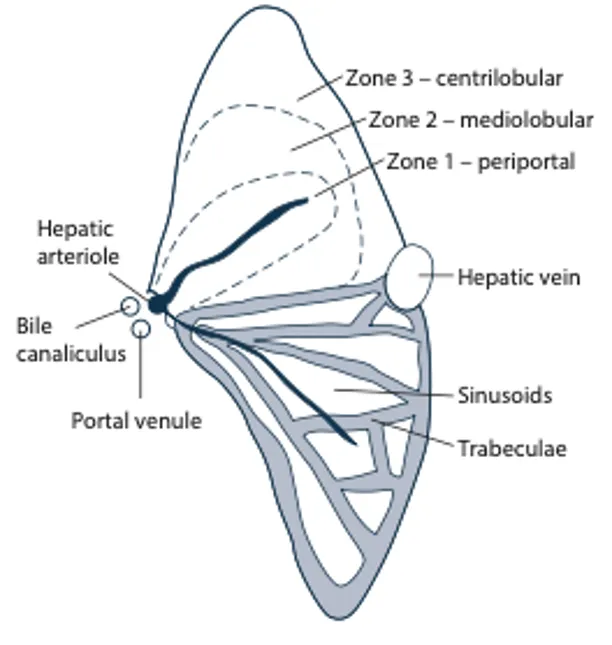
Functional unit
Acinus
- Diamond-shaped area
- Approximately 100,000acini in a human liver
Acinus blood flow
- Blood flows from portal triad towards terminal vein
- Supply: terminal branches of hepatic artery, portal vein
- Drainage: hepatic venules via sinusoids
Acinus can be divided into three zones
- Zone 1:
- AKA: periportal
- Hepatocytes closes to portal triad
- Blood rich in oxygen (due to proximity of hepatic artery)
- Mitochrondria-rich cells (important in oxidative metabolism and protein synthesis)
- Zone 2:
- AKA: mediolobular
- Hepatocytes between zone 1 and 2
- Intermediate oxygen content and enzyme activity (between zone 1 + 3)
- Zone 3:
- AKA: centrilobular
- Hepatocytes in periphery of acinus but closes to central vein
- Oxygen poor blood (compared to zone 1)
- Rich in smooth endoplasmic reticulum and CYP450 (important in drug and toxin biotransformation)
- Area most likely to be damaged during low perfusion states / hypoxic injury
- Area most like be damaged in states where high toxic metabolites present due to CYP450 action (ie. Site of accumulation of NAPQI in paracetamol overdose)
Other cell types within liver
- Hepatocytes – 60%
- Kuppfer cells – 10%
- Others: sinusoidal, peri sinusoidal and biliary epithelial cells
Functions - Overview of functions of liver
Immune
- Contains Kupffer cells (specialised macrophages)
- Reticuloendothelial component filters bacteria from portal blood
- Produces complement (part of innate immune system)
Storage
- Micronutrients
- Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
- Water soluble vitamins (folic acid, B12)
- Macronutrients
- Lipids (fatty aids, cholesterol, lipoproteins)
- Amino acids
- Glucose and other sugars
- Blood
- Approximately 500ml
Acid base
- Ammonia and urea cycle
Biotransformation
- Phase 1 reactions: oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis
- Phase 2 reactions: glucuronidation, sulphation, acetylation
Metabolism
- Carbohydrates: glucogenesis, gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
- Lipids: beta oxidation of fatty acids
- Proteins: transminates or deaminates proteins
Digestive
- Produces bile (required for emulsification of dietary lipids)
Endocrine
- Synthesis of: clotting factors, acute phase proteins, albumin, steroid binding and other hormone binding proteins
- Converts T4 to T3
- Activates vitamin D
Author: Suzanne Luong