Q2i: MoA Anti-platelet drugs
Definition
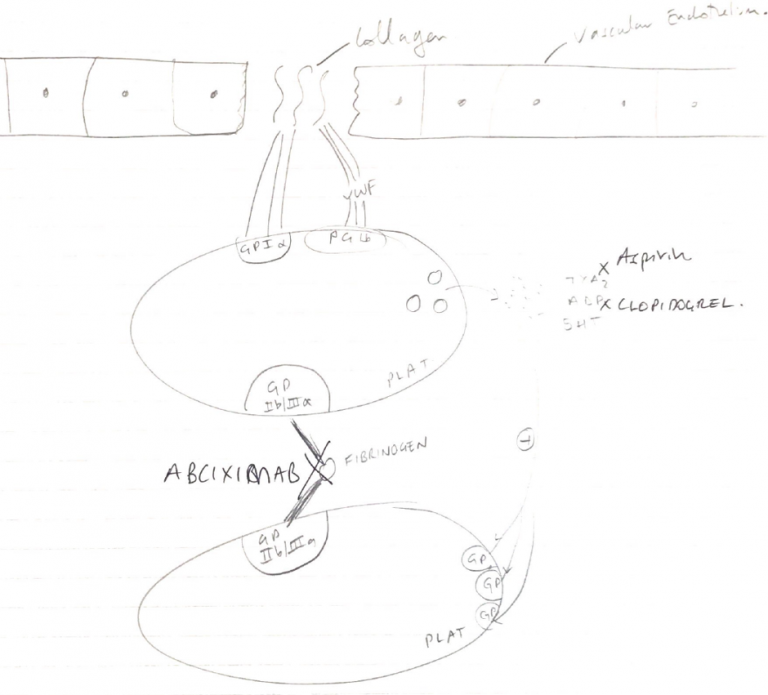
Anti-platelet agents: drugs which interfere with normal adhesion & aggregation of platelets
Classes of Antiplatelets
- COX inhibitors → aspirin
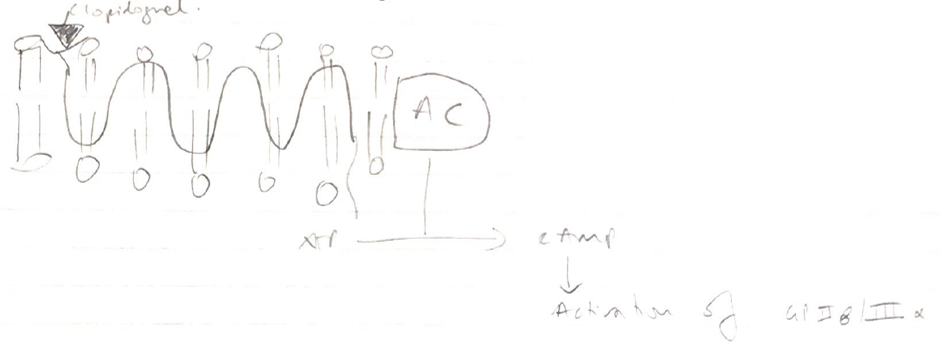
- ADP inhibitors → clopidogrel, ticagrelor
- IIb/IIIa inhibitors → tirofidan, abciximab
- Phosphodiesterase (PPD) inhibitors → dipyridamole
Cox Inhibitors
- Arachidonic acid
↓ (COX)
Prostaglandin
↓ (thromboxane synthetase)
TXA2
- MoA
- TXA2 causes platelets to ∆shape, release granules & aggregate
- Aspirin = irreversible acetylation of COX → inactivated
- A-nucleus platelet undergo pr synthesis – COX inhibited for platelet lifespan (10 days)
Dipyridamole
Mechanism 1:
- Inhibits phosphodiesterase enzyme which breaks down cAMP
- ↑cAMP blocks platelet aggregation by ADP
Mechanism 2:
- Inhibits reuptake of Adenosine by platelets