U1ii: Describe the physiology of Glucagon
- Definition: A polypeptide hormone → 1° CATABOLIC HORMONE
- Synthesis + storage: pancreatic α – cells
Release
- Controlled by metabolic products
- ↓GLUCOSE = 1° stimulant for release
- ↑BSL = inhibits release
↑ Secretion
Hypoglycaemia
α – acids:
- Arginine
- Glycine
- Alanine
- Serine
CCK, gastrin, secretin
Adrenaline
Exercise/stress
↓ Secretion
Hyperglycaemia
FAs
Somatostatin
Glucagon Metabolism
- t½ 5 – 10 mins
- Metabolised in liver
Glucagon Receptor
- GPCR in hepatocytes
- Glucagon binds Glucagon receptor
- Activates AC
- ↑cAMP → activates protein kinases
Glucagon Actions
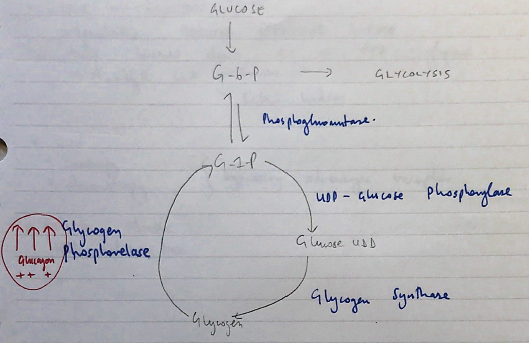
- CHO metabolism
- Glycogenolysis → ↑BSL (liver)
- Acts on skeletal m. & AT to break down peripheral glycogen → Pyruvate & lactate
- Pyruvate goes to Krebs
- Lactate to liver for Gluconeogenesis via CORI CYCLE
- Inhibits cell use of Glucose for fuel → FAs/ketones as 1° E source
- Protein Metabolism
- ↑uptake of α-acids by liver
- ↑gluconeogenesis
- Inhibits protein synthesis
- Lipid Metabolism
- Stimulates HORMONE SENSITIVE LIPASE
- Which breaks down AT → FFAs + glycerol
- CVS
- Smooth Muscle
- GI relaxation