U1iv: List hormones secreted by pituitary gland & function + outline control of secretion of hormones from pituitary gland
Definition
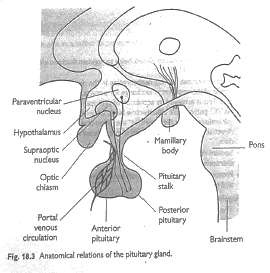
Pituitary Gland: small gland, 1cm in diameter, 1g weight, which lies in Sella Turcica (bony cavity at base of brain) → connected to hypothalamus by Pituitary stalk
Hypothalamic - Pituitary Axis
- Hypothalamus has major neuro-endocrine role in CNS → controls APG + PPG
- Hypothalamus ↔ APG
- APG derived from buccal ectoderm (Rathke’s pouch)
- APG controlled by hypothalamic releasing/inhibitory factors
- Hypothalamic hormones released into portal system
- NA, DA, serotonin controls release of hypothalamic hormones
- Portal circulation in Pituitary Stalk transports hypothalamic hormones to APG where they exert their effects
- APG
- Agranular secretory cells
- Granular secretory cells
Hypothalamic Hormone
GHRH
Action on APG
GH release
Causing
Growth in tissues
Hypothalamic Hormone
DA
Action on APG
Inhibits PROLACTIN release
Causing
Prolactin → lactation ∴DA inhibits this
Hypothalamic Hormone
TRH
Action on APG
TSH release
Causing
Thyroid release T4 + T3
Hypothalamic Hormone
CRF
Action on APG
Release ACTH
Causing
Adrenals release cortisol
Hypothalamic Hormone
GnRH
Action on APG
Release LH + FSH
Causing
Ovaries → release O → ovulation
Testes → testosterone → sperm production
Feedback Control APG
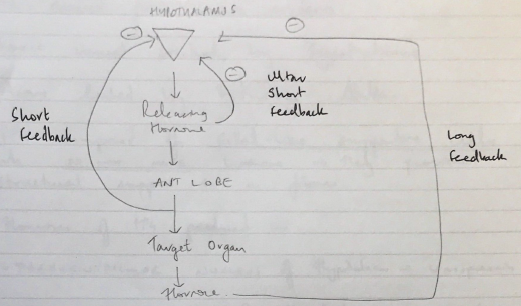
3 levels of – ve feedback
- Long: hormones produced by peripheral organs exert –ve feedback to Hypothalamus + anterior pituitary (TH, sex H, adrenocortical)
- Short: Anterior pituitary hormones exert –ve feedback on hypothalamic inhib/releasing hormones
- Ultra-short: hypothalamic inhib/releasing factors inhibit their own secretion
Hypothalamus ↔ PPG Axis
- PPG derived from brain ectoderm
- Direct neural control by hypothalamus
- Axons linked by Pituitary Stalk
- PPG composed of Glial-like supportive cells which DO NOT MAKE hormone → they provide structural support to nerve fibres
- Hormones of PPG produced in:
- Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus → vasopressin
- Supraoptic nucleus of hypothalamus → oxytocin
- Ach stimulates release Vaso + oxy ↔
- NA inhibits their release
Hypothalamic Hormone
Vasopressin
Action on
Renal tubules
Causing
H2O reabs from distal tubules + collecting ducts
Hypothalamic Hormone
Oxytocin
Action on
Breasts, uterus
Causing
Lactation
Uterine contraction
Regulation of ADH → Osmolarity + blood volume
- ADH is synthesised in cell bodies of supraoptic + paraventricular nuclei
- ADH primarily in Supraoptic Nuclei (but some PVN)
- Transported via carrier proteins to nerve endings in PPG
- Take several days to reach PPG
- ADH → causes anti-diuresis
- Normal plasma osmolality = 280mOsm/kg
- Tightly regulated within 1 – 2%
- Osmoreceptors in/near hypothalamus
- ↑osmolarity of ECF
- Fluid is pulled out of osmoreceptor cells by osmosis
- ↑nerve signals in hypothalamus
- Transmitted down along fibres of SON & PVN
- Causes exocytosis of granules containing ADH
- ↓blood volume esp 10 – 25%
- Intense release of ADH
- Even if ECF is hypotonic
∴Although not as sensitive, the volume sensor overrides the osmolarity sensor
Regulation of Oxytocin → Cervical stimulation + suckling
- Oxytocin 1° formed in Paraventricular Nuclei (& some SON)
- Pregnant uterus
- Stimulation of cervix
- Sends signals to hypothalamus
- ↑oxytocin secretion
- Causes powerful contraction of pregnant uterus
- Milk ejection
- Suckling of nipple
- Sends signals to PVN & SON of hypothalamus
- ↑oxytocin release by PPG
- Oxytocin carried to breasts in blood
- Causes contraction of myoepithelial cells surrounding mammary glands
- Allows milk to flow