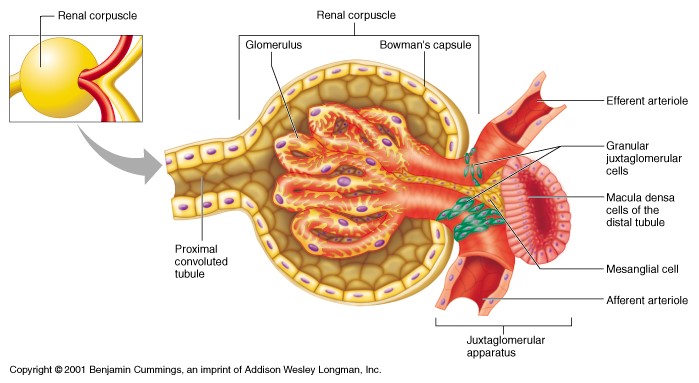
U1vi: Physiology of RAAS
Renin
- Definition = peptide hormone
- Synth + storage
- From PRORENIN
- Synthesised in Juxtaglomerular Granular Cells
- Which are mainly located in medial tunica of aff. arteriole
- Stored in vesicles
- Release
↑ cAMP (stimulatory)
- Catecholamines (β1 receptor)
- PGI2 & E2
- NO (inhib cAMP degradation via ↑GMP)
- Milrinone (PDEI = ↑cAMP)
↑Ca2+ (inhibitory)
- ↑Aff a. perfusion = ↑juxtaglom [Ca2+]
- Control of release
↑ Renin
- NO, PGI2, PGE2 = ↑renin (↑cAMP)
- NA = β1 stimulation of β1 receptor in juxtaglom. Cells = ↑renin (↑cAMP)
- Arterial P inverse relation to renin secretion
- ↓pressure outside autoregulatory range for GFR = ↑renin
- ↓[NaCl] = detected by Macula Densa = ↑renin
- Metabolism: renin t½ ∝ 80min
- Actions: it’s only function is to split ANGIOTENSINOGEN → AI
↓ Renin
- AII → direct inhibition via AT1 receptor (↑Ca2+ = ↓Renin)
Ace
- Enzyme of ENDOTHELIAL CELLS
- Converts AI → AII by removing 2 α-acids
- Most conversion occurs as blood passes through lungs
- Also inactivates Bradykinin
Angiotensinogen
- Synthesised by liver
- ↑release stimulated by glucocorticoids, oestrogen, TH, AII
Angiotensin II
- Definition: glycoprotein effector of RAAS
- Synthesis: rate limiting step is renin ∴anything which ↑renin = ↑AT II formed by
- Metabolism: t½ 2 mins, metabolised by peptidases
- Actions:
- Agonist at Receptors AT1 & AT2 (GPR)
- AT1
- GPCR
- Gq → phospholipase C → ↑Ca2+
- AT2
- GPCR
- Opens K+ channel & ↑NO production
- Abundant in foetal life → in adults, mostly concentrated to brain
- AT1 receptors responsible for most actions
- Vascular smooth m.
- Adrenal cortex
- Kidney
- Brain
Vasc Smooth M
- Strong pressor → ↑MAP
Adrenal Cortex
- ↑Aldosterone secretion → ↑Na+ = ↑circulatory volume
Renal
- Contraction of Mesangial cells → VC aff > eff = ↓GFR
- ↑Na+ @ PT
- ↓Renin secretion (because ↑ Ca2+ via AT1 receptor) = –ve feedback
NB: AII stimulates local release of Prostaglandins which antagonises renal VC
Brain
- ↑ outflow → ↑MAP
- Activates thirst centre → ↑circulatory volume
- ↑ADH
- ↑ACTH secretion
- ↑Vasopressin production
Angiotensin III
- 40% pressor activity of AII
- 100% Aldosterone stimulating activity of AII
Aldosterone
- Definition: the 1° MINERALOCORTICOID is a steroid hormone produced by Zona Glomerulosa
- Synthesis:
Cholesterol
↓
Pregnenolone
↓
Progesterone
↓
Aldosterone
- Cells of Adrenal Cortex do not store the hormones they secrete, they produce & release them on demand
- Release: diurnal → more than 70% secreted between 0700 – 1000h
- Control of release:
- ↑AII ***
- ↑K+
- ↑ACTH → catalyses cholesterol → pregnenolone
- ↑Atrial stretch
- Metabolism
- t½ 20 mins
- Transported bound to proteins
- 90% inactivated by single pass through liver
- Actions
- Binds intracellular receptors
→ ∆ DNA transcription
→ ↑Na/K/ATPase on BM of kidney, colon, bladder
Aldosterone Action in the Kidney
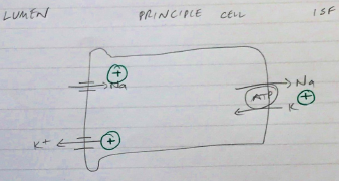
Principle Cells
- 70% cells
- Secrete K → depending on load:
- Active transport via Na/K/ATPase
Aldosterone (+)
- ↑Na+ reabs
- ↑K+ excretion
- Enhances absorption by promoting more Na/K/ATPase insertion on Basolateral Membrane
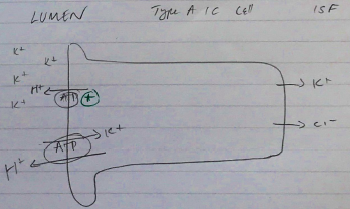
Type A Intercalated Cells
- 30% cells
- Reabsorbs K+
- Active transport via K/H/ATPase
- Because of Na/K exchange in Principle Cells
- Lumen of Type A Intercalated cells has high [K+]
- ↑H+/ATP activity
- ∴not all K+ lost
- H+ secreted → ALKALINE
- Cl– for electroneutrality → HYPERCHLORAEMIA
Overall
- ↑Na+ reabs → H2O follows → ↑circulatory volume
- H+ loss → ALKALOSIS
- ↑Cl – reabs → Hyperchloraemia