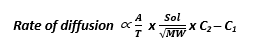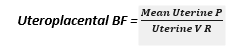V1iii: Gas exchange across placenta & Double Bohr & Haldane effects
Definition: Placenta = organ which is the interface between mother + foetus during pregnancy
- Transfer of CO2 + O2 is by DIFFUSION down partial pressure gradients, influenced by:
- FICK’S LAW
- DOUBLE BOHR + HALDANE EFFECT
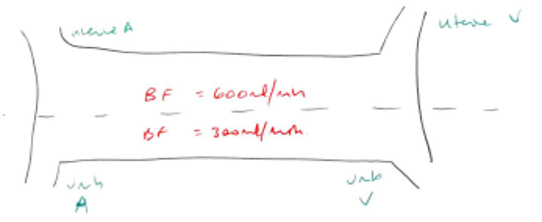
- BLOOD FLOW
- Hb AFFINITY/TYPE OF Hb
Double Bohr + Haldane Effects
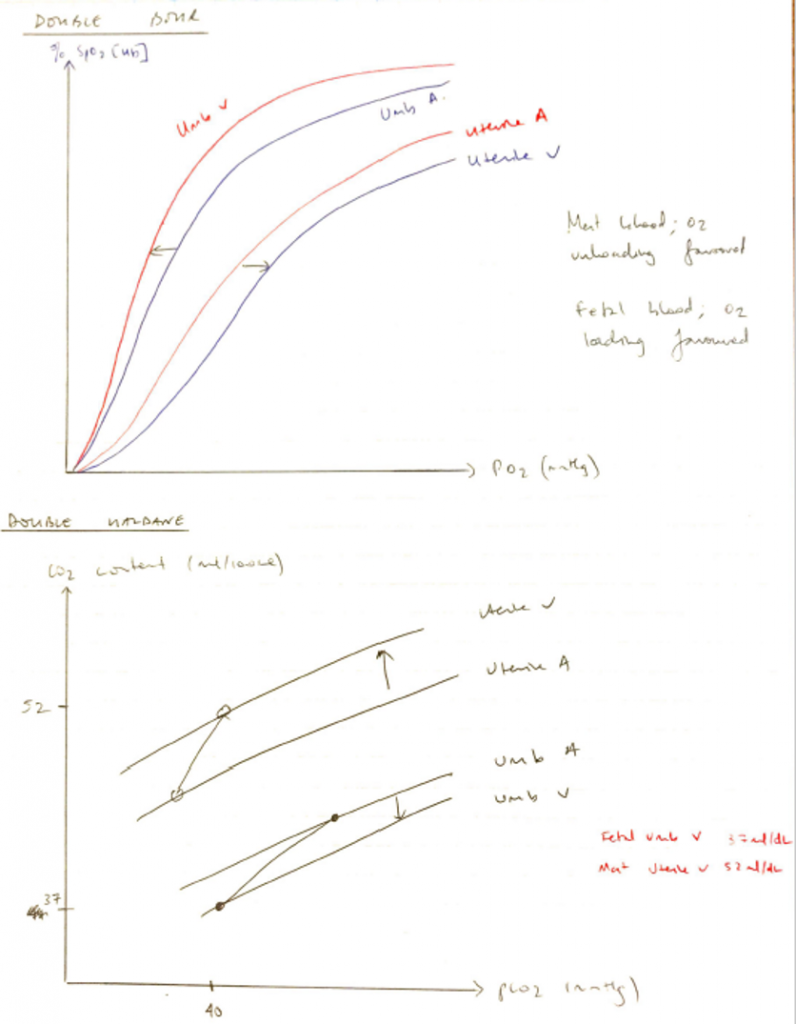
- Explains that foetal ODC shifts L) & maternal ODC shifts R)
- Foetal Hb releases CO2 to maternal blood
- HbF undergoes L) shift (becomes alkalotic)
- Gives itself greater O2 affinity
- CO2 reaches maternal blood
- ↑H+ → maternal Hb ODC shifts R)
- Offloads O2 easily

Type of Hb
• HbF
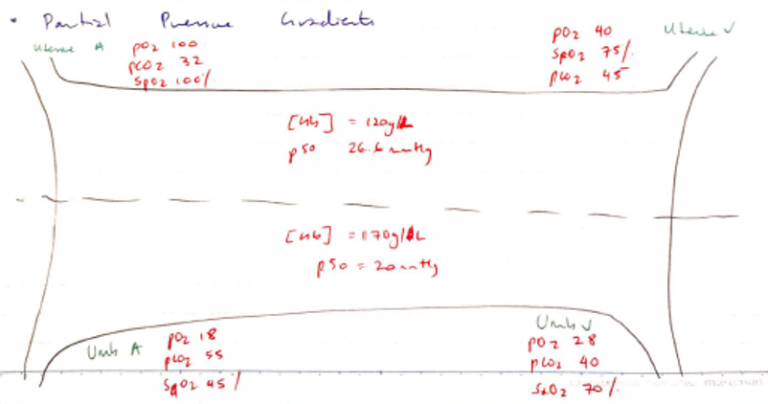
- [Hb] = 17g/dL → ∴↑capacity for O2 carriage
- pSO 20mmHg → ∴ high O2 affinity
- 2α + 2γ chains → as β chains
• Maternal Hb
- 2α + 2β → 2,3 DPG bonds β-chain ) & facilitates O2 offloading
- [Hb] = 12g/dL
- P50 = 27mmHg