Xi: Anatomy of the femoral vein
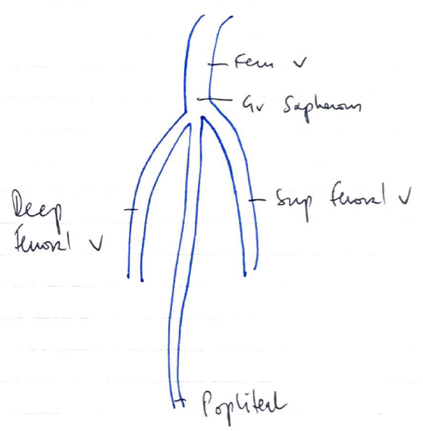
Origin
- Drains from popliteal vein
- Lies in intermediate compartment of femoral sheath
- Drains to external iliac vein (at inguinal ligament)→ common iliac vein → IVC
Course
- Common femoral vein → proximal to confluence with deep femoral vein
Borders
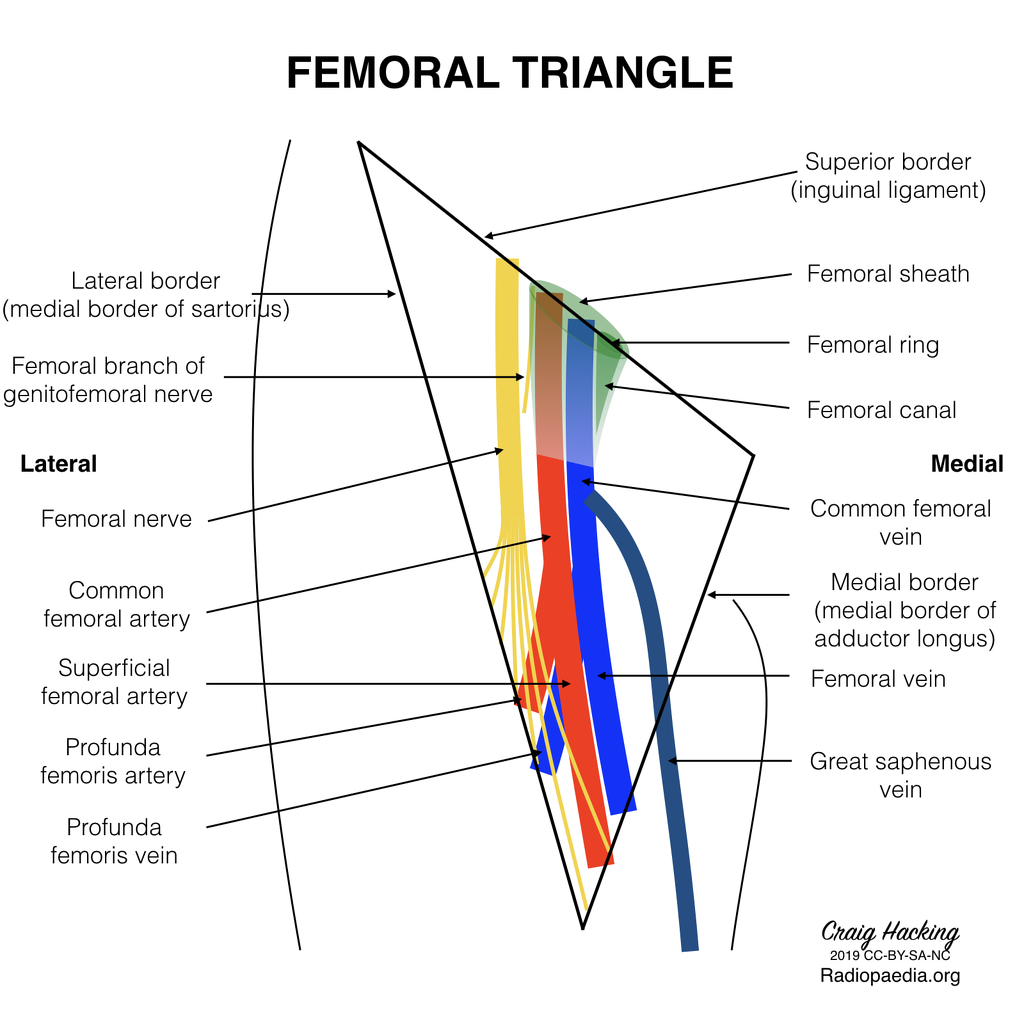
Femoral triangle
- Superior: Inguinal ligament
- Lateral: Medial border of sartorius muscle
- Medial: Lateral border of adductor longus muscle
- Superficial: Skin, subcutaneous fat, superficial fascia, fascia lata
- Deep: Muscular fascia of pectineus, psoas & iliacus muscles
Landmarks
- Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
- Pubic ramus
- Inguinal ligament
- Femoral sheath
Laterally → Medially (NAVEL)
Relationships
- Distally: vein lies posterolateral to superficial femoral artery
- Proximally (apex of femoral triangle): vein lies posterior to artery
- Base of femoral triangle (within femoral sheath): vein lies medial to artery
- Femoral artery (midpoint between anterior superior iliac spine and pubic symphysis)
- Femoral vein MEDIAL to pulsation 0.5-1cm
Tributaries
- Greater saphenous vein
- Deep femoral vein
- Lateral circumflex femoral veins
- Medial circumflex femoral veins
Structures Needle Passes Through (Superficial → Deep)
- Skin
- Subcutaneous tissue
- Fascia (encloses femoral vessels)
- Femoral vein
- Medial: medial compartment of femoral sheath (femoral canal: lymph vessels, nodes, fatty tissue)
- Lateral: fibrous septum separating intermediate compartment & lateral compartment (containing femoral artery) and further lateral (femoral nerve)
- Posterior: posterior fascia & pectineus
Approach/Positioning
- Slight external rotation of hip, palpate pulse, medial to arterial pulsation
- Folded towel under ipsilateral buttock to slightly extend hip
- Proceduralist on ipsilateral side of patient
Femoral Artery Course
- Continuation of external iliac artery at level of inguinal ligament
- Enters femoral triangle deep to midpoint of inguinal ligament, lateral to femoral vein
- Passes through triangle, exits at apex, enters adductor canal (Hunter’s canal)
- Exits adductor canal by passing through adductor hiatus in adductor magnus (at level of junction between middle and lower third of thigh) → becomes popliteal artery
- Several branches
- Profunda femoris: chief artery to thigh, arises from lateral aspect of femoral artery, 2-5cm below inguinal ligament
- Perforating arteries: perforate adductor magnus → contributes to supply of muscles in medial & posterior thigh
- Lateral femoral circumflex artery: supply lateral thigh muscles
- Medial femoral circumflex artery: supply neck and head
- Superficial epigastric
- Superficial iliac circumflex
- Superficial & deep external pudendal arteries
- Profunda femoris: chief artery to thigh, arises from lateral aspect of femoral artery, 2-5cm below inguinal ligament
Author: Novia Tan