15B07: Exam Report
Draw and label a cross section of the lumbar epidural space (50% of marks). Describe the pharmacology of bupivacaine (50% of marks).
35% of candidates passed this question.
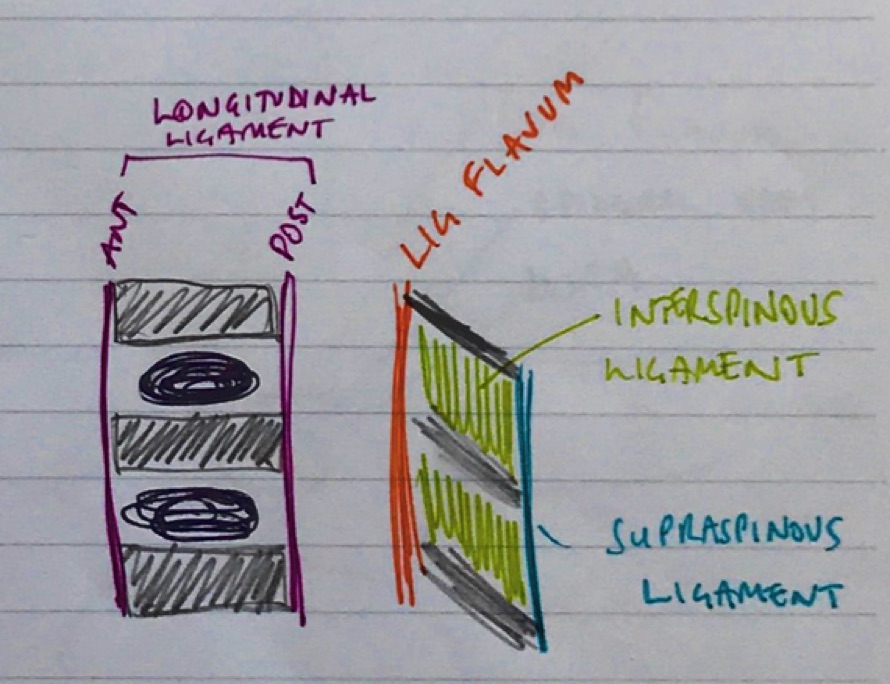
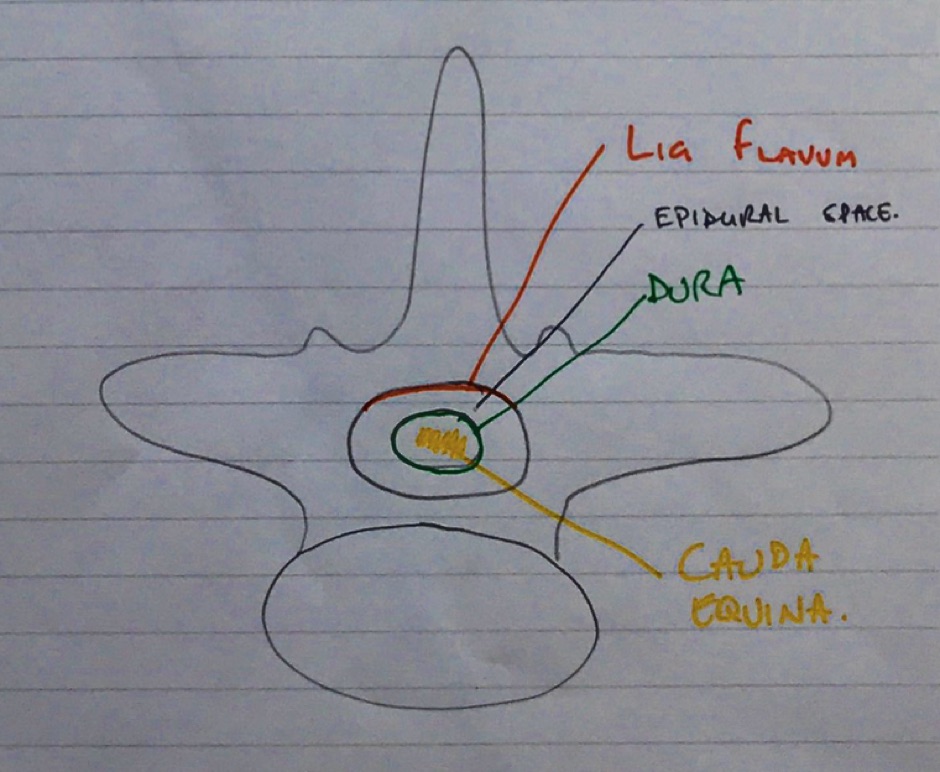
It was expected answers would include a diagram of a cross section and label the lumbar epidural space and the key landmarks namely dura, subarachnoid space, epidural space.
Most candidates were able to give a schematic representation even if not being able to draw.
Some candidates confused the subdural space with the epidural space.
Pharmacology of bupivacaine needed to cover both pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Several candidates addressed only one of these components and so missed the opportunity to score marks.
Xvi / 15B07: Anatomy relevant to lumbar puncture
Definition
Lumbar puncture is a diagnostic/therapeutic procedure whereby CSF is removed from the spinal canal.
Surface anatomy
- L1/L2 = termination of spinal cord
- L4/L5 for needle insertion
- L4 = top of ASIS
- Midline → between spinous processes
Lumbar vertebrae
- 5 lumbar vertebrae
- Structural support of the body
- Protection of spinal cord
- Largest vertebral bodies
- Spinal cord bound by:
- Anterior – vertebral body
- Lateral – pedicles & T-process
- Posterior – lamina + spinal process

Spinal canal
- Spinal cord
- Meninges
- Fatty tissue
- Venous plexus
Bupivacaine
Bupivacaine
Chemical
Amide local anaesthetic
Use
Local anaesthesia
Presentation
Clear colourless solution
Racemic (S- & R- enantiomers)
Concentrations of 0.25% and 0.5%
+/- Adrenaline 1:200,000 and preservative sodium metabisulphite
Hyperbaric solution of 0.5% contains 80mg/ml glucose (specific gravity 1.026)
Dose
1-2mg/kg up to a maximum of 150mg
Toxic Dose
Max dose 3mg/kg
Route
Peripheral n blocks, epidural, spinal
Onset
Slower cf lignocaine
DoA
T1/2b = 0.3-0.6hrs
MoA
Unionised diffuses across neuronal cell memb
Becomes ionized within cell
Binds and OPENS Na+ ch → blocks them
↓depol of membrane →Cardiac myocyte, Motor & sensory n fibre APs blocked
Bupi is x4 more potent cf lignocaine & prolonged DoA, but slower onset
PD
CNS
- Reversible neural blockade
- Levobupi produces less motor block but longer sensory block following epidural administration
CVS
- Reduces SVR
- Negative inotropy
- Cardiotoxic: binds myocardial proteins & blocks Na ch to ↓rate of increase Ph0 cardiac AP
- Levobupi has less cardiotoxicity
PK
A
Dose & concentration dependant
IC > Caudal > Epidural > Brachial Plx > Subcut
+Adr = delayed absorption
Highly lipid soluble, take up into fat is rapid
Drug has direct vasodilatory effect
D
95% PPB to a1 glycoprotein
Vd 1L/kg
M
Low extraction ratio drug => less influence by HBF cf lignocaine
Primarily liver metabolised via conjugation w glucuronic acid
Main metabolic is 2,6 pipecoloxylidine (catalysed by P450 3A4)
E
Clearance 7ml/min/kg
T1/2b = 0.3-0.6hrs
Metabolites in urine. 16% unchanged
Adverse Effects
Drug interactions: propranolol
Cardiotoxicity
Systemic toxicity of LAs → neurotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, death
Bupivacaine
Chemical
Amide local anaesthetic
Use
Local anaesthesia
Presentation
Clear colourless solution
Racemic (S- & R- enantiomers)
Concentrations of 0.25% and 0.5%
+/- Adrenaline 1:200,000 and preservative sodium metabisulphite
Hyperbaric solution of 0.5% contains 80mg/ml glucose (specific gravity 1.026)
Dose
1-2mg/kg up to a maximum of 150mg
Toxic Dose
Max dose 3mg/kg
Route
Peripheral n blocks, epidural, spinal
Onset
Slower cf lignocaine
DoA
T1/2b = 0.3-0.6hrs
MoA
Unionised diffuses across neuronal cell memb
Becomes ionized within cell
Binds and OPENS Na+ ch → blocks them
↓depol of membrane →Cardiac myocyte, Motor & sensory n fibre APs blocked
Bupi is x4 more potent cf lignocaine & prolonged DoA, but slower onset
PD
CNS
- Reversible neural blockade
- Levobupi produces less motor block but longer sensory block following epidural administration
CVS
- Reduces SVR
- Negative inotropy
- Cardiotoxic: binds myocardial proteins & blocks Na ch to ↓rate of increase Ph0 cardiac AP
- Levobupi has less cardiotoxicity
PK
A
Dose & concentration dependant
IC > Caudal > Epidural > Brachial Plx > Subcut
+Adr = delayed absorption
Highly lipid soluble, take up into fat is rapid
Drug has direct vasodilatory effect
D
95% PPB to a1 glycoprotein
Vd 1L/kg
M
Low extraction ratio drug => less influence by HBF cf lignocaine
Primarily liver metabolised via conjugation w glucuronic acid
Main metabolic is 2,6 pipecoloxylidine (catalysed by P450 3A4)
E
Clearance 7ml/min/kg
T1/2b = 0.3-0.6hrs
Metabolites in urine. 16% unchanged
Adverse Effects
Drug interactions: propranolol
Cardiotoxicity
Systemic toxicity of LAs → neurotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, death