Noradrenaline
Chemical
Endogenous catecholamine neurotransmitter released from postganglionic sympathetic n. endings
Also accounts for 20% adrenal medulla secretions
Use
to ↑SVR
Presentation
Clear, colourless solution 1mg/mL
Brown ampoule → prevent light oxidation
Must be diluted in D5W to provide sufficient acidity to prevent oxidation
1 pH D5W = 4, pH 0.9% NaCl = 6
Dose
Infusion 1 – 20mcg/min
Route
Central vein
Onset
Immediate: tachyphylaxis with prolonged infusions
MoA
α1 = α2 > β1 > β2
Potent α agonist
Equal β1 cf. adrenaline
Little β2 activity
α1 → Gq → stimulates Phospholipase C → ↑IP3 & DAG → ↑Ca2+
Smooth m. vasoconstriction
Cardiac: weak +ve inotropy
Metabolic: ↑BSL
α2 → Gi → inhibits AC → ↓cAMP → ↓Ca2+
CNS: ↓symp. outflow
Peripheries: inhibits NA release from nerve terminals
Platelets: ↓plat. aggregation
β1 → GS → ↑AC →↑cAMP → ↑Ca2+
Heart: +ve inotropy, +ve chronotropy, +ve dromotropy
Renal: ↑renin, ↑AII
Metabolic: ↑lipolysis, ↑FFAs
PD
CVS
Intense VC all vascular beds = ↑↑SVR
↑HR
↑FoC
Reflex ↓HR
Renal, hepatic, cerebral & skeletal m. BF all ↓
Resp
Small ↑MV
Metabolic
↑BSL
↑FFA
Renal
↑Renin
PK
A
IV administration
D
25% uptake via 1 lung passage
M
Rapid metabolism t½ = 2 mins
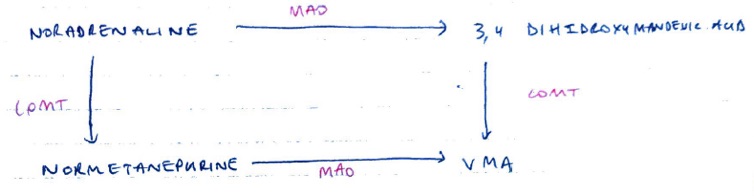
E
Metabolites conjugated to glucuronic acid for renal excretion
Adverse Effects
Extravasation → necrosis
Headache
Anxiety
NB CAUTION: Patients taking MAO inhibitors
PREGNANCY = ↑contraction of pregnant uterus, foetal bradycardia & asphyxia