Bi: Explain the concept of pharmacokinetic modelling of single and multiple compartment models
- PK compartment = mathematical concept describing a space in the body the drug is occupying – it does not correspond to anatomy/volume
- Compartment models work by dividing the body into a number of hypothetical compartments
- NB: these are all mathematical concepts, there is no anatomical equivalent
- They are used to help us understand the ∆ plasma [ ] of a drug over time
One Compartment Model
- Assumes body is one homogenous unit
- Drug is given & achieves instant distribution throughout body & equilibrates instantly b/w tissues
INPUT (dose) → [DRUG IN BODY] → OUTPUT (elimination)
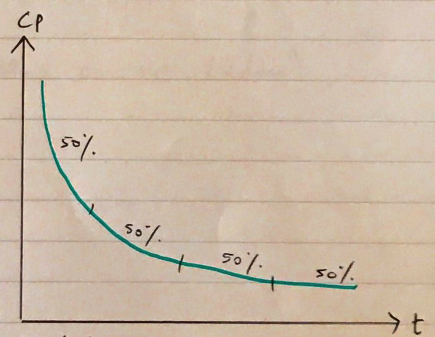
- Drug is then eliminated in a [ ] dependent manner (exponentially)
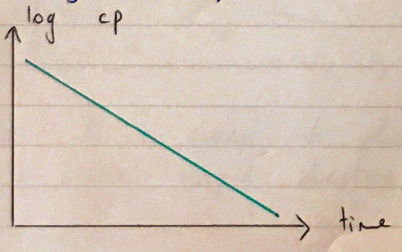
Graphically displays as a linear model
Highly hydrophilic drugs – AMINOGLYCOSIDES – follow this model because they are confined to ECF & have poor tissue penetration
Two Compartment Model
- Central compartment = plasma
- Peripheral compartment = tissues
- Drug enters K01 central compartment
- Drug eliminated K10 central compartment
- From central compartment drug redistributes to peripheral compartment K12
- Drug cannot be eliminated from peripheral compartment, must return to central compartment K21
- When drug administered to central compartment there is a rapid decline in [ ] due to K12
- K12 continues until equilibrium b/w both compartments
- Then drug is eliminated K10
- As that happens drug will move K21 down its [ ] gradient to then be eliminated K10
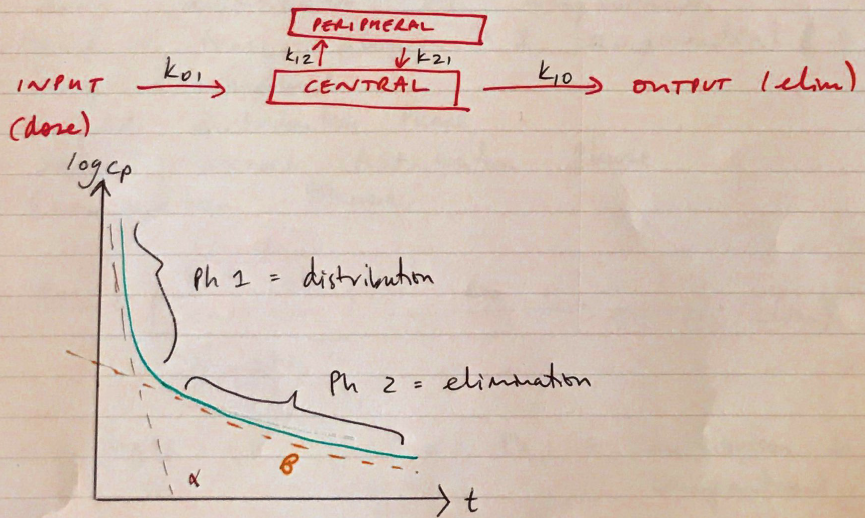
logCp vs time is used to distinguish from 1 compartment model
- α = initial rapid decline, distribution from Central → Peripheral compartment
- β = elimination from central compartment
- ∴t ½ α = distribution half life
- ∴t ½ β = elimination half life
Propofol & 2 Compartment Model
- After initial induction dose 1.5 – 2.5mg/kg, there is rapid LOC → drug taken up by lipophilic CNS tissues
- The PPF distributes to peripheral tissues, Ph 1 at constant rate α
- If another dose isn’t given, patient will wake up
- If a continuous infusion is given, the peripheral compartment will become saturated with PPF
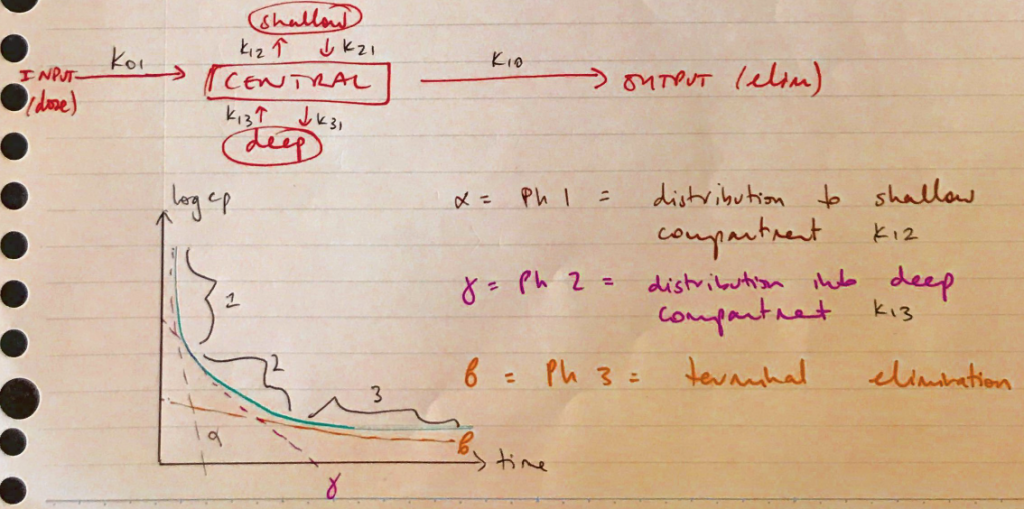
Multicompartment Model
- Drug distributes >1 compartment
- logCp vs time shows >1 expotential
- Drug administered
- Rapid distribution phase
- Second slower distribution phase
- Elimination phase