B SYL2017:OBA with shock
Definition
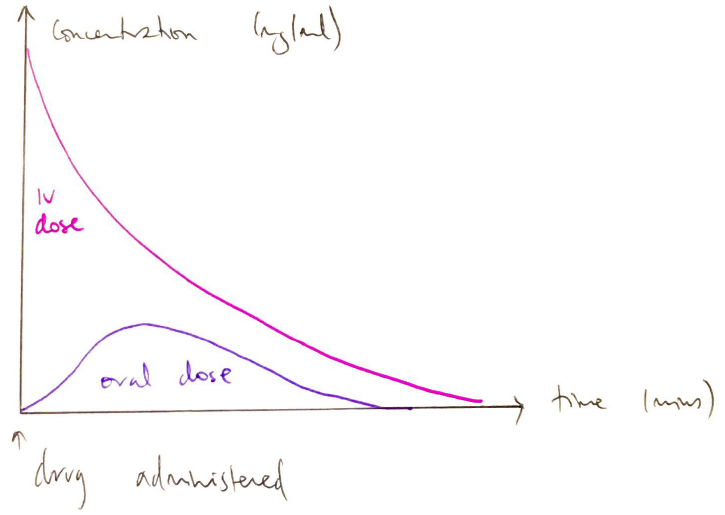
ORAL BIOAVAILABILITY = fraction of dose given orally that reaches systemic circulation
Factors Affecting Oral Absorption
- Rate of diffusion/absorption
- First pass
- Patient factors
- Pharmaceutical prep
- Physiochemical interactions
Absorption
- Absorption = ability of drug to cross gut wall
- Usually passive, governed by diffusion
- Fick’s law
- ↑absorption with:
- ↑SA of gut
- ↓thickness of diffusion distance
- ↓MW of drug
- ↑solubility of drug → pKA
- ↑[ ] gradient
- pKa → degree of ionisation affects solubility e. aspirin = unionised in stomach → rapid absorption
First Pass Effect
- First pass = proportion of drug absorbed, delivered to liver by portal circulation & metabolised before reaching systemic circulation
- ↑1st pass = ↓OBA e. M is fully absorbed (F = 1) but significant 1st pass (0.67)
∴ OBA = 1 – 0.67 = 53% (v. poor)
- Pre-systemic elimination can occur
- Gut wall (oestrogen)
- Portal circulation (aspirin → salicylic acid)
- Liver (majority)
- Hepatic enzyme inducer (phenytoin) = ↑first pass = ↓OBA
- Hepatic enzyme inhibitor (amiodarone) = ↓first pass = ↑OBA
Patient Factors
- Malabsorption i.e. Crohn’s
- Trauma → ↓gastric emptying
- Blood flow → ischaemic gut ↓rate of diffusion
Pharmaceutical Prep
- MW = ↑size = ↓absorption
- PPB = ↑PPB = ↓absorption
- Lipid formation = disperses quicker = ↑absorption
Physiological Interactions
- Milk = ↓tetracycline OBA
- Gut enzymes = inactivate insulin orally
Oba Alteration With Shock
- Shock = cellular & tissue hypoxia whereby O2 exceeds supply
Absorption
- ↓SA (dead gut) = ↓absorption
- ↓thickness/inflammation = ↑absorption
- ↓blood flow = ↓absorption
- ↓SA (dead gut) = ↓absorption
First Pass
- Hepatic enzyme dysfunction = ↓first pass = ↑OBA
Physiochemical Interactions
- Shocked patients = multiple meds = altered enzyme function → alter hepatic enzyme induction & 1st pass/OBA