G4iii: Define a portal system. Describe the anatomy & function of three portal systems in the body
- Portal system = arrangement where blood is collected from one set of capillaries passes through another vessel (portal) to another set of capillaries before entering the systemic circulation
3 Portal Systems
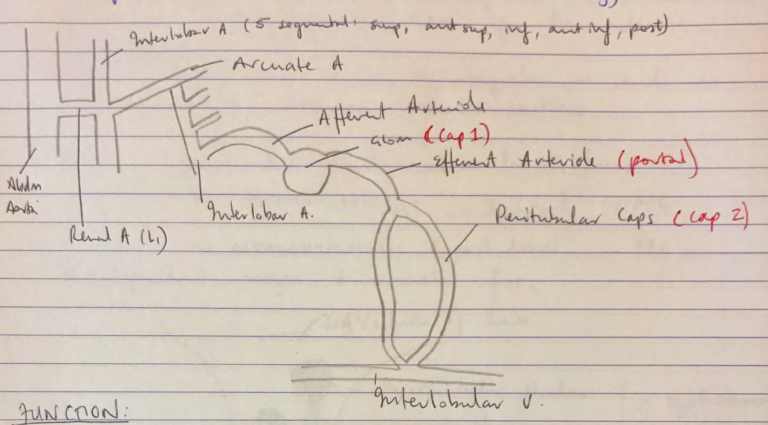
1. Liver
- Deoxygenated blood from: distal oesophagus, SB, colon, rectum, spleen
↓
Drain into sup. mesenteric v., inf. Mesenteric v., splenic v.
↓
All join to form PORTAL V (portal vessel)
↓
Drains into HEPATIC SINUSOIDS (caps 2)
↓
R), Middle, L) hepatic veins
↓
Drain into IVC
- Function:
- Portal circulation carries nutrients, absorbed drugs, old RBCs to the liver
- Liver as an immune organ filters for Ag removal & metabolises absorbed nutrients for synthesis/storage/presentation to systemic circulation
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
- Hypothalamus forms floor & walls of 3rd ventricle
- It is the central relay station for the endocrine system
- Gathers signals from environment → integrates → sends on info/commands via hormones + neurotransmitters
- Pituitary gland lies directly under hypothalamus
- ADENOHYPOPHYSIS (ant lobe) = APG
- NEUROHYPOPHYSIS (post lobe) = PPG
NB: Independent origins & separate functions
APG
- No nervous connection to hypothalamus
- Hypothalamus linked to APG via HYPOPHYSEAL PORTAL SYSTEM
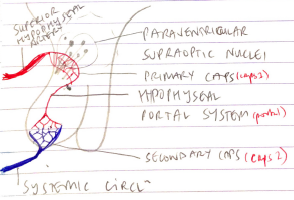
Hypothalamus secretes hormones into PIRMARY CAPS (caps 1)
↓
Hormones travel down HYPOPHYSEAL PORTAL SYSTEM (portal)
↓
Hormones diffuse OUT of SECONDARY CAPS (caps 2) into pituitary tissue
Function: connects hypothalamus to APG, allows rapid exchange of hormones
- GnRH, CRH, GHRH, TRH