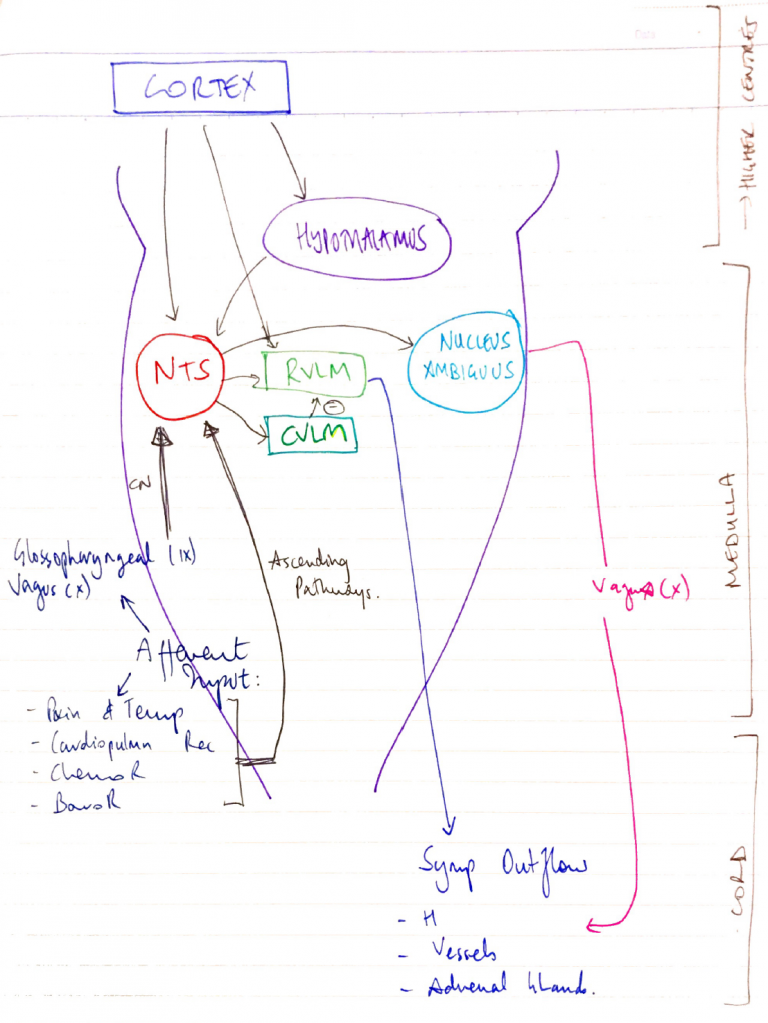
G4iv: Describe the role of the vasomotor centre and the ANS in the regulation of CO & VR
- Cardiovascular System is controlled by the CNS & integration of Afferent Information
- Arterial BP is the 1° controlled variable
- Centres of CNS influencing CV performance:
- Medulla Premotor Sympathetic Cells
- Medulla Premotor Parasympathetic Cells
- Cerebral Cortex
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebellum
- Periaqueductal Grey Matter (PAG)
- The MEDULLA integrates all afferent info & alters ANS activity accordingly
Central Sympathetic Cells
- Symp. control starts in neurons located in ROSTRAL VENTROLATERAL MEDULLA (RVLM)
- RVLM neurons have spont AP activity
- ∴Basal Symp. Tone
- fibres from:
- Medulla
- NTS
- Hypothalamus
- Higher Centres
- CVLM (caudal ventrolateral medulla)
- Excited by excitatory α-acids, Vasopressin, Angiotension, ACh
- Inhibited by GABA, Encephalins, Catecholamines
Central Parasympathetic Cells
- fibres originate from DORSAL VAGAL NUCLEUS & NUCLEUS AMBIGUUS
- Direct inhibition from Medulla Insp. Neurons = ↓firing = tachycardia of inspiration
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
- Where afferents (CN X & IX terminate)
- Other 2° order afferents also terminate here
- Via interneurons communicate with SC, Medulla, Hypothalamus, C. Cortex
- NTS transmits info from BARORECEPTORS
↑BP →
NTS
NUCLEUS AMBIGUUS → ↑Parasymp. Output
CVLM activation → inhibits RVLM → ↓symp. output to Heart / vessels / kidney / medulla
- NTS receives a lot of info
- CV Afferents
- Cortex
- Hypothalamus
- RVLM
Cerebellum
- Controls posture & coordination of movement
- Regulates CV system in response to muscle/joint activity
PAG
- Produce defence reaction in response to nociception/threat
- Supply specific cells of RVLM to induce specific ∆ in vascular beds
Hypothalamus
- ‘Defence Area’
- Inhibits BaroR reflex at NTS
- Stimulates RVLM cells & inhibits Vagal Output
Oppositely
- ‘Depressor Area’
- Enhances BaroR reflex
Limbic
- Activates ‘Rage Behaviour’ → ↑HR, ↑BP, VD
- Enhances ‘Playing Dead’ → severe ↓HR & HypoT
Cortex
- Important for CV responses at onset of exercise