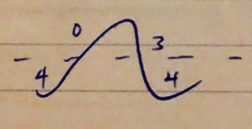G5ii: What is the Valsalva manoeuvre? Explain the cardiovascular response & include graphs in your answer
Definitions
Valsalva = the action of forced expiration against a closed glottis after full inspiration
Aim: To Test Autonomic Function
- Uses the CVS feedback loop (sensor → C → effector) known as the BaroReceptor
- To cause maximal vagal outflow
- To terminate AVNRTs
Phases:
- 4 phases of P/Vol ∆ in Great Vessels
- With resultant ∆ in SNS/PNS outflow from vasomotor centre
- Named for Italian Anatomist who first used it to expel pus from middle ear
ITP = intrathoracic pressure, ITBV = intrathoracic blood volume, BP = blood pressure, BAROR = Baroreceptor, HR = heart rate
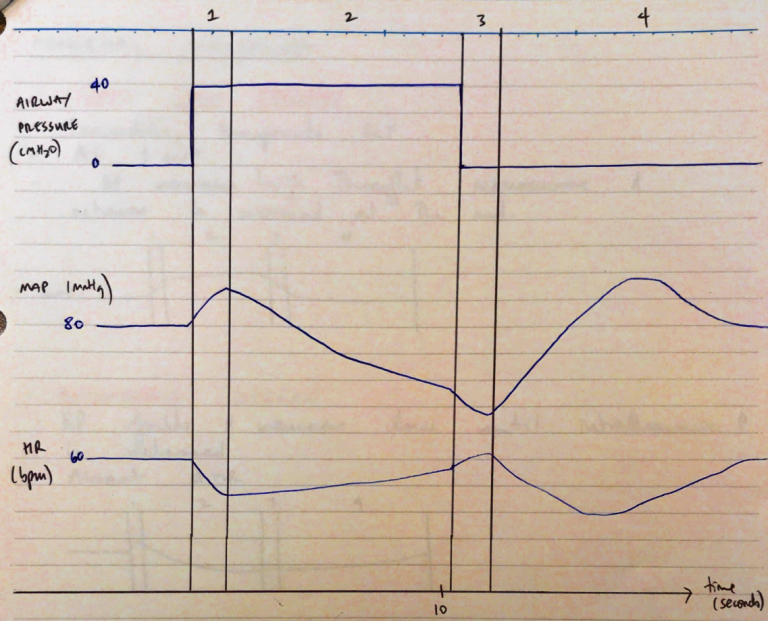
Phase 1: Onset of Straining
- ITP – sharp ↑ITP
- ITBV – expels blood from thoracic vessels = ↑CO
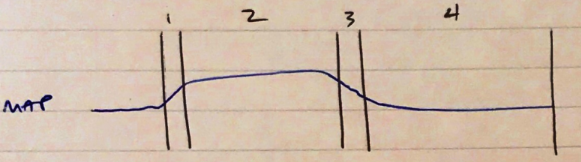
- BP – ↑BP (BP = CO x SVR)
- BAROR – Detect high P → inhibits symp. outflow & ↑parasymp. outflow
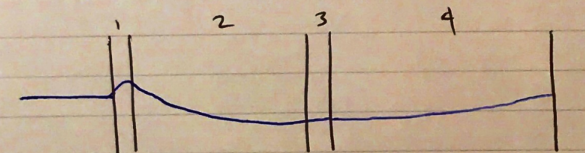
- HR – ↓HR
Phase 2: Sustained Straining
- ITP – remains high
- ITBV – low (high ITP prevents blood returning to thorax)
- BP – ↓BP
- BAROR – ↓afferent d/c to vasomotor centre NTS releases symp. inhibition → ↑symp. outflow
- H = ↑HR, ↑FoC
- Resistance Vessels = VC = ↑SVR
- Capacitance Vessels = VC = ↑VR
- HR – ↑HR
Phase 3: Release of Glottic Pressure
- ITP – pressure released → returns to normal
- ITBV – venous blood pools in pulm. vessels ∴LV preL ↓ → by F-S → ↓CO → ↓BP
- BP – ↓BP
- BAROR – Cont to ↓afferent d/c
- Vasomotor centre cont. ↑ symp. outflow to restore BP
- HR – ↑HR
Phase 4: Overshoot
- ITP – normal
- ITBV – restored to R & L side of heart
- BP – ↑BP
- BAROR – Overshoot of BP (↑CO to VC peripheries)
- Detected by BaroR
- Vasomotor centre:
→ Inhibits symp. outflow
→ Profound vasal response
- HR – ↓↓↓HR
Abnormal Valsalva
Hypovolaemia/Ventilated
- Changes are exaggerated