G6i: Describe the ECG changes seen with hyperkalaemia (30 marks) + Outline the pharmacological principles of drugs used in the management of severe hyperkalaemia (70 marks)
- Definition ↑K+ = K > 5.5mol/L
Role of K+
- Major intracellular cation → maintains intracellular tonicity
- Generation of RMP
- Na/K/ATPase
Problem of ↑K+
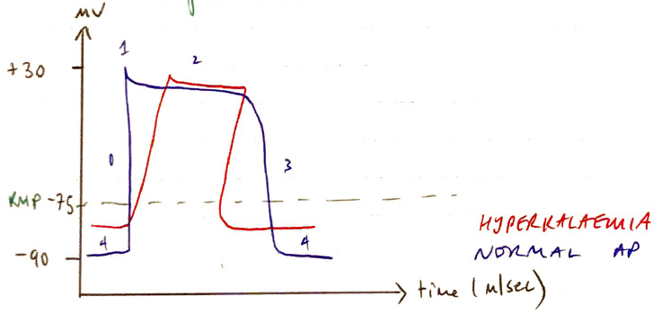
- RMP is less negative ∴ membrane more excitable
- Refractory period initially ↓ but as K > 8mol/L, induces post-repolarisation refraction which prolongs refractory period
- Shortened AP duration
- ↓conduction velocity
- VMAX = rate of rise of AP
- VMAX ∝ RMP because the membrane potential at onset of depol. determines the no. of Fast Na+ channels activated
- As RMP becomes less negative = less Na+ channels activated → ↓VMAX
- ↓VMAX = slows impulse conduction through myocardium
ECG ∆ of ↑K+
K+ (mol/L)
K+ (mol/L)
Reason
5.5 – 6.0
Peaked Tw
Shortened repolarisation
Shortened duration AP
↑myocyte excitability
> 6.5
P waves fluttering
Slowed conduction velocity
> 7.0
Widened QRS
Prolonged PR
Slowed conduction velocity further as ↑RMP
> 8.5
QRS widens further to blend with T-wave → SINE WAVE
Hyperkalaemia MX
Principles of Tx
- Stabilise myocardium
- More K+ intracellularly
- Excrete K+ from body
- Tx cause
1) Stabilise myocardium
- Drug: Ca2+ gluconate 10%
- Dose: 10mL
- Onset: 3 mins
- Duration: 30 – 60 mins
- MoA: 3 mechanisms
- Threshold: Ca2+ shifts threshold to be less -ve so difference is maintained
- VMAX: restoring threshold will normalise VMAX & Na+ channel activation to restore conduction velocity
- Impulse propagation: Ca2+ dependent AP propagation (SA & AV nodes) restored
2) Move K+ intracellularly
- Drug: Insulin & D5W
- Dose: Actrapid 10 units & 50ml of 50% glucose
- Onset: 10mins
- Duration: 4-6hrs
- MoA: Increases Na/K/ATPase activity (3Na out: 2K in) → therefore, drives K intracellularly. Glucose prevents hypoglycaemia
- Drug: Salbutamol
- Dose: 5mg neb
- Onset: immediate
- Duration: 90mins
- MoA: Increases activity of Na/K/ATPase of sk m and also activates Na/K/2Cl transporter → therefore drives K intracellularly
- Drug: NaHCO34%
- Dose: 50mmol slowly IV over 10 mins
- Onset: immediate
- Duration: 30mins
- MoA: Increases plasma pH → activates K/H antiporter → H extrac/K intrac
3) EXCRETE K+ FROM BODY
- Drug: Calcium Resonium
- Dose: 45mg po
- Onset: 3hrs (max at 12h)
- Duration: 24hrs
- MoA: Calcium salt, large & insoluble, binds K+ in colon, prevents reabsorption, promotes excretion
- Drug: Frusemide
- Dose: 20-80mg IV
- Onset: minutes
- Duration: 2-3hrs
- MoA:
Inhibits Na/K/2Cl transporter on TAL
Reducing Na & H2O reabsorption
More NaCl reaches collecting duct
Collecting duct tries to reabsorb as much Na+ as possible
-ve charge in lumen left by Cl–
Attracts +ve charge of K+
K+ lost in urine