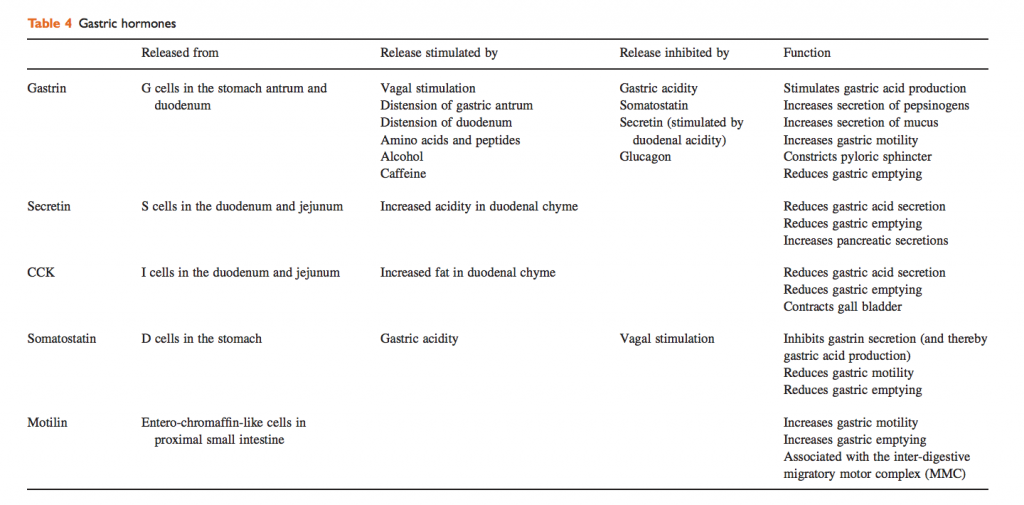
O1iii: Describe the hormonal response to a meal
Gut function is regulated by the ANS, enteric nervous system and by paracrine and endocrine hormones released by hormone secreting cells in the mucosa of the gut (enteroendocrine cells).
Cephalic Phase
- Initiation of GI secretions in preparation of a meal
- Vagal stimulation
- Ach:
- Enterochromaffin cells cause release of histamine
- Acts on histamine receptors on gastric parietal cells
- Increase gastric HCl secretion
- G-cells→secretion of Gastrin
- Enterochromaffin cells cause release of histamine
Gastric Phase
- Gastric wall stretch and peptide content in gastric lumen→stimulates G-cells in antrum→ secretion of gastrin
- Gastrin:
- A peptide hormone
- Acts on CCK B receptors on enterochromaffin cells
- Increased histamine release→HCl secretion
- stimulates secretion of Pepsinogen by chief cells
- Increases Antral pump function
- Decreases LES pressure
- Promotes gastric emptying
Intestinal Phase
Secretin
- Release stimulated by acidic pH of gastric contents
- Peptide hormone
- Secreted by Duodenal S cells
- Inhibits gastric emptying
- Increases pancreatic secretion of a bicarbonate rich fluid
Cholecystokinin
- Protein and FFA content in the duodenum stimulates secretion
- Peptide hormone
(GRID)
- Gall bladder contraction and release of bile for absorption of fats
- Relax sphincter of oddi
- Increases pancreatic secretion of enzymes for digestion of fats and proteins
- Decreased gastric emptying
Motilin
- Stimulated by high pH of intestinal chyme
- Increases gut motility to propel chyme forward
- Initiates Migrating Motor Complex (MMC)
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide
- Secreted by Jejunum
- Stimulated by CHO, FAs, a-acids
- Decreases gut motility
- Decreases acid secretion
- Activates insulin release
As nutrients absorbed from intestine
Insulin
- Released when BSL > 5
- Increases hepatic glucose uptake and glycogenesis, protein and lipid synthesis
- Increases skeletal muscle glucose uptake and glycogenesis, protein synthesis
- Increases adipocyte lipid storage
Leptin
- Released by adipose tissue in response to increased fat stores
- Supresses appetite
Glucagon-Like Peptide
- Stimulated by fat/carb meals
- Decreases gastric emptying
- Promotes satiety
Long after meal