N1iv / 16A05: Bile
16A05: Exam Report
Describe the composition, formation and functions of bile.
31% of candidates passed this question.
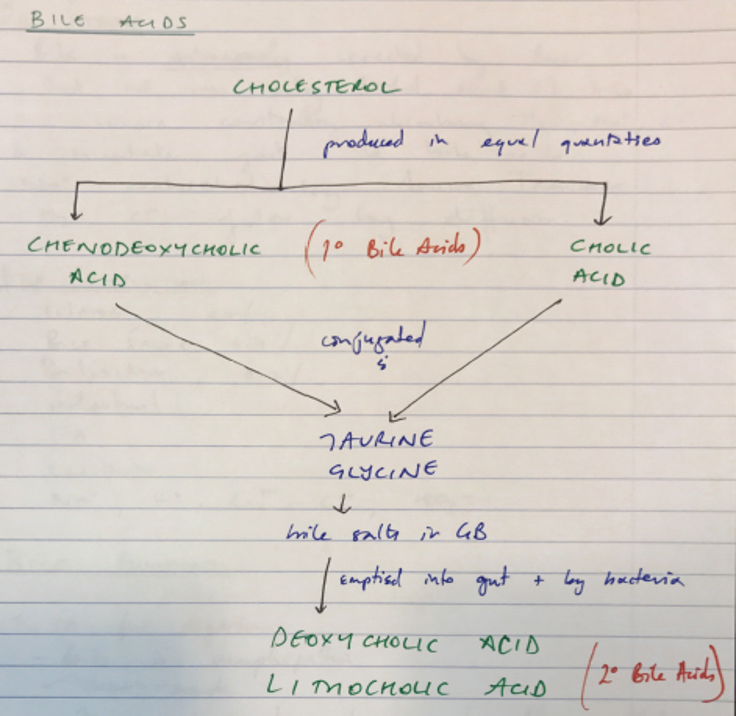
Bile is produced by hepatocytes, excretion via cannaliculus and biliary tree. It is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. Bile contains water, bile acids and bile salts, bile pigments and electrolytes. Some detail was expected regarding each of these and comment on “Primary bile acids”, conjugation with taurine and glycine and production of “bile salts”. It was often not appreciated bacteria in gut produce “secondary” bile acids such as deoxycholate and lithocholic acid. Additional credit was given for discussing “Unconjugated bilirubin” being derived from “heme” component of haemoglobin (85%) is carried via albumin to liver for conjugation via UDP-gluconuryl transferase to “conjugated bilirubin” and that gut bacteria generate water soluble urobilinogen, enterohepatic recycling and excretion in urine.
The major role of bile is in lipid, cholesterol and lipid soluble vitamin absorption with a minor role in excretion of bile pigments. It was expected candidates would describe the emulsification of fat via bile salts and lipid micelle formation to facilitate absorption.
N1iv / 16A05: Describe the composition, formation & functions of bile
Functions of Bile
1. Fat digestion & absorption
- Digestion → bile acids help emulsify large particles → small particles, to allow LIPASE maximal SA
- Absorption → acid absorption of fat via intestine
2. Excretion of waste
- Especially bilirubin
Bile Secretion
- Liver produces 1L/day
- Hepatocytes secrete large amounts of bile acids & cholesterol into Bile Canaliculi
- Bile flows in canaliculi → empties into terminal bile ducts → progressively larger ducts until reaches HEPATIC DUCT & CBD
- Then bile empties into:
- As bile travels through bile ducts, a solution of Na+ & HCO3– is secreted by epithelial cells of ducts → this ↑bile volume & role is to neutralise acid from stomach when it gets to duodenum
Bile Storage
- Bile is continuously secreted by liver
- But GB can only hold 60mL of bile
- ∴mucosa constantly absorbing H2O, Na+, Cl– to concentrate just the bile acids
- Na+ reabsorbed by ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- H2O, Cl– follow by diffusion
Bile Composition
- WATER 97%
- BILE SALTS 8.7%
- BILIRUBIN 0.2%
- Cholesterol
- FA
- Lecithin
- Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl–, HCO3–
Bile Functions
1. ↑ SA for digestion
- Bile is amphipathic molecule
- This ↓surface tension & allows fat globules to break into smaller particles for maximal SA of lipase to act on
2. Emulsification & formation of MICELLE
- Bile salts help absorb FA, cholesterol & other lipids
- By forming micelles → allows fat transport through mucosa for absorption
- Without this, 40% bile salts are lost in faeces = severe ADEK deficiency
- Allows absorption of ADEK!
3. Excretion of bilirubin
- Conjugated bilirubin is excreted in bile by ACTIVE TRANSPORT → in ileum/colon is converted to UROBILINOGEN by bacteria → enters enterohepatic circulation →excreted in urine OR further oxidised to STEROCOBILIN → excreted in faeces
Enterohepatic Circulation
- 95% of bile salts are reabsorbed
- Half by diffusion in early SI
- Half by active transport @ distal ileum
↓
Enter portal circulation
↓
Liver
↓
Salts are absorbed by hepatic cells
↓
Re-secreted into bile
KA “Enterohepatic circulation”
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou