G6ii / 22B10 / 16B17: Aortic vs Radial waveform
22B10: Exam Report
Draw a labelled diagram of both the aortic root and radial artery pressure waveforms in a young adult using the same axis (60% marks). Explain the factors that account for the differences between these two waveforms (40% marks)
21% of candidates passed this question.
This question required the integration and understanding of cardiovascular monitoring with what influences the changes as the arterial pulse moves through the vascular tree.
In general, the waveforms drawn were often of a poor standard, with little attention given to accurately representing the different shapes, correct axis (pressure and timing) and labelling.
The description of the differences was of a better standard however, there were often contradictions between what was drawn and described.
For example, several answers correctly described a delay in the systolic peak seen in the radial artery, but this was not illustrated in the diagram.
The windkessel effect was often correctly mentioned but not further explained to help describe the changes seen in the waveforms.
Interruptions to the arterial traces from the anacrotic and diacrotic notches, the origins of the diacrotic hump, and insuria were often incorrect and poorly explained.
The examiners reported that answer template structure was not a major issue, but a lack of integration of the waveform and translation of that knowledge into a description of the cardiac cycle was often poorly done.
16B17: Exam Report
Draw a labelled diagram of both the aortic root and radial artery pressure waveforms in a young adult using the same axis (60% of marks). Explain the factors that account for the differences between these two waveforms (40% of marks).
41% of candidates passed this question.
A well labelled diagram drawn clearly to demonstrate the salient features of the aortic and radial arterial pulses was expected. This would include the different systolic pressure, the absence of a dicrotic notch in the radial pulse (instead a diastolic hump), the narrowness and the delay of the radial pulse, garnered many marks.
Marks were lost for insufficient explanation such as the distance needed to travel for the pressure wave accounting for the delay, the sharper rise and decline of the radial pulse due to loss of the WIndkessel effect and the different compliance and the loss of the dicrotic notch due to summation and damping out of high frequency components of the pressure wave.
G6ii / 22B10 / 16B17: Draw a labelled diagram of both the aortic root & radial artery pressure waveforms in a young adult using the same axis (60 marks) + Explain the factors that account for the difference between these two waveforms (40 marks)
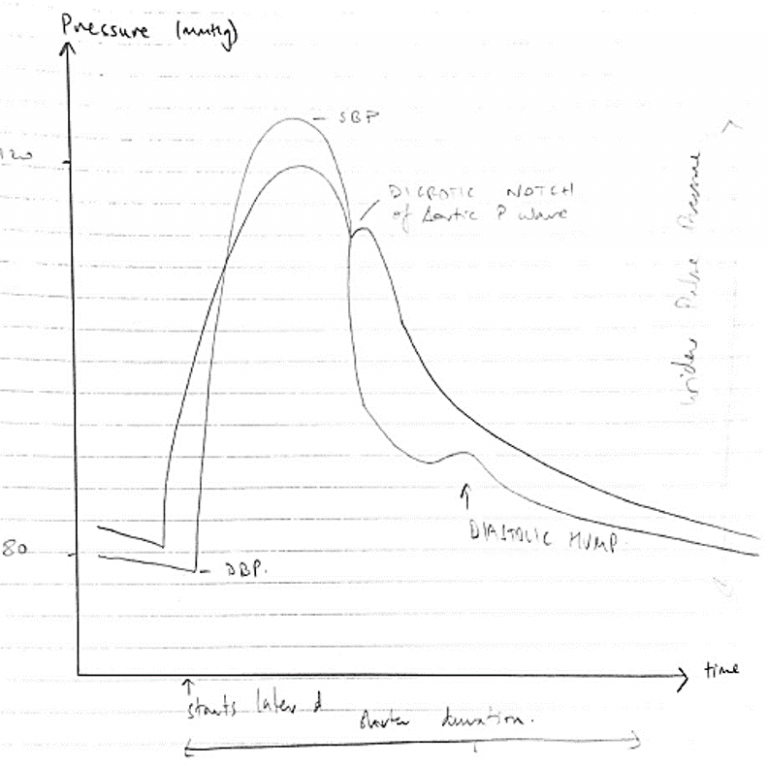
Aortic Pressure Waveform
- Due to ejection of blood from LV → Aorta in Systole
Systole
- Follows R wave on ECG
- Steep upstroke when AoV opens
- Reaches peak = SBP
- Declines
- Dicrotic notch = closure of AoV
Diastole
- Follows T wave on ECG
- Gradual ↓pressure ‘arterial run off’ in diastole
- Due to Windkessel Effect → Potential E stored in Aortic Elastic Wall in systole converted to Kinetic E that promotes blood flow in diastole
Radial Pressure Waveform
- Transmission of pressure wave to periphery
- Does not mean there is blood flow because pressure waves travel much faster
Differences with Aortic P waveform:
- Displays much later
- ~180 sec after R wave
- Because of time taken for spread of depol. → ejection →Transmission of P wave to Radial A → catheter → Transducer
- Absence dicrotic notch
- Due to summation & damping out of high frequency components of pressure wave
- Degree of damping ∝ compliance * resistance
- Arterioles = major resistance vessels & less compliance move distally
- Prominent ‘diastolic hump’
- Due to reflection & resonance
- Sharper rise & decline
- Due to ↓compliance of peripheral vessels
- Sharper upstroke – ↓vessel compliance & summation of waveforms
- Sharper downslope → &∴loss of Windkessel effect
- Widened pulse pressure
- Due to higher resistance → requires higher P more distally
- Despite morphological differences → MAP aorta only slightly greater cf. RADIAL A.
Addit Notes: Aortic A Waveform In Elderly
- ↓Myocardial function = ↓contractility = slower upstroke
- ↓Aortic compliance = higher Peak Pressure
→ In effect, there is less difference in Aortic & Radial Waveforms in elderly
- LV pump → AoV opens → ejects blood
- Initiates a pressure wave
- Propagates down aorta & branches faster than actual flow of blood
- ∴Peripheral Pulse is due to transmission of this pressure & is distinct from blood flow
NB: In fact! A pulse wave can be recorded even when Radial A. is occluded & there is no flow
- Pulse = mechanical activity (i.e. heart pumping)
- ECG wave = electrical activity
- NB: neither guarantee flow
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou