F1i / 16B24: Strucure of Trachea Main Bronchi
16B24: Exam Report
Outline the tracheal (60% of marks) and left and right main bronchial anatomy (40% of marks) in an adult.
14% of candidates passed this question.
To pass this question, the following were required for each section (trachea and main bronchi): landmarks; basic structural anatomy; and important relations (major vessels; major nerves; major structures).
Marks were also allocated for innervation, and blood supply and venous drainage of the trachea.
Most unsuccessful answers did not address a number of these areas. Overall, the answers were better for tracheal anatomy compared to bronchial anatomy.
A structured approach to anatomy questions works well and this was again the case (i.e. relations / blood supply / etc.
F1i / 16B24: Outline the tracheal (60 marks) and left and right main bronchial anatomy (40 marks) in an adult
Trachea & Main Bronchi = Extrapulmonary conducting airways of the tracheobronchial tree
Trachea
R+L Bronchi
Structure
Trachea
Cricoid -> Main Bronchi
11cm long
Anterior: 22 C shaped cartilaginous rings
Post: trachealis muscle
R+L Bronchi
R+L Main bronchi branch off trachea at T5 (R) and T6 (L)
R main = 3 lobar
*R main is shorter, wider, more vertical
L main = 2 lobar
FN
Trachea
Conducting airway
R+L Bronchi
Conducting airway → supply specific lobes of lung
Layers
Differences
Trachea
Mucosa =
cilitated, pseudostratified columnar epithelium w
goblet (mucous cells),
brush cells (air quality) and neuroendocrine cells
Submucosa = dense connective tissue, mucous glands
Cartilaginous layer – Hyaline C shaped cartilage
Adventia – connective tissue
R+L Bronchi
Mucosa = cilitated, pseudostratified columnar epithelium w goblet (mucous cells), brush cells (air quality) and neuroendocrine cells
Muscularis = continuous layer of smooth muscle that dilates/constricts independent of lung volume
Submucosa = dense connective tissue, mucous glands
Cartilage layer – supporting plates that become smaller distally
Adventia – conn tissue
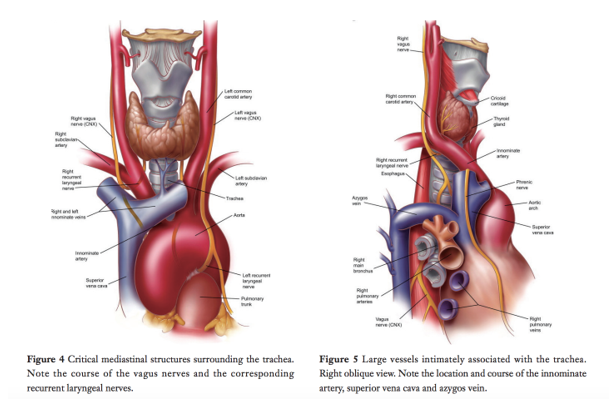
Major Structures (Fig 4 &5)-
(Fig 4 &5)-
Trachea
R+L lobes thyroid – anterior to cervical trachea
sthmus of thyroid crosses tracheal ring 3
Oesph – L posterior border of trachea
Vertb bodies – R posterior border
RIGHT Recurrent laryngeal n – dives under R subclavian where it recurs and ascends up to cricoid cartilage
LEFT Recurrent laryngeal n – dives under arch and lateral to ligamentum arteriosum where it recurs and ascends up to cricoid cartilage
Brachiocephalic (1st branch aortic arch) runs L->R over anterolat surface of trachea just under thyroid
L Common Carotid (next arch branch) comes off arch midline to trachea and runs up lateral L border
SVC runs R border trachea to RA
Azygous V runs along R lateral vertb column and joins SVC superior to R tracheobronchial angle
Pulmonary Trunk – anterior to carina – branches with bronchi and runs arterial vessels anterior to bronchi corresponding
R+L Bronchi
L main – crosses ant to oesph
Arterial
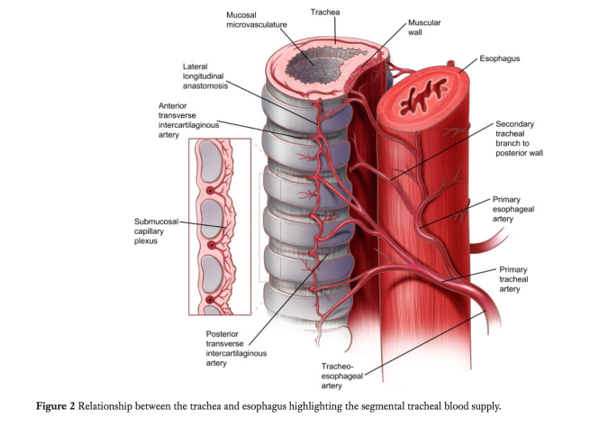
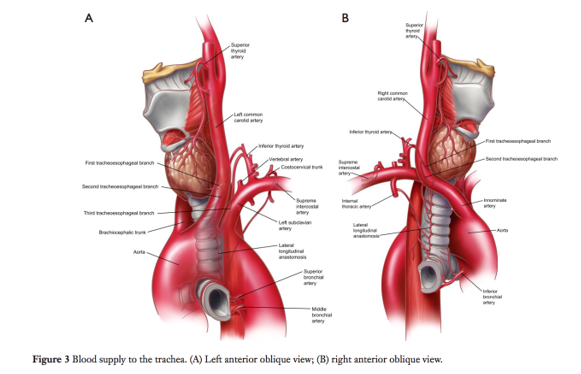
(Fig 2&3)
Trachea
Upper Trachea:
Inferior thyroid arteries
Give off tracheoesophageal branches
Lower Trachea:
Bronchial arteries direct from aorta
Arteries of the trachea enter laterally and branch sup&inf in longitudinal fashion (Fig 2)
R+L Bronchi
Bronchial arteries (sup, middle and inf) arise from Aorta
Venous
Trachea
Inf thyroid veins
R+L Bronchi
Bronchial veins
Nervous
Trachea
Trachealis muscle – Symp & Parasymp fibres
Pain – Vagus (X)
R+L Bronchi
Vagus (X)
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou