F6iii / 17B06: Explain the effect of VQ mismatch on O2 transfer & CO2 elimination
17B06: Exam Report
Describe the effects of Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) inequality on the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) in arterial blood.
48% of candidates passed this question.
Overall answers lacked sufficient detail on a core area of respiratory physiology. Answers expected included a description of V/Q ratios throughout the lungs and an explanation of how V/Q inequality lowers PaO2.
F6iii 17B06: Explain the effect of V/Q mismatch on O2 transfer & CO2 elimination
V/Q Importance
- 1° function of lung → oxygenate blood & remove CO2
- V/Q ratio determines partial pressure of gases in lungs
- Alveolar ventilation = 4L/min
- Pulmonary BF = 5L/min
- ∴if uniform, every alveolus would have an ideal ratio 0.8 → not the case!
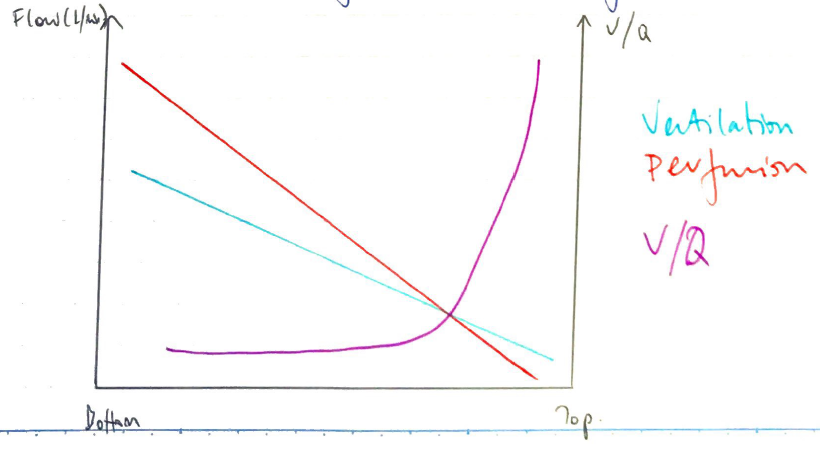
Regional V/Q Differences
- In upright lung
- Ventilation increases apex → base due to ↑compliance
- Perfusion increases apex → base due to ↑hydrostatic pressure
- But not uniformly, perfusion ↑↑↑much more
V
Q
V/Q
PaO2
PaCO2
Apex
V
0.24
Q
0.07
V/Q
3.3
PaO2
132
PaCO2
28
Base
V
0.82
Q
1.29
V/Q
0.67
PaO2
89
PaCO2
42
Therefore:
- High V/Q apex, low V/Q base
- PO2 decreases apex → base
- PCO2 increases apex → base, but much less cf. PO2
- ∴↓pH apex → base
- Volume less in apex
Definitions
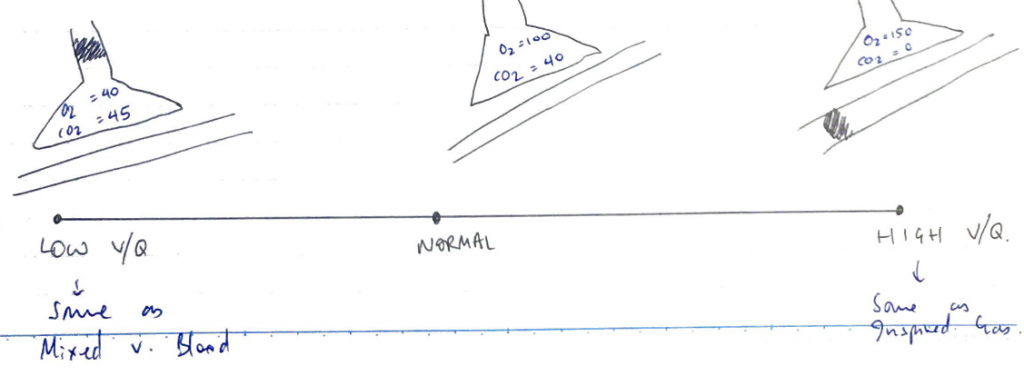
- V/Q scatter: not all alveoli have the same V/Q ratio. V/Q scatter is responsible for the natural A – a gradient.
NB: less V/Q scatter supine because the vertical gradient is much less
- Dead space: VT that does not partake in gas exchange
- V/Q = ∞
- Shunt = blood that enters the arterial circulation without passing through ventilated lung
- V/Q = 0
Effect on PaO2
- V/Q inequality ↓O2 content of arterial blood
- Alveoli @ base have greater blood flow
- The high V/Q units at Apex cannot compensate
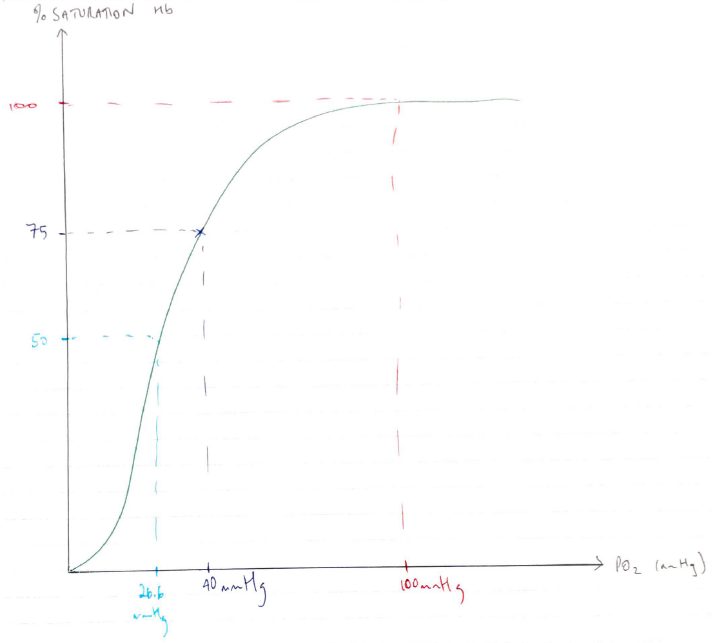
- ODC is sigmoid shaped
- So alveoli with high V/Q & PAO2 are not ↑O2 content of blood much further, because Hb here is fully saturated
- ↑portion of dissolved blood is not going to ↑CaO2 much
- Alveoli with low V/Q which have O2 content similar to mixed venous blood can ↓CaO2 significantly because it is on steep part of ODC
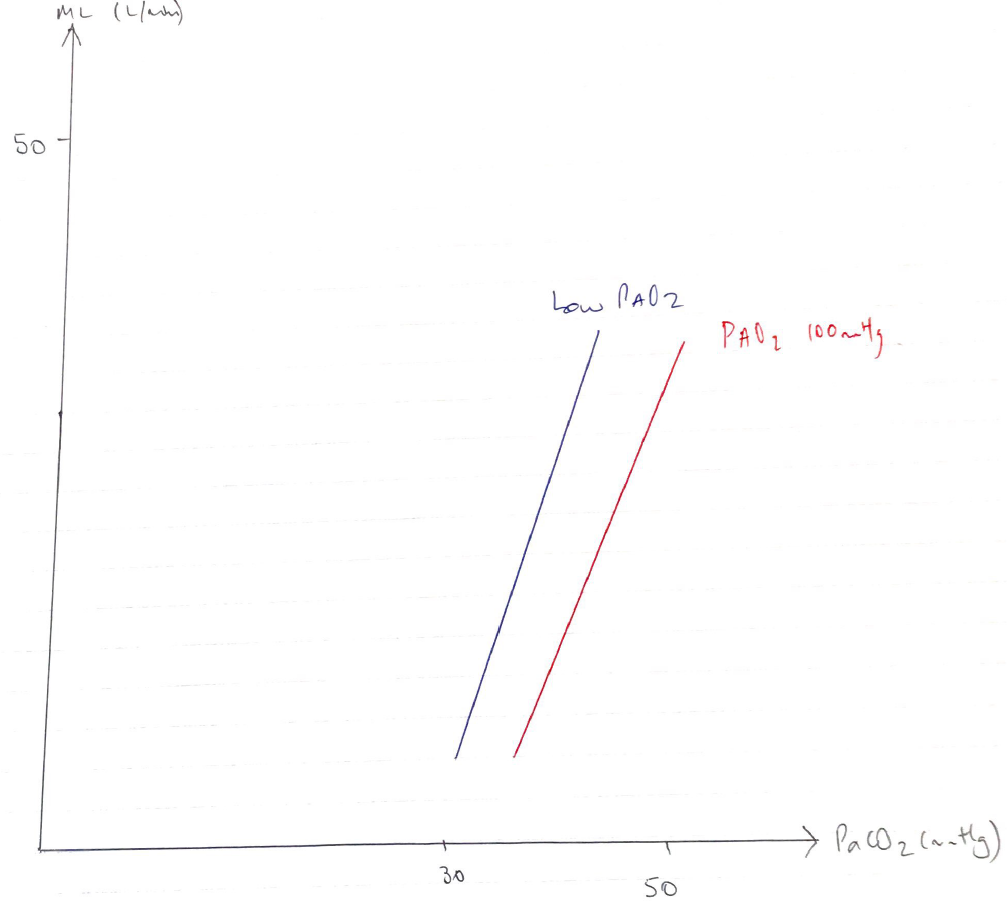
Effect on PaCO2
- V/Q inequality does not have such drastic effect on PaCO2 because of linear shape CO2 dissociation curve
- There is immediate ↑MV with slight ↑PaCO2 so that high V/Q compensate for low V/Q in terms of CO2 excretion
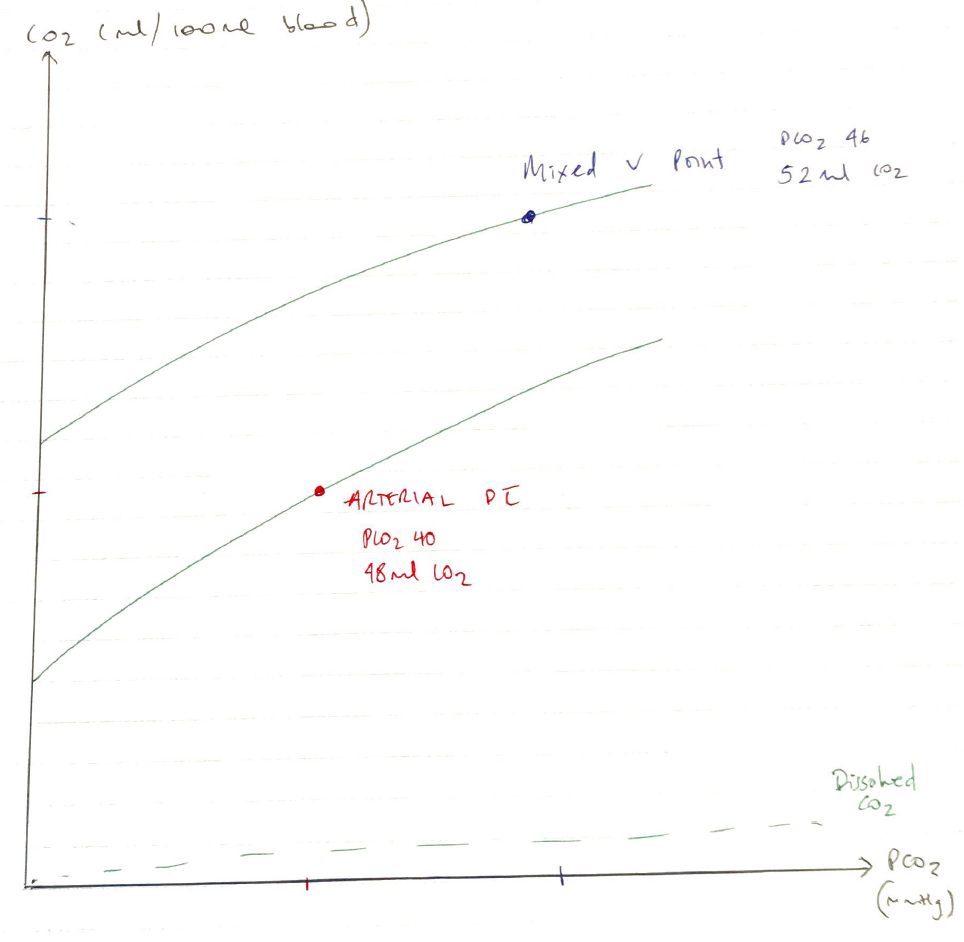
- ↑PCO2 = ↑MV in linear fashion
- Slope of ↑depends on PAO2 (alveolar)
- ↓PAO2 = ventilation & slope of the line is steeper
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou