G7ii / 17B08: Classify calcium channel antagonists and give one example of each class
17B08: Exam Report
Classify calcium channel antagonists and give one example of each class (30% of marks). Describe the pharmacology of Nimodipine including important drug interactions (70% of marks).
19% of candidates passed this question.
The classification was done well. Most candidates demonstrated that they had a structure for a “drug” question, but were often challenged to fill in the detail of that structure and failed to deliver enough content to secure a pass. Many candidates wrote a generic answer for calcium channel blockers instead of the specifics of nimodipine.
Frequently the pharmacokinetic data recounted was incorrect. Candidates failed to distinguish between absorption and bioavailability. The difference between oral and intravenous dosing was often omitted. Few answered the section on important drug interactions.
G7ii / 17B08: Classify calcium channel antagonists and give one example of each class (30 marks). Describe the pharmacology of Nimodipine including important drugs interactions (70 marks)
Calcium Channel Blockers
- Class 4 antiarrhythmics
- Diverse & structurally unrelated
- All block Ca2+ channels
- Classified on basis of CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
Dihydropyridines → Nimodipine
- Block Ca2+ channel of peripheral arteries
- Via extracellular modulation of Ca2+ channel
- Prevents Ca2+ entry into smooth m. cell
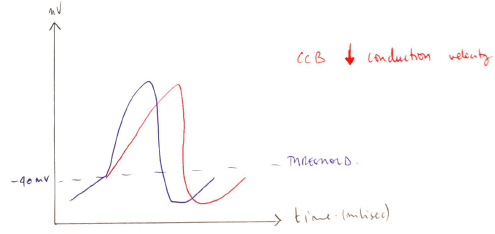
Benzothiapines → Diltiazem
- Intermediate between the other 2
- Predominate effect = AV NODE
- Inhibits inward Ca2+ current
- ↓rate conduction of AV Node → ↑PR interval
Phenylalkylamines → Verapamil
- Predominant AV Node, SA Node
- Physically occludes Ca2+ channel
- ↓rate conduction → ↑PR interval
Nimodipine
Nimodipine
Chemical
CCB → DIHYDROPYRIDINE → cerebral selective
Use
- Prevent & treat cerebral vasospasm (i.e. delayed cerebral ischaemia post-SAH)
- Migraine
Presentation
IV: 200mcg/mL
PO: 30mg tablets
Dose/Route
IV via CVC: 1mg/hr first hour → 2mg/hr for 5 – 14 days
PO: 60mg QID
MoA
Specificity for cerebral arterioles
↓
Prevent Ca2+ entry into L-type Ca2+ channels
↓
Electromechanical decoupling
↓
Relaxation of cerebral vascular smooth m.
↓
VD of cerebral vessels
PD
CVS: ↓SVR, ↓CO
CNS: ↑CBF 20%
- Negates ‘steal’ effect of SAH
- ↓M+M of these patients significantly
PK
A
OBA 20% 2° 1st pass
D
99% PPB, VD 2L/kg
M
Liver → demethylated + dehydrogenated → into INACTIVE pyridine analogue → further degradation
E
50% → renal excretion of metabolites
30% → faecal
t ½ B = 7hrs
*** Dose adjustment for liver impairment
Adverse Effects
- Flushing
- Headache
- Nausea
- ↓BP
- Abnormal LFTs
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou