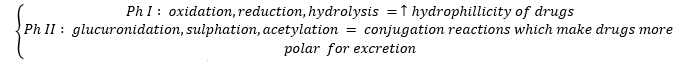N1i / 17B20 / 17A22 / 13B04: Function of the liver
17B20: Exam Report
Outline the functions of the liver.
86% of candidates passed this question.
This is a very straightforward question testing breadth of knowledge rather than depth. It was well answered by the majority of candidates.
17A22: Exam Report
Outline the functions of the liver.
56% of candidates passed this question.
Most candidates attempted a structure however did not expand the answers within the categories: e.g. a passing mention of glucose homeostasis is insufficient to score full marks for the carbohydrate metabolism category.
13B04: Exam Report
Briefly outline the functions of the liver.
88.9% of candidates passed this question.
This question was generally well answered with a good response being in some structured format, e.g. a mention, followed by a description for each function of the liver. For questions asking to outline a particular topic, a general overview of the topic is expected and not merely a “dot-point” list of the functions of the liver without actually delving into the way the liver does those functions. In general candidates should avoid making broad-brush statements, which do not get them any marks like “the Liver is the major organ in the body”. Candidates were expected to list, and provide an overview for each, function of the liver.
N1i /17B20 / 17A22 / 13B04: Outline the functions of the liver
Carb Metabolism
- Glucose taken up by portal system to transport to hepatocytes
- Glucokinase of hepatocytes converts glucose →G6P so that diffusion gradient maintained
- Glycogen formed from G6P
- Glycogen formation & breakdown controlled by Glycogen Synthetase & Glycogen Phosphorylase
- ↑[portal blood sugar] = ↑[insulin] = glycolysis, ↑pyruvate dehydrogenase, ↑Acetyl CoA, ↑glycogen synthetase, inhibits gluconeogenesis & glycogenolysis
- Gluconeogenesis allows maintenance of constant BGL, 1° for brain requirement
Lipid Metabolism
- β-oxidation: FAs →Acetyl CoA which occurs in cytoplasm of all cells
- Acetyl CoA →used as E, fat storage, ketone synthesis
- FA synthesis (from Acetyl CoA)
- Ketogenesis (from Acetyl CoA)
- Cholesterol metabolism
- Controlled by HMG-CoA
- 80% of synthesised cholesterol is converted into bile
- Bile production
- 1L/day
- Emulsifies dietary fats & vits ADEK for absorption
Protein Metabolism
Anabolic
- Synthesises plasma proteins inc Albumin & clotting factors
- Oxidative deamination of amino-acids
Catabolic
- Amino acid degradation:
- Transamination
- Deamination
- Decarboxylation
- Breakdown of amino acids produces NH3 →liver converts this to Urea in Ornithine cycle
- Creatinine synthesised by liver →used by skeletal m. for E
Endocrine
- Synthesis of 25 hydroxycholecalciferol from cholecalciferol in starvation, to be converted to calcitriol in kidney
- Secretes angiotensinogen
- Synthesises EPO in foetus
- Metabolises steroid hormones & thyroxine
Storage
- Vits ADEK, riboflavin, folic acid, B12
- Vit A →10 month
- Vit D →3 month
- Vit B12 →12 month
- Glycogen →400g
- Blood 500mL
- Iron storage →as ferritin
- Hepatocytes have large amounts of Apoferritin (protein)
- Apoferritin reversibly combines with iron
- ∴acts as blood iron buffer
Immunological
- RES – tissue macrophages & monocytes distributed throughout body
- Kupffer cells of liver line sinusoids →remove bacteria, endotoxins, denature proteins
Acid-Base
- Metabolism of lactate, ketones, NH3
- Synthesis of Albumin (weak acid)
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou