F2i / 19A16: Describe the role of CO2 in the control of alveolar ventilation
19A16: Exam Report
Describe the role of carbon dioxide in the control of alveolar ventilation
57% of candidates passed this question.
Better answers considered the role of CO2 in the control of alveolar ventilation in terms of sensors, central processing and effectors – with an emphasis on sensors.
Features of central and peripheral chemoreceptors should have been described in detail.
The PCO2/ventilation response curve is best described using a graph, with key features of the curve identified (including gradient and axes).
Various factors affecting the gradient of this curve and how CO2 affects the response to hypoxic drive should be described.
F2i / 19A16: Describe the CO2 in the control of alveolar ventilation
1° function of lungs is to exchange CO2 & O2
→ to maintain normal levels of PO2 & pCO2 in arterial blood
→ This is kept in tight regulation by the control of ventilation
- Hypercapnia = PaCO2 > 45mmHg
- PaCO2 = the most important factor controlling ventilation
- PaCO2 is kept within +/- 3mmHg of normal value
- For every ↑PaCO2 1mmHg = ↑MV 2 – 3L/min
3 elements to Resp Control System
- SENSOR
- CENTRAL CONTROLLER
- EFFECTOR
CO2 primary role in sensory capacity:
Neurological
Central ChemoR
- Ventral surface of Medulla
- Neurological origins of Vagus (X) & Glossopharyngeal (IX)
- Bathed in brain ECF
- Composition of which determined by CSF & BF
- pH 7.32, impermeable to H+, less buffering capacity due to ↓[protein]
- CO2 diffuses across BBB
- Converted with CO2 + H2O ⇄ H2CO3 ⇄ H+ + HCO3–
- ↓pH CSF → ↑firing of afferents to Resp Centre → ↑MV
- NEGATIVE FEEDBACK SYSTEM
- Cerebral VD 2° ↑pCO2 enhances diffusion of CO2 into CSF
Peripheral chemoR
- Carotid bodies: sensitive to ↑PaCO2, ↓PaO2, ↓pH
- Aortic bodies: sensitive to ↓PaO2, ↑PaCO2 but not pH
- Fast responders to ↑PaCO2, but only 5% of total response → majority is Central ChemoR
- ↑PaCO2 = ↓Intracellular ATP & ↑NA, Dopamine, ACh release → ↑AP firing → resp centre → ↑MV
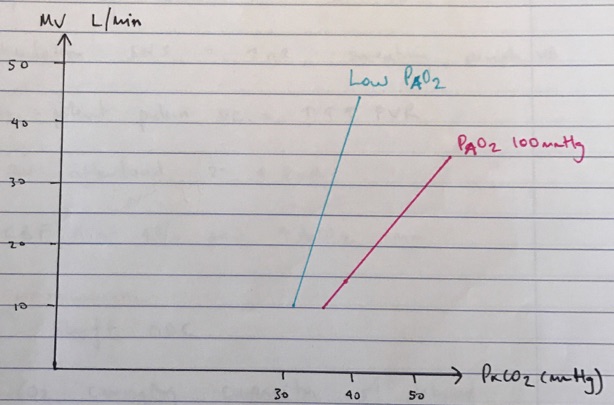
- ↑pCO2 = ↑MV
- Slope of line depends on PAO2 (Alveolar)
- ↓PAO2 = ventilation & slope of the line is steeper
Respiratory
- CO2 primary determinant of alveolar ventilation
- ↑MV 2 – 3L/min for ↑pCO2 1mmHg
- ∴↑WOB
- Arterial hypoxaemia (Alv. Gas Equation)
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou