F1i / 19B05: Describe the anatomical course and relations of the trachea and bronchial tree (to the level of the segmental bronchi).
19B05: Exam Report
Describe the anatomical course and relations of the trachea and bronchial tree (to the level of the segmental bronchi).
24% of candidates passed this question.
Better answers included details of the significant structures related to the cervical and mediastinal trachea and bronchi. The lobar branches and bronchopulmonary segments requiring naming to attract full marks. Many answers lacked sufficient detail or contained inaccuracies regarding vertebral levels and key structural relations. Some candidates discussed the general anatomy of the airway, including the larynx, structure of the airways, blood supply and innervation. This did not attract marks.
F1i / 19B05: Describe the anatomical course and relations of the trachea and bronchial tree (to the level of segmental bronchi)
Trachea
Structure:
- Extends from Cricoid Cartilage → 1° Bronchi
- 11cm long (extends 15cm w inspiration owing to elastic fibres)
- Anterior, C-shaped cartilaginous rings (prevent collapsing)
- Posteriorly → TRACHEALIS MUSCLE; smooth muscle which bridges the gap btw C-shaped cartilage
- 16 – 20 tracheal rings
Histology: 4 layers
- Mucosa
- Ciliated, pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- With ciliated cells, mucous (Goblet) cells, brush cells, small granule (neuroendocrine) cells, BM, L.Propria
- Submucosa
- Dense connective tissue, mucous glands
- Cartilaginous layer
- Hyaline C-shaped cartilage
- Adventitia
Structural Relations:
- Cervical & Thoracic parts of Trachea
- Extends from Larynx (C6) to Carina (T5-7)
- Larynx is superior
- Oesphagus and vertebrae are posterior
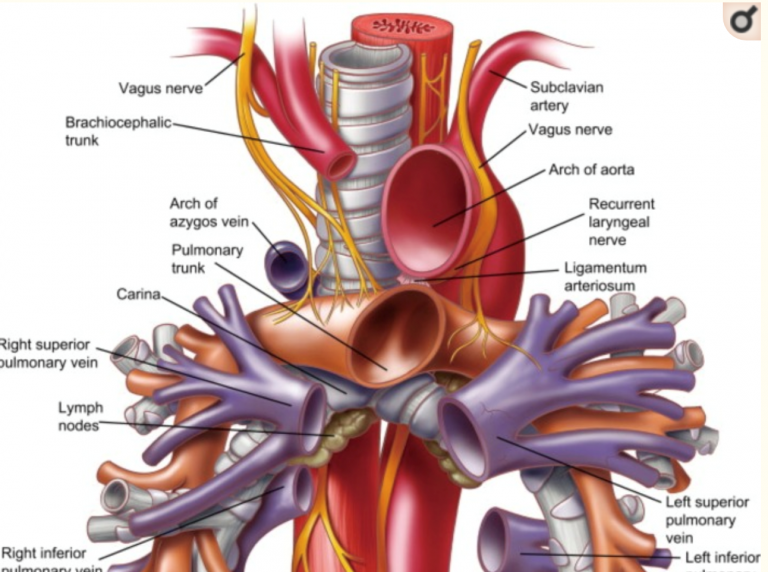
- Near its lower end deviates slightly to R, resulting in L main bronchus crossing anterior to oesophagus
- Aortic arch is first anterior to trachea, then on its L side immediately superior to L main bronchus
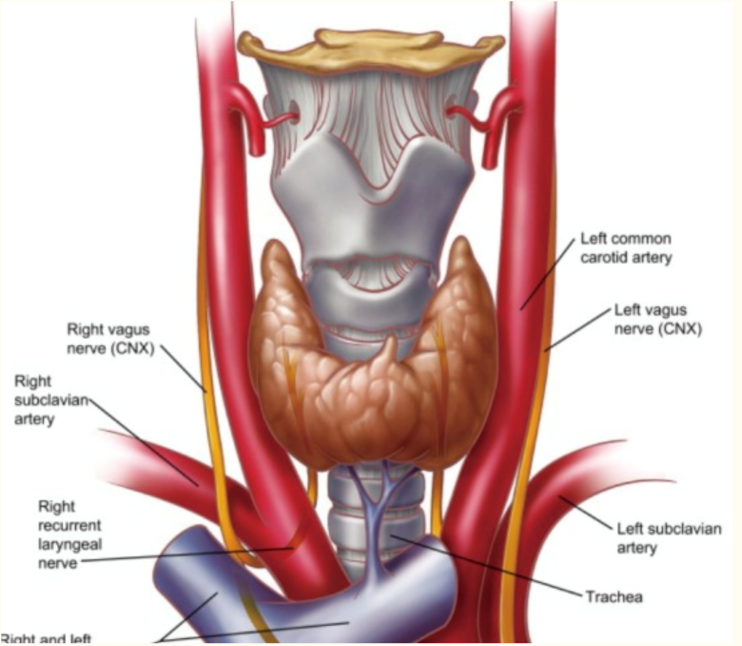
- R & L lobes of thyroid gland sit anteriorly to cervical trachea, isthmus crosses 2-3rd tracheal ring
- R & L recurrent laryngeal nerves enter larynx btw thyroid and cricoid cartilages either side of proximal trachea
- Brachiocephalic A (1st branch aorta) runs L-to-R over anterior aspect of trachea
- L Common Carotid A, next branch of aorta, runs superior from R-to-L over anterolateral trachea
- Pulmonary Trunk is anterior to Carina
- IVC is to the Right
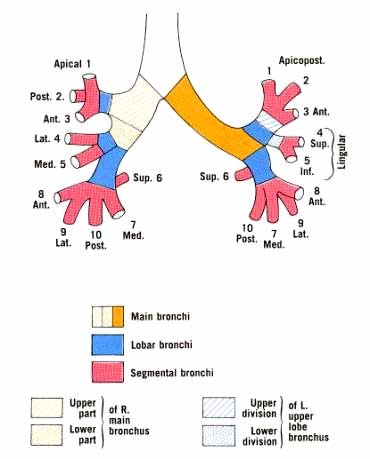
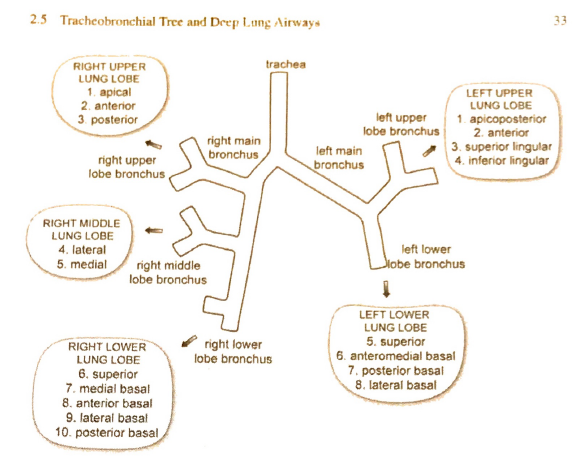
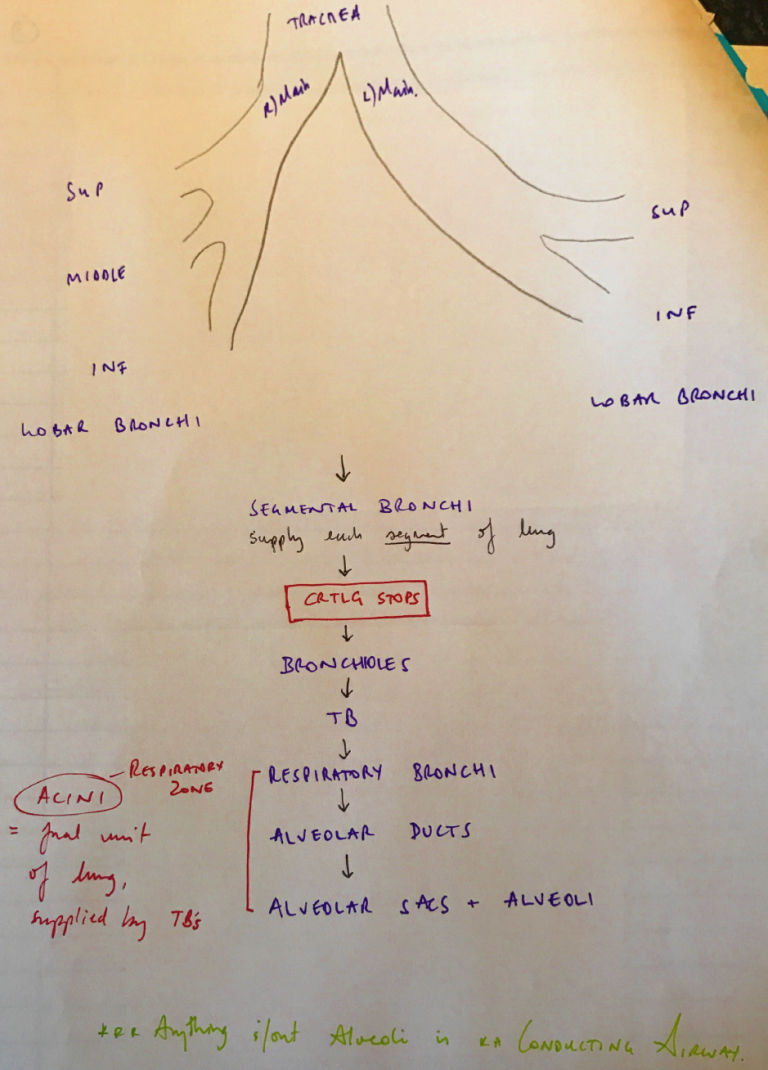
Main, Lobar, Segmental Bronchi
Histology
Bronchi have supporting cartilage plates + a circumferential layer of smooth m. KA MUSCULARIS
- MUCOSA = pseudostratified epithelium
→ Ciliated (caudal mucous), Goblet (mucous), Brush (rec’s), granule (neuroendocrine), Basal (reserve population cells)
- MUSCULARIS = continuous layer smooth m. which dilates/constricts independent of lung VOLUME
- SUBMUCOSA = loose connective tissue
- CARTILAGE LAYER = plates → become smaller more distally
- ADVENTITIA = dense connective tissue connecting bronchioles to adjacent structures
Structural Relations
- R) Main Bronchus
- Passes posterior to R) PA, IVC & Asc Aorta
- Azygos V passes over superior surface to enter IVC
- Oesph is posterior
- L) Main Bronchus
- Passes posterior to L) PA but anterior to Desc Thoracic Aorta
- Vagus passes anterior and posterior to main bronchi
Blood/Lymph/Nerves:
- Blood: Bronchial Arteries & Veins
- Lymph: Deep lymphatic plexus
- Nerves: Vagus
Bronchioles (transitional zone)
- Initially ciliated columnar epithelium → transform into simple ciliated columnar epithelium
- Goblet cells stop @ Terminal Bronchioles (TBs)
- Thick layer smooth m.
- TBs have CLARA CELLS → secrete protein which prevents luminal adhesion in the event that the airway collapses on itself
Respiratory Zone
- Resp Bronchi → Alveolar Ducts → Alveolar Sacs + ALVEOLI
- Alveolar Sacs = last generation (blind ending)
Function
- Conducting: conducts air ⮂ alveoli
- Upper branches: CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
- Heat + humidify air
- Trap foreign particles
- Move mucous caudally
- Lower branches: CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM
- Allows for gas exchange
- Cartilage disappears distally to facilitate gas exchange
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou