Biii / 20A15 / 17B22: Define bioavailability (10 marks). Outline factors which affect it (90 marks)
20A15: Exam Report
Define bioavailability (10% of marks). Outline the factors which affect it (90% of marks).
49% of candidates passed this question.
Many candidates spent time defining and describing aspects of pharmacokinetics which were not relevant to the question. E.g. clearance, volume of distribution and half-life. Candidates who scored well utilised a structure which incorporated the headings of the factors which affect the bioavailability of medications with a simple description as to the nature of the effect. These factors
included: the physical properties of the drug, the preparation, patient factors, the route of administration and metabolism amongst others.
17B22: Exam Report
Define bioavailability. Outline the factors which affect it.
33% of candidates passed this question.
Many candidates did not specify that bioavailability describes the proportion/fraction of drug reaching the systemic circulation (to differentiate from the portal circulation). Some candidates considered only factors impacting absorption from the GI tract or stated that bioavailability related only to orally administered drugs. Candidates failed to provide an equation, or got equations or graphs wrong. Nearly all candidates failed to provide a comprehensive list of factors affecting bioavailability.
Biii / 20A15 / 17B22: Define bioavailability (10 marks). Outline factors which affect it (90 marks)
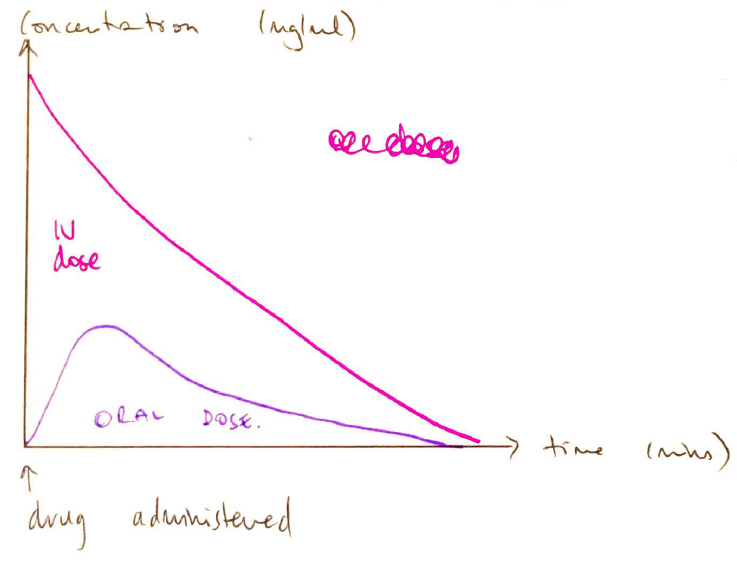
Definition
- Bioavailability = fraction of drug reaching the systemic circulation, compared with the amount if the same dose of drug was given IV
∴ by definition an IV drug has a bioavailability of 100%
Measurement
- Plot the plasma [ ] of a test dose v. IV dose
- Calculate AVC for both
Factors Affecting Bioavailability
2) First Pass Effect
- First pass metabolism
- Proportion of drug absorbed, delivered to liver by portal circulation & metabolised before reaching systemic circulation
- Morphine fully absorbed
- Significant 1st pass 0.67
- ∴ low OBA 33% (1 – 0.67)
- Transdermal sublingual & distal rectum all avoid 1st pass metabolism
- Hepatic enzyme inducer (phenytoin) = ↑drug metabolism by liver = ↓bioavailability
- Hepatic enzyme inhibitors (amiodarone) = ↓drug metabolism = ↑bioavailability
3) Patient Factors
- Malabsorption i.e. Crohn’s
- Trauma = ↓gastric emptying
- Blood flow = lead gut = ↓absorption
4) Pharmaceutical Prep
- MW, ↑size = ↓absorption
- PPB, ↑ = ↓absorption
- Liquid formulation = disperses quicker = ↑abs.
5) Physiochemical Interactions
- Milk ↓tetracycline abs
- Gut enzymes = inactivate insulin
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou