G3v / 20A19 / 18B06 : Discuss the determinants of venous return to the heart
20A19: Exam Report
Discuss the determinants of venous return to the heart.
67% of candidates passed this question.
The factors that influence VR are captured in 2 formulae; VR = CO, and VR = (MSFP-RAP) / Venous Resistance. Candidates that used these as the backbone structure of their answer scored well. Quite a few candidates failed to consider factors that affect left heart CO also effect VR. Recognising that CO does = VR appeared to elude some candidates.
18B06: Exam Report
Outline the determinants of venous return to the heart.
31% of candidates passed this question.
Answers should have included a description of the need for a pressure gradient for flow and a discussion on right atrial pressure, mean systemic filling pressure and resistance to blood flow. The discussion of each of these factors included definitions, normal values, factors affecting them and the direction of change on venous return. Diagrams were not essential, but their use assisted some candidates in explaining the effects of RAP on venous return.
G3v / 20A19 / 18B06: Discuss the determinants of venous return to the heart
Definition
Venous Return (VR) = the volume of blood returning to the Right heart (L/min)
Cardiac Output (CO) = the volume of blood ejected from the Left heart (L/min)
Since heart & vessels form a complete closed circuit, flow must be the same no matter where it is measured
∴CO ∝ VR
CO & VR are just terms for flow at different points of the circuit
CO = VR, otherwise pooling of blood will occur somewhere along the circulation
VR = CO
Determinants of CO
- 5L/min in healthy adult
CO = HR x SV = VR
- SV is determined by preL, C, afterL
- Cardiac factors: HR & contractility → not affected by vascular tree
- Coupling factors: preL & afterL → depend on both H & vascular tree
Autoregulation of CO
- VR = CO at all times → due to autoregulation
- Homeometric: ↑FoC due to ↑contractility from internal ↑Ca2+ availability
- Heterometric:
- Starling Mechanism → to match RV & LV outputs
- SA Node stretch → ↑HR
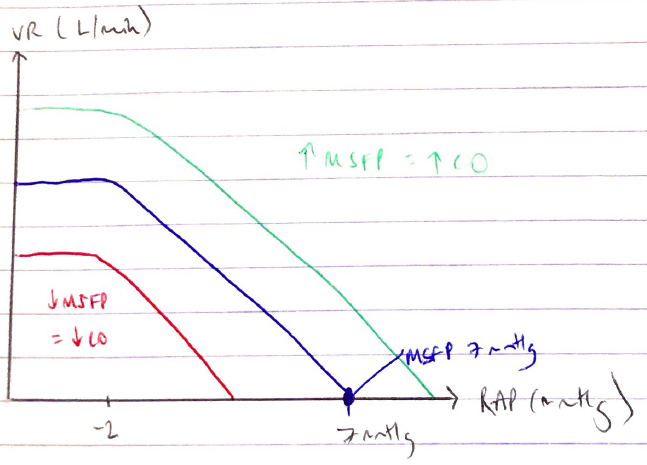
VR = (MSFP-RAP)/RVR
Factors
Normally
MSFP
7mmHg
RAP
0mmHg
Resistance to VR
1.4mmHg

- These normal values give VR = 5L/min → gives CO = 5L/min
1) MSFP
- Pressure in systemic circulation where there is no flow
- ↑blood vol = ↑MSFP
- ↑symp. activity = ↑MSFP
- ↑muscular pump = pushes blood to RA via 1-way-valves = ↑MSFP
- Supine posture = without muscular pump → blood pools in venous system → ↓MSFP
Normal MSFP = 7mmHg → at this value VR = 5L/min
- ↑MSFP = ↑VR
- ↓MSFP = ↓VR
- Both arterial & venous pressures equilibrate when all flow stops → this by definition is the MSFP
- All flow ceased → ∴VR & CO = 0L/min
2) RAP
- Normal RAP = 0mmHg (gives VR = 5L/min)
- ↑RAP = ↓VR
- ↓RAP = ↑VR → up to a point
- At RAP ≤ –2mmHg the vascular function curve plateaus
- Due to collapse of veins → sucks walls of veins together → preventing any VR
- RA affected by RA filling, RA compliance, RA emptying & RV emptying
3) Venous Resistance
- ↑resistance in veins = ↓VR
- Normal venous resistance = 1.4mmHg (VR = 5L/min)
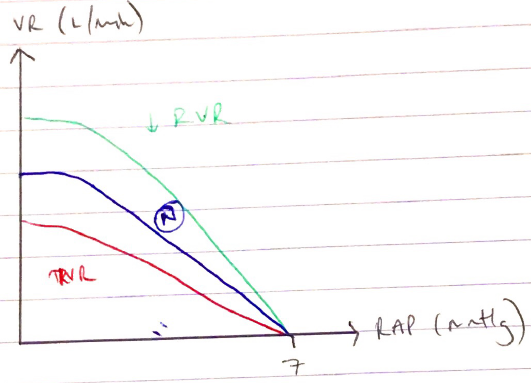
- Resistance to VR conferred by raised intrathoracic pressure & erect posture
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou
