G7i / 21A01: Describe the pharmacology of adrenaline
21A01: Exam Report
Describe the pharmacology of adrenaline
90% of candidates passed this question.
Adrenaline is a level 1 drug and is commonly used in intensive care. A comprehensive explanation of the drugs MOA, PK, PD and side effect were expected. Candidates who scored well generally provided a factually accurate, detailed and well-structured answer. Overall, the quality of answer provided for this question was of a high standard.
G7i / 21A01: Describe the pharmacology of adrenaline
Adrenaline
Adrenaline
Chemical
Naturally occurring catecholamine with mixed direct α & β activity, produced by adrenal medulla
The prototype sympathomimetic
Use
Inotropy
Cardiac arrest
Anaphylaxis
Vasoconstrictor
Presentation
Clear solution
100mcg – 1mg/mL
Brown ampoule → deteriorates on exposure to air/light
Excipients: sodium metabisulphite, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, water
Dose
Inotropy (IV)
1 – 2mcg/min = β2 receptors
2 – 6mcg/min = β1 & β2 receptors
>10mcg/min = β & α receptors
Cardiac arrest = 1mg (IV)
Anaphylaxis = 100mcg – 1mg (IV)
Vasoconstriction = 1:200,000 diluted with lignocaine
Route
IV
ETT
Subcut
Epidural space
Onset
Immediate, effect lasting 1 – 5 mins
MoA
Agonist of adrenergic receptors; β2 > β1 > α1 = α2
- β2 → GS → activates AC → ↑cAMP
- Cardiac = ↑Ca++
- Smooth muscle = inhibits MLC CK
- Liver = activates glycogen phosphatase
- NB: MAST CELL stabilisation by β2 agonism of MC
- β1 → GS → activates AC → ↑cAMP
- Cardiac = +ve inotropy, +ve chronotropy, +ve dromotropy
- Metabolic = lipolysis
- ↑RENIN → ↑AII → VC
- α1 → Gq → stimulates phospholipase C → ↑IP3 & DAG
- IP3: smooth muscle VC
- IP3: cardiac → weak +ve Inotropy
- DAG: metabolic → ↑BSL
- α2 → Gi → inhibits AC → ↓cAMP
- CNS : ↓symp. outflow
- Peripheries : inhibits NA release by –ve feedback
- Platelets : ↓platelet aggregation
PD
CVS
+ INOTROPY, + CHRONOTROPY, + DRONOTROPY
↑CO
↑Myocardial O2 consumption
Coronary dilatation
VC peripherally
RESP
↑MV
Bronchodilation
↑PVR
Mast cell stabilisation
RENAL
↑Bladder sphincter tone = difficulty voiding
↓Renal blood flow
METABOLIC
↑BMR
↑Plasma glucose
Gluconeogenesis
↑FFA
CNS
Pupil dilatation
GI
↓Secretions & ↓ tone
PK
A
Slow after IM/SC injection
Good tracheal mucosal absorption
Inactivated PO
D
M
Metabolised by mitochondrial MAO & COMT in liver, kidneys, blood
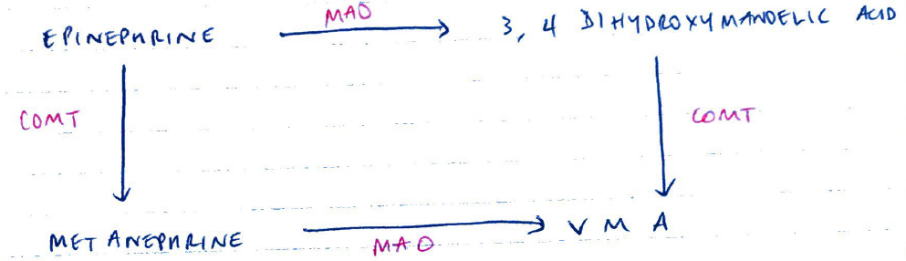
Metanephrine & VMA are conjugated with glucuronic acid
E
Inactive metabolites excreted in urine
Adverse Effects
Arrhythmias
Myocardial ischaemia
Cerebral bleed
Lactaemia (from aerobic glycolysis) ; ↑glycolysis, ↑glycogenolysis, ↑release of sk & lactate reserves → all for ENERGY
Tremor
Author: Krisoula Zahariou