U1vi / 21A13: List the cell types in the anterior pituitary gland. Outline their secretions, control and target organ effects
21A13: Exam Report
List the cell types in the anterior pituitary gland. Outline their secretions, control and target organ effects.
40% of candidates passed this question.
Few candidates described cell types as chromophils and chromophobes. There were many errant references to chromaffin cells which are found mainly in the adrenal medulla, and to staining on H&E. Chromophil cells stain by absorbing chromium salts. Few candidates mentioned that the hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary are peptides. Most candidates outlined the hypophyseal-portal system well. Knowledge of TSH and ACTH control and target organ effects were good. Similar knowledge for LH, FSH, PRL and GH was much more sporadic.
U1vi / 21A13: List the cell types in the anterior pituitary gland. Outline their secretions, control and target organ effects
The Anterior Pituitary Gland is the anterior lobe of pituitary gland which sits in the Sella Turcica and connects to the Hypothalamus via the Pituitary Stalk. The APG is a major organ of the endocrine system essential for growth, development, homeostasis, metabolism & reproduction
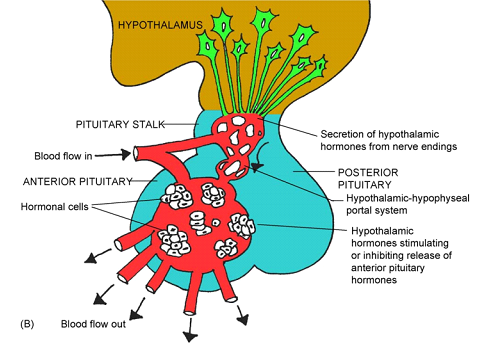
The hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system connecting the Hypothalamus to the Anterior Pituitary
Cell Types
There are 5 major cell types
Cell Type
Corticotropes
Popn
10%
Stain
Basilic
Hormone Produced
ACTH & MSH
Cell Type
Thyrotropes
Popn
10%
Stain
Chromophobic
Hormone Produced
TSH
Cell Type
Gonadotropes
Popn
10%
Stain
Chromophobic
Hormone Produced
LH, FSH
Cell Type
Somatotropes
Popn
50%
Stain
Acidic
Hormone Produced
GH
Cell Type
Lactotropes
Popn
10-25%
Stain
Acidic
Hormone Produced
PRL
Hormones
⦁ Hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary are peptides
- Mnemonic: FLAT PEG (FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, Prolactin, [endorphins], growth hormones)
Hormonal Secretions
FSH
LH
Control
↑ secretion with GnRH
↓ secretion with negative feedback
Target Organ Effects
- LH → Ovulation and luteinisation of ovarian follicles (females); testosterone secretion (males)
- FSH → Ovarian follicle development (females); spermatogenesis (males)
Hormonal Secretions
ACTH
Control
- ↑ secretion → by (i) ↑ corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF ↑ with stress, ↓ BGL, infection, injury, exercise, Etc.), (ii) catecholamines, and (iii) ADH
- ↓ secretion → -ve feedback with ↑ GC and androgen levels
Target Organ Effects
- (i) ↑ glucocorticoid synthesis and release (from all 3 layers of cortex → esp zona fasciculata and reticularis)
- (ii) ↑ androgen (cholesterol & steroid) synthesis and release (from zona fasciculata and reticularis)
- (iii) +ve trophic actions on adreno-cortical cells
Hormonal Secretions
TSH
Control
- ↑ secretion → (i) ↑ TRH levels (via Gq) 2° to cold exposure in neonates, (ii) oestrogen
- ↓ secretion → (i) -ve feedback with ↑ free thyroid hormones levels (esp FT3), (ii) ↓ TRH levels 2° to trauma/stress, (iii) Glucocorticoids, (iv) Somatostatin, (v) Dopamine
Target Organ Effects
- (i) ↑ synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormone (T4 [90%] and T3 [10%])
- (ii) ↑ size (hyperplasia and hypertrophy of follicular cells) and vascularity of thyroid gland → facilitates further thyroid hormone synthesis
Hormonal Secretions
Prolactin
Control
under tonic inhibitory control by DA from hypothalamus → PRL secretion occurs with (i) PRF release (due to suckling response), or (ii) TRH release
Target Organ Effects
- (i) During pregnancy → promotes mammary gland and ductal development
- (ii) Following delivery → (a) promotes lactation (↑ production of fat and lactose) and (b) causes amenorrhoea (PRL suppresses LH secretion)
Hormonal Secretions
Growth Hormone
Control
- ↑ secretion → GHRH, nutritional factors (starvation, ↓ BGL, ↓ plasma FFA), stress, excitement, trauma
- Alpha adrenergic, dopaminergic, serotoninergic agonist, opiod and aa stimulate GH release
- ↓ secretion → GHIH, -ve feedback by somaomedins (IGF-1)
Target Organ Effects
- Releases somatomedins (IGF-1 from liver) → anabolic actions on skeletal/cartilage growth → causes proliferation of chondrocytes and osteoblasts and protein uptake by osteogenic cells → epiphyseal growth or periosteal growth(if epiphyses fused)
- Protein metabolism → ↑ a.a. uptake into cells and ↑ protein synthesis
- Fat metabolism → ↑ lipolysis in adipose tissue, ↑ utilisation of FFA for energy in peripheral tissues (via β-oxidation), ↑ ketogenesis
- CHO metabolism → anti-insulin effect via ↑ glycogenesis and ↓ glucose uptake by tissues (\↑ BGL)
Author: Huiling Tan