I1iii / 22B14: Describe the physiological role, distribution & regulation of K+
22B14: Exam Report
Describe the physiological role, distribution and regulation of potassium ions (K+ )
51% of candidates passed this question.
The best answers demonstrated an appreciation of the multiple roles of potassium in normal physiology and described the integrated regulation of potassium concentration/distribution as opposed to many answers that seemed to focus purely on the renal handling of a filtered potassium load.
I1iii / 22B14: Describe the physiological role, distribution & regulation of K+
Defintion
Chemical element with atomic no. 19. Second most common cation in the body
Quantify
- ICF 150mmol/L
- ECF 3.5 – 5mmol/L
- 90% ICF
- 8% bone (ion-exchange)
- 2% ECF
- Total body K+ = 45mmol/kg
Role
- Intracellular tonicity
- Major determinant RMP → muscle & nerve excitability
- Na/K/ATPase of all PM
- Intracellular processes (pr & glycogen synthesis)
Importance of Regulation
- ECF K+ is closely regulated
- ↑K+ ECF = ↓RMP (approaches zero, ∴potential across PM becomes less)
= ↑excitability & ↓conduction velocity
= potential for life threatening arrhythmias
- ↓K+ ECG = ↑RMP
= ↓excitability & ↑conduction velocity
Movement of K+ Across PM
K+ IN
Adrenaline
- ↑Na/K/ATPase activity
Insulin
- ↑Na/K/ATPase activity
K+ OUT
Acidosis
- H+/K+ exchange
Cell lysis
Exercise/cell depolarisation
- Sux ↑ECF K+ 1mmol/L
- Muscle cells release K+ into T-tubules but with disturbed muscle architecture
Regulation
- Intake: 5000mg/day → not regulated
- Output
- Sweat 10mmol/day
- Faeces 10mmol/day
- Renal = major regulation of K+ balance
- K excreted = K filtered – K reabsorbed + K secreted
- K freely filtered by glomerulus
- 15% load excreted
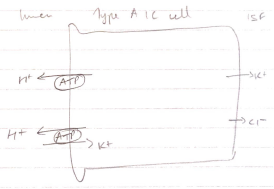
- Distal segments most important for tweaking K+ secretion
PCT
- Reabsorbs 55%
- PARACELLULAR DIFF. due to SOLVENT DRAG
Thick Asc. LoH
- Reabsorbs 30%
- Co-transporter Na/K/2Cl (driven by Na/K/ATPase)
- Paracellular diff. → due to +ve transtubular potential
Regulation
1. Plasma K level
- Na/K/ATPase highly sensitive to plasma K
- ↑↑↑upregulated by hyperK
- K+ secretion in collecting duct
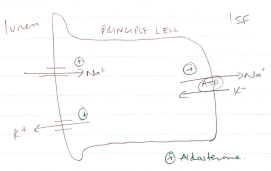
2. Aldosterone
- Stimulated by hyperK
- Directly stimulated by adrenal cortex
- ↑no Na/K/ATPase channels in distal nephron
3. Na+ Delivery to Distal Nephron
- ↑Na+ delivery
- ↑Na+ reabsorption
- ↑K secretion
4. Flow Rate to Distal Nephron
- K secretion ∝ flow rate
- ↑K+ delivery = ↑K+ secretion