2019 - Multiple Choice Questions
What type of receptors are opioid receptors?
- G protein coupled receptors
- Intracellular receptors
- Ligand gated ion channels
- Tyrosine kinase receptors
Which of the following organs has the HIGHEST total blood flow?
- Brain 750ml/min
- Heart 250ml/min
- Kidneys 1200ml/min
- Liver 1500ml/min
A characteristic of enantiomers is they:
- Are linked by a double bond
- Are superimposable – they are mirror images of eachother
- Exhibit tautomerism – structural isomerism – midazolam wh ionized at pH4 but at pH 7.4 changes into an unionized ring, lipid solb to cross BBB
- Have a centre of chirality
The resting membrane potential of a large peripheral nerve fiber is:
- -40mV
- -60mV
- -70mV
- -90mV

Total body water is approximately equal to:
- 0.07 L/kg
- 0.21 L/kg
- 0.60 L/kg
- 1.00 L/kg
0.6 x 70kh = 42L
The actions of vitamin D include:
- Elimination of calcium from the gut – increases
- Enhanced absorption of phosphate from the gut
- Excretion of phosphate from the kidney – increases phosphate reabsorption
- Inhibition of osteoblast activity – increases blast activity
You need phosphate and calcium to make bone
Phase 0 of depolarisation in a cardiac pacemaker cell occurs due to:
- Equalisation of potassium efflux and calcium influx
- Potassium efflux exceeding calcium influx
- The onset of calcium influx
- The opening of fast sodium channels
A right shift of the oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve can be caused by:
- A PaC02 of 55 mmHg
- A decreased 2,3-diphosphoglycerate
- A decreased hydrogen ion concentration
- An increased proportion of Haemoglobin F
- CO2
- H
- 2,3 DPG
- temp
- HbF causes L shift
Frusemide has the following effect:
- Acutely increases serum urate concentration
- Increases the production of cerebrospinal fluid
- Produces a hypertonic urine
- Pulmonary and systemic vasodilation
Adenosine is a naturally occurring nucleoside that:
- Causes an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance – decreases PVR
- Has a negative inotropic effect
- Has a plasma half-life of 2 minutes – <10sec
- Requires dose adjustment in end-stage renal failure – metabolized in RBC by phosphorelation
Digoxin toxicity is increased by:
- Hypermagnesaemia
- Hypocalcaemia
- Hypokalaemia
- Hyponatraemia
In states of hypokalemia, or low potassium, digoxin toxicity is actually worsened because digoxin normally binds to the ATPase pump on the same site as potassium. When potassium levels are low, digoxin can more easily bind to the ATPase pump, exerting the inhibitory effects
What is the mechanism of action of phentolamine?
- Alpha adrenoreceptor antagonist
- Centrally acting alpha 2 agonist
- Direct vasodilator
- Potassium channel activator
What is the mechanism of action of metoclopramide?
- Anticholinergic
- Antihistamine
- Antidopamine
- Serotonin (5-HT2) antagonist
In states of hypokalemia, or low potassium, digoxin toxicity is actually worsened because digoxin normally binds to the ATPase pump on the same site as potassium. When potassium levels are low, digoxin can more easily bind to the ATPase pump, exerting the inhibitory effects
What is the mechanism of action of clopidogrel?
- Adenosine diphosphate (ADR) receptor antagonist
- Adenosine reuptake inhibitor
- Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor
- Glycoprotein llb/llla receptor antagonist
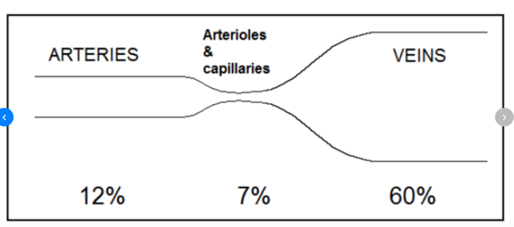
The total blood volume is distributed such that the majority is within the:
- Arteries
- Pulmonary circulation
- Systemic capillaries
- Veins
Thiopentone is MOSTLY associated with which of the following adverse effects?
- Adrenocortical suppression
- Bradycardia and metabolic acidosis
- Exacerbation of acute intermittent porphyria
- Raised intracranial pressure
What percentage of renal blood flow is distributed to the medulla under normal physiological conditions?
- 5 to 10%
- 10 to 20%
- 40 to 50%
- 85 to 90%
How much heparin is 1 mg of protamine able to inhibit?
- 100iU
- 200 iU
- 300 IU
- 400 IU
Which of the following gastrointestinal secretions has the HIGHEST pH?
- Bile 7-8
- Gastric secretions 2.3-3.5
- Pancreatic juice
- Saliva
The normal pH of arterial blood is 7.4. This translates to a hydrogen ion concentration of:
- 10 nmol/L
- 40 nmol/L
- 70 nmol/L 7.15
- 100 nmol/L